Let's analyze the difference between replace into and replace in MySQL
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces the detailed explanation of the difference between replace into and replace in MySQL. The article introduces it in detail through sample code, which will be a certain reference for everyone's study or work. Value, hope it helps everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
This article is just a starting point. I have never paid attention to the difference between replace into and replace before. After testing in multiple scenarios, I can't find any essential difference between the two when inserting data? If anyone knows the details, please leave a message to let me know, I would be very grateful! ! !
0. Background of the story
[Table structure]
CREATE TABLE `xtp_algo_white_list` ( `strategy_type` int DEFAULT NULL, `user_name` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `status` int DEFAULT NULL, `destroy_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, `updated_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, UNIQUE KEY `xtp_algo_white_list_UN` (`strategy_type`,`user_name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin # `strategy_type`,`user_name` 这两个是联合唯一索引,多关注后续需要用到!!!
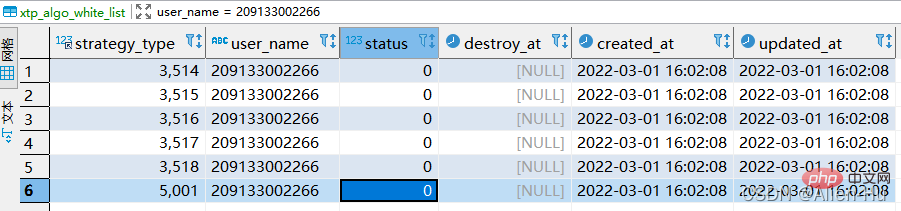
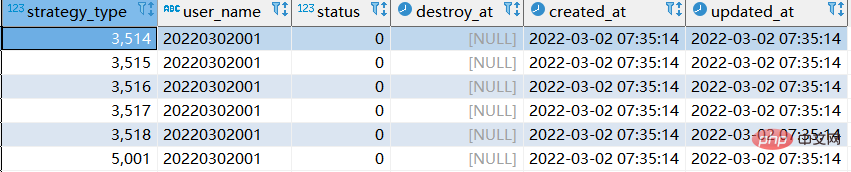
- According to the data of account 209133002266 in the table, re-insert a user 20220302001 so that the strategy_type & status & destroy_at fields in the newly generated data are consistent with those of user 209133002266. Using update to update one by one is also possible, but it is slower. The effect of using replace into will be much higher, but in-depth research found that there are also some pitfalls
replace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`)
select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
# replace into 后面跟表格+需要插入的所有字段名(自动递增字段不用写)
# select 后面选择的字段,如果根据查询结果取值,则写字段名;如果是写死的,则直接写具体值即可
# 可以理解为,第一部分是插入表格的结构,第二部分是你查询的数据结果
Copy after login
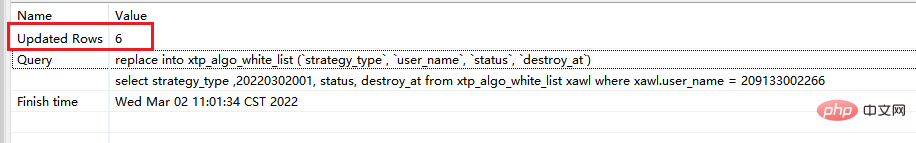
2. There is a unique way When indexing—replace into & and replace effectsstep1: First execution of sqlreplace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266; # replace into 后面跟表格+需要插入的所有字段名(自动递增字段不用写) # select 后面选择的字段,如果根据查询结果取值,则写字段名;如果是写死的,则直接写具体值即可 # 可以理解为,第一部分是插入表格的结构,第二部分是你查询的数据结果
replace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
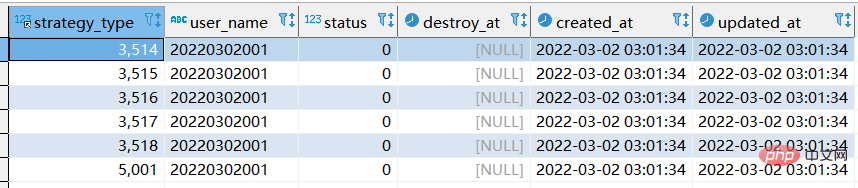
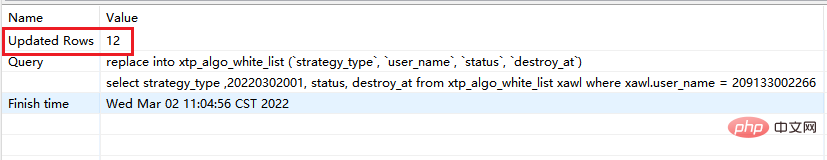
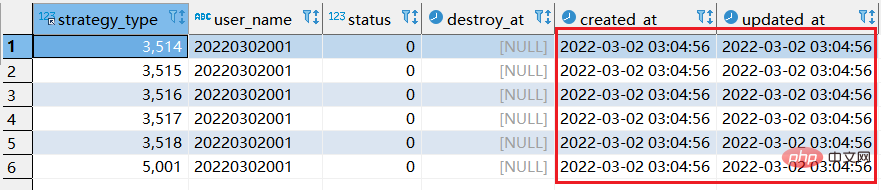
# 此时执行的是replace replace xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
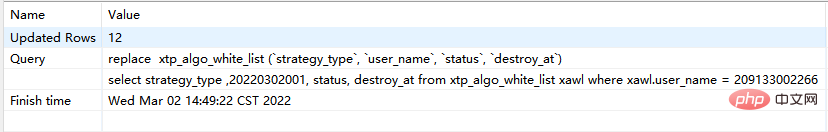
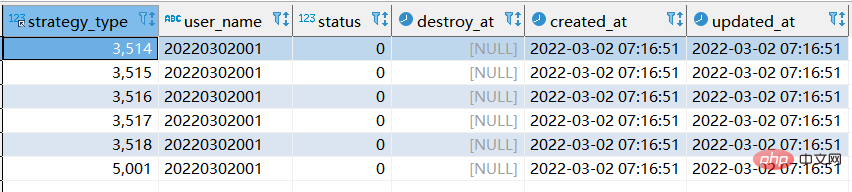
- When new data already exists, replace into and replace are the same.
