What principle does an optical disc use to read and write information?
Optical disc is a memory that uses the "laser" principle to read and write information. Optical disc is a medium that uses laser scanning to record and read out information; it is a device that uses laser principles to read and write. It is a rapidly developing auxiliary memory that can store various texts, sounds, graphics, and images. and animation and other multimedia digital information.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The optical disc (English: Optical disc, also translated as optical disc) was invented by American inventor James Russell (English: James Russell (inventor)) in 1965. The format stored at that time was still Mainly analog signals (Analog). It is a medium that uses laser scanning to record and read out information. It became popular around the mid-1990s and has the ability to store a large amount of data. A 12cm CD-R can store approximately 1 hour of MPEG1 video, 74 minutes of music, or 680MB of data.
An optical disc is an item that uses optical information as a storage carrier and is used to store data. Divided into non-rewritable optical discs, such as CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, etc.; and rewritable optical discs, such as CD-RW, DVD-RAM, etc.
Optical disc is a device that uses laser principles to read and write. It is a rapidly developing auxiliary memory that can store various multimedia digital information such as text, sound, graphics, images, and animations. .

Structure
- ##SubstrateIt is each The material used as the carrier of functional structures (such as grooves, etc.) is polycarbonate (PC), which has excellent impact toughness, wide operating temperature range, good dimensional stability, weather resistance, and non-toxicity. Generally speaking, the substrate is a colorless and transparent polycarbonate plate. In the entire optical disc, it is not only the carrier of grooves, etc., but also the physical shell of the entire optical disc. The substrate of a CD disc has a thickness of 1.2mm and a diameter of 120mm. It has a hole in the middle and is circular, which is the shape of the disc. The reason why the optical disc can be picked and placed at will mainly depends on the hardness of the substrate. In the eyes of readers, the substrate may be the bottom part. However, for optical discs, the same is not true. If you turn the smoother side of the disc (the side the laser head faces) toward you, the surface side is the substrate. It should be noted that in terms of substrate, there is no difference between CD, CD-R and CD-RW.
- Recording layerThis is where the signal is recorded during burning. Its main working principle is to apply a special organic dye to the substrate for laser recording information. Due to the different reflectivity before and after burning, when signals of different lengths are read via laser, 0 and 1 signals are formed through changes in reflectivity, thereby reading information. By 2013, there were three major categories of organic dyes on the market: Cyanine, Phthalocyanine and AZO. One-time recording CD-R discs mainly use (phthalocyanine) organic dyes. When the disc is burned, the laser will burn the organic dyes coated on the substrate, directly burning Record "pits" one after another, so that the states with and without "pits" form signals of '0' and '1'. These "pits" one after another cannot be recovered, that is After being burned into a "pit", it will remain in its current state permanently, which means that the disc cannot be erased or written repeatedly. This series of "0" and "1" information forms a binary code to represent specific data. Here, it is important to note that for rewritable CD-RW, what is applied is not an organic dye, but a certain carbonic substance. When the laser is burning, It's not about burning "pits" one after another, but changing the polarity of the carbonic material. By changing the polarity of the carbonic material, a specific "0" and "1" code sequence is formed. The polarity of this carbon material can be changed repeatedly, which means that the optical disc can be erased and written repeatedly.
- Reflective layerThis is the third layer of the optical disc. It is the area that reflects the laser beam of the optical drive. The data in the optical disc is read by the reflected laser beam. Its material is 99.99% pure silver metal. This is easier to understand. It is just like the mirror we often use. This layer represents the silver reflective layer of the mirror. When the light reaches this layer, it will be reflected back. Generally speaking, our optical discs can be used as mirrors because of this layer.
- Protective layerIt is used to protect the reflective layer and dye layer in the optical disc to prevent signal damage. The material is light-cured acrylic. The DVD/-R series used in the market also needs to add a gluing part to the above process.
- Printing layerThe place where the disc’s customer logo, capacity and other related information is printed. This is the back of the disc. In fact, it can not only mark information, but also play a certain role in protecting the disc. The birth of the compact disc ended the audio and video era of video tapes.
Reading technology
1) CLV technology: (Constant-Linear-Velocity) constant line Speed reading method. Technology used in less than 12x speed optical drives. It is to keep the data transfer rate constant while changing the speed of the spinning disc at any time. The rotation speed of reading the inner edge data is much faster than that of the outer edge.
