How to loop through the first few elements of a php array
Implementation steps: 1. Define a variable and assign it to 0, which is used to control the number of loop elements. The syntax is "$con=0;"; 2. Use the foreach statement to loop through the array, the syntax is "foreach($ arr as $k=>$v){//loop body;}"; 3. In the loop body, each loop traverses an element, and sets the variable "$con" to increase by 1. When the value of the variable "$con" When it is N, just use the break statement to jump out of the loop, the syntax is "$con ;if($con==N){break;}".

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, PHP version 8.1, DELL G3 computer
In the php array, you can use the foreach statement and break statement to loop through the first N elements.
Implementation steps:
Step 1: Define a variable and assign it a value of 0, which is used to control the number of loop traversals (number of elements) number).
$con=0;
Step 2: Use the foreach statement to loop through the array
foreach is a statement specially designed for traversing arrays, and is a commonly used method when traversing arrays. It provides great convenience in traversing arrays
The foreach statement traverses arrays regardless of array subscripts, and can be used for discontinuous index arrays and associative arrays with strings as subscripts.
This statement has two syntax formats:
Syntax format 1:
##
foreach ($array as $value){
//循环体语句块;
}- Syntax format 2:
foreach ($array as $key => $value){
//循环体语句块;
}Step 3: In the loop body, set the variable $con to increment by 1. When the value of the variable $con is N, use the break statementJump out of the loop
- Each time the loop traverses an element, add 1 to the value of variable $con
- Then determine whether the value of variable $con is N, if so Then use the break statement to jump out of the loop
- If not, continue to traverse the elements
$con++;
if($con==N){ //循环遍历前N个元素
break;
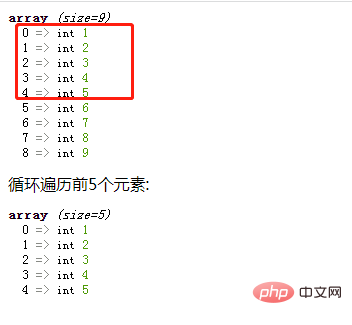
}Complete sample code: Loop through the first 5 elements
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$arr=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var_dump($arr);
$con=0;
foreach($arr as $k=>$v){
$res[$k]=$v;
$con++;
if($con==5){ //循环遍历前5个元素
break;
}
}
echo "循环遍历前5个元素:";
var_dump($res);
?>
Expand knowledge: Break out of the loop statement break and continue
1. Use the continue statement
The function of the continue statement is to jump out of this loop and then execute the next loop (abandon the code after the continue statement and proceed to the next loop). Let’s take a look at the code example below.Example 1: Output all even numbers between 1 and 10 (even numbers can be divisible by 2)
<?php
for ($i = 1; $i <= 10; $i++) {
if($i % 2 != 0) {
continue;
}
echo $i.' <br>';
}
?>for ($i = 1; $i <= 10; $i ){}
The statement can loop to get all numbers between 1~10if($i % 2 != 0)
statement is used to judge whether the value of$ican be divided evenly by 2. If it cannot be divided evenly, the value in()is true, thecontinue;statement will be executed.- In the loop body, use the
if($i % 2 != 0)
statement to make a judgment. If the value of $i can be divided by 2, use "echo $i" output; if the value of $i cannot be divided evenly by 2, thecontinue;statement will be triggered, jump out of this loop (without output), and execute the next loop.

2. Use break statement
The break statement is used to jump out of the current syntax structure. It can terminate the code of the loop body and immediately jump out of the current loop and execute the code after the loop. The difference between break and continue is that the continue statement only ends the current loop, while the break statement terminates the execution of the entire loop. Use the code in Example 1 above and replace continue; with break;. What will be output?
<?php
for ($i = 1; $i <= 10; $i++) {
if($i % 2 != 0) {
break;
}
echo $i.' <br>';
}
?>Nothing is output. Why is this happening? Let’s analyze it:
At the beginning of the forx loop,$i=1, is 1 less than 10? Of course, then start executing the if($i % 2 != 0) statement in the loop body;
() is true, then the "break;" statement in the if is executed, jumping out of the entire loop directly, and there is no chance to execute "echo $i.' '" statement.
PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to loop through the first few elements of a php array. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Variables, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.