2) CAV technology: (Constant-Angular-Velocity) constant angular velocity reading method. It uses the same speed to read the data on the disc. However, the data transmission speed on the inner edge of the optical disc is lower than that on the outer edge. The farther out, the better the speed of the optical drive is reflected. Double speed refers to the highest data transfer rate.
3) PCAV technology: (Partial-CAV) regional constant angular velocity reading method. It is a new technology that combines CLV and CAV. It uses CLV technology to read outer edge data and CAV technology to read inner edge data to improve the overall data transmission speed.
Disc type
CD: (Compact-Disc) disc. The CD starts with liad-in (the position where data starts to be recorded); then comes the Table-of-Contents area, which records data from the inside and outside; after recording, a lead-out data track is added to mark the end of the recording. On CD discs, analog data is passed through a large burner to carve many small pits on the CD that are invisible to the naked eye.
CD-DA: (CD-Audio) A disc used to store digital audio effects. In 1982, SONY and Philips jointly developed the Red Book standard to store sound data in the form of audio tracks. CD-ROMs are compatible with this specification of musical film capabilities.
CD-G: (Compact-Disc-Graphics) CD-DA added graphics to become another format, but it failed to be promoted. It was an attempt at a multimedia computer.
CD-ROM: (Compact-Disc-Read-Only-Memory) read-only disc drive. In 1986, SONY and Philips jointly developed the Yellow Book standard to define the format of archive data. Two types, MODE1 for computer data storage and MODE2 for compressed video image storage, are defined, making CD a universal storage medium. Bits such as debugging codes and correction codes are also added to ensure that the computer data can be read completely and without error.
GD-ROM: (Gigabyte Disc) Gigabyte Disc is a multimedia disc produced by Yamaha and launched by Sega of Japan in 1998 for media recording and game consoles, with maximum storage The capacity is 1GB, which is used to replace the 650MB-700MB capacity CD-ROM discs prevalent on the market at that time. GD-ROM is produced by Yamaha. Its working principle is to repackage and compress data on the basis of the original CD-ROM to increase storage capacity. GD-ROM data cannot be copied with a conventional CD recorder due to its construction and production factors.
CD-PLUS: In 1994, Microsoft announced a new enhanced CD standard, also known as CD-Elure. It puts the CD-Audio sound effects on the first track of the CD, and then puts the data files. In this way, the CD will only read the previous audio tracks and not the data tracks, achieving the benefits of dual-use computers and speakers.
CD-ROM XA: (CD-ROM-eXtended-Architecture) In 1989, SONY, Philips, and Microsoft formed a white paper standard that expanded the CD-ROM standard. It is divided into two types: FORM1, FORM2 and an enhanced CD standard CD.
VCD: (Video-CD) laser video disc. It is a white paper standard jointly formulated by SONY, Philips, JVC, Matsu**a, etc. It refers to a laser film and television disc that plays full motion and full screen.
CD-I: (Compact-Disc-Interactive) is a green paper standard jointly developed by Philips and SONY. It is an interactive CD-ROM system. In 1992, full-motion video image playback was achieved.
Photo-CD: In 1989, KODAK launched the Orange Book standard for photo CDs, which can store 100 high-resolution photos in five formats. Corresponding commentary and background music or interludes can be added to create an audio electronic picture collection.
CD-R: (Compact-Disc-Recordable) In 1990, Philips released a multi-segment write-once optical disc data format. Belongs to Orange Book standards. Adding a one-time recording dye layer to the disc allows for recording.
CD-RW: Add a rewritable dye layer on the disc, and data can be written repeatedly on the disc multiple times using laser.
SDCD: (Super-Density-CD) is produced by TOSHIBA, Hitachi, Pioneer, Panasonic, JVC, Thomson, Mitsubishi, Timewamer etc. to develop an ultra-density optical disc specification. It provides 5GB of storage on both sides, and the data compression ratio is not high.
MMCD: (Multi-Mdeia-CD) is a multimedia CD formulated by SONY, Philips, etc. It provides 3.7GB storage capacity on one side and has relatively high data compression.
HD-CD: (High-Density-CD) High-density disc. large capacity. The single-sided capacity is 4.7GB, the double-sided capacity is up to 9.4GB, and some reach 7GB. HD-CD discs use the MPEG-2 standard.
MPEG-2: In 1994, the moving image and its sound coding standard formulated by the ISO/IEC organization. Compression and decompression of broadcast quality images and stereo signals.
DVD: (Digital-Versatile-Disk) digital versatile disc, based on MPEG-2 standard, has a large capacity of 4.7G and can store 133 minutes of high-resolution full-motion film and television programs, including A Dolby Digital surround sound track, the image and sound quality are unmatched by VCD.
DVD RW: A DVD disc that can be written repeatedly, also called DVD-E. A standard jointly released by HP, SONY, and Philips. The capacity is 3.0GB and uses CAV technology to obtain higher data transfer rates.
PD optical drive: (PowerDisk2) is a writable optical drive and CD-ROM combined by Panasonic into one, including LF-1000 (external) and LF-1004 (built-in) Two types. The capacity is 650MB, the data transmission rate is 5.0MB/s, and it uses a micro laser head and a precision electromechanical servo system.
DVD-RAM: A business-readable and writable DVD standard established and announced by the DVD Forum Association. It has high capacity but low price, not slow speed and high compatibility.
UMD: (Universal Media Disc) The UMD disc independently developed by Sony Computer Entertainment (referred to as SCEI, often referred to as SCE) is called "Universal Media Disc (Universal Media Disc)" UMD disc It was officially recognized as a standard specification by the international standards organization Ecma International on June 21, 2005. Dimensions (approx.): 65mm×64mm×4.2mm, with plastic protective shell. UMD disc uses 660nm red laser double-layer recording method, with a maximum capacity of 1.83GB. UMD discs are used as PSP game discs, but in Sony's plan, this new generation of small discs will be widely used in various audio and video products. Sony Music, Sony Movies, etc. under the Sony Group have exhibited MTV and movie clips stored using UMD. The 2013 UMD specifications include "UMDAudio" and "UMDVideo", which adopt the new generation H.264/AVC image compression standard and Sony's independently developed ATRAC3Plus audio compression standard.
BD-ROM: (Blu-ray Disc) BD-ROM is a read-only disc of Blu-ray Disc. It is an external storage medium that can store a large amount of data. It can be called "Blu-ray Disc". ".
BD is one of the next generation optical disc formats after DVD, used to store high-quality audio and video and high-capacity data storage. It should be noted that the title "Blu-ray Disc" is not the official Chinese name of this product. It is an unofficial Chinese name that people in the Chinese world choose for themselves to make it easier to remember. SONY itself has not helped determine the Chinese name of this product. Correct name. Blu-ray Disc is a next-generation optical disc specification planned by the "Blu-ray Disc Association: BDA" composed of SONY, Panasonic and other companies. Led by SONY, it began to comprehensively promote related products in 2006. Blu-ray disc is named because it uses a blue laser beam with a wavelength of 405 nanometers (nm) to read and write (DVD uses a red light reader with a wavelength of 650 nanometers, and CD uses a wavelength of 780 nanometers). The reason why "Blue-ray" is not used in the English name of Blu-ray Disc is that the word "Blue-ray Disc" is popular, colloquial and descriptive in Europe and the United States, so it cannot constitute permission to apply for a registered trademark. Therefore The Blu-ray Disc Alliance removed the English word e to complete the trademark registration. On February 19, 2008, as HD DVD leader Toshiba announced that it would withdraw from all HD DVD-related businesses at the end of March, the battle for the next-generation optical disc format that had lasted for many years officially came to an end. In the end, the Blu-ray Disc led by SONY won.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What principle does an optical disc use to read and write information?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 2024 CSRankings National Computer Science Rankings Released! CMU dominates the list, MIT falls out of the top 5
Mar 25, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
2024 CSRankings National Computer Science Rankings Released! CMU dominates the list, MIT falls out of the top 5
Mar 25, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
The 2024CSRankings National Computer Science Major Rankings have just been released! This year, in the ranking of the best CS universities in the United States, Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) ranks among the best in the country and in the field of CS, while the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) has been ranked second for six consecutive years. Georgia Tech ranked third. Then, Stanford University, University of California at San Diego, University of Michigan, and University of Washington tied for fourth place in the world. It is worth noting that MIT's ranking fell and fell out of the top five. CSRankings is a global university ranking project in the field of computer science initiated by Professor Emery Berger of the School of Computer and Information Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. The ranking is based on objective
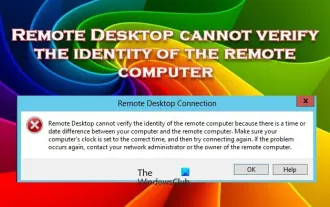 Remote Desktop cannot authenticate the remote computer's identity
Feb 29, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Remote Desktop cannot authenticate the remote computer's identity
Feb 29, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Windows Remote Desktop Service allows users to access computers remotely, which is very convenient for people who need to work remotely. However, problems can be encountered when users cannot connect to the remote computer or when Remote Desktop cannot authenticate the computer's identity. This may be caused by network connection issues or certificate verification failure. In this case, the user may need to check the network connection, ensure that the remote computer is online, and try to reconnect. Also, ensuring that the remote computer's authentication options are configured correctly is key to resolving the issue. Such problems with Windows Remote Desktop Services can usually be resolved by carefully checking and adjusting settings. Remote Desktop cannot verify the identity of the remote computer due to a time or date difference. Please make sure your calculations
 What is e in computer
Aug 31, 2023 am 09:36 AM
What is e in computer
Aug 31, 2023 am 09:36 AM
The "e" of computer is the scientific notation symbol. The letter "e" is used as the exponent separator in scientific notation, which means "multiplied to the power of 10". In scientific notation, a number is usually written as M × 10^E, where M is a number between 1 and 10 and E represents the exponent.
 Fix: Microsoft Teams error code 80090016 Your computer's Trusted Platform module has failed
Apr 19, 2023 pm 09:28 PM
Fix: Microsoft Teams error code 80090016 Your computer's Trusted Platform module has failed
Apr 19, 2023 pm 09:28 PM
<p>MSTeams is the trusted platform to communicate, chat or call with teammates and colleagues. Error code 80090016 on MSTeams and the message <strong>Your computer's Trusted Platform Module has failed</strong> may cause difficulty logging in. The app will not allow you to log in until the error code is resolved. If you encounter such messages while opening MS Teams or any other Microsoft application, then this article can guide you to resolve the issue. </p><h2&
 What does computer cu mean?
Aug 15, 2023 am 09:58 AM
What does computer cu mean?
Aug 15, 2023 am 09:58 AM
The meaning of cu in a computer depends on the context: 1. Control Unit, in the central processor of a computer, CU is the component responsible for coordinating and controlling the entire computing process; 2. Compute Unit, in a graphics processor or other accelerated processor, CU is the basic unit for processing parallel computing tasks.
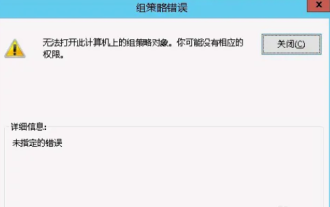 Unable to open the Group Policy object on this computer
Feb 07, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Unable to open the Group Policy object on this computer
Feb 07, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Occasionally, the operating system may malfunction when using a computer. The problem I encountered today was that when accessing gpedit.msc, the system prompted that the Group Policy object could not be opened because the correct permissions may be lacking. The Group Policy object on this computer could not be opened. Solution: 1. When accessing gpedit.msc, the system prompts that the Group Policy object on this computer cannot be opened because of lack of permissions. Details: The system cannot locate the path specified. 2. After the user clicks the close button, the following error window pops up. 3. Check the log records immediately and combine the recorded information to find that the problem lies in the C:\Windows\System32\GroupPolicy\Machine\registry.pol file
 What is disc formatting
Aug 17, 2023 pm 04:02 PM
What is disc formatting
Aug 17, 2023 pm 04:02 PM
Disc formatting refers to the process of rebuilding and clearing the disc's file system. During the disc formatting process, all data will be completely deleted, and the file system will be re-established to re-store data on the disc. Disc formatting can be used to protect data security, repair disc failures, and remove viruses. When formatting a disc, you need to back up important data, select an appropriate file system, and wait patiently for the formatting to complete.
 What should I do if steam cannot connect to the remote computer?
Mar 01, 2023 pm 02:20 PM
What should I do if steam cannot connect to the remote computer?
Mar 01, 2023 pm 02:20 PM
Solution to the problem that steam cannot connect to the remote computer: 1. In the game platform, click the "steam" option in the upper left corner; 2. Open the menu and select the "Settings" option; 3. Select the "Remote Play" option; 4. Check Activate the "Remote Play" function and click the "OK" button.