- Subsequently delete all 20220302001, execute SQL once and twice, and find that the effects of replace into and replace are the same [Summary:] When there is a unique index restriction, if the newly added data will be restricted by the unique index, the data will only be inserted once. If it already exists, it will be deleted first and then inserted. At this time, replace into has the same effect as replace.
3. When there is no unique index—replace into and replace
We will delete the joint unique index of strategy_type & user_name and delete all data of the 20220302001 user. The final table structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE `xtp_algo_white_list` ( `strategy_type` int DEFAULT NULL, `user_name` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `status` int DEFAULT NULL, `destroy_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, `updated_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
1) The specific situation of the replace function
step1: Execute the following replace corresponding sql:
replace xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
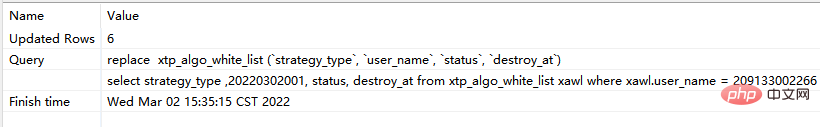
 #step2: Execute replace again corresponding to sql:
#step2: Execute replace again corresponding to sql:
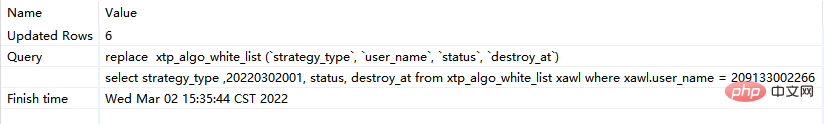
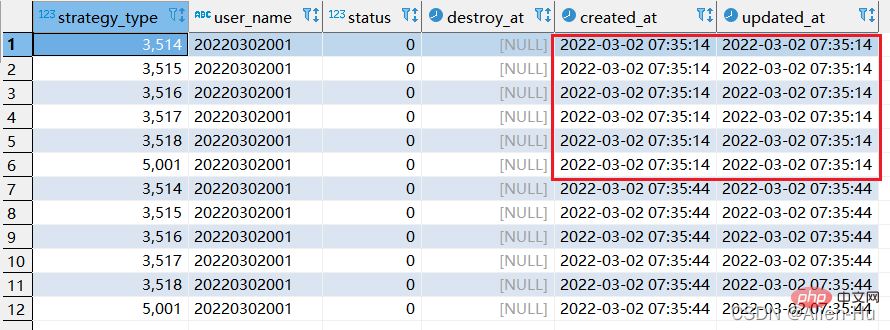
- If the above sql is executed later, the data will continue to increase 2) The specific situation of the .replace into function
Before executing, clean the data , delete all the data of 20220302001
step1: execute the following replace into corresponding sql:
replace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
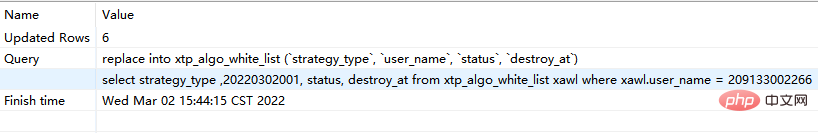
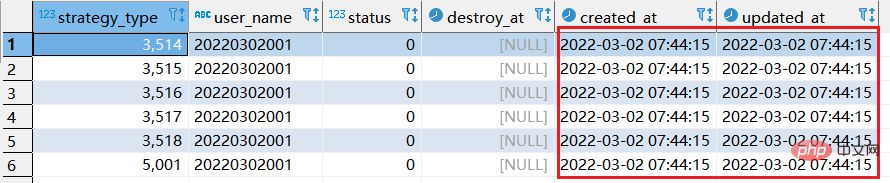
step2:再次执行replace into 对应sql:
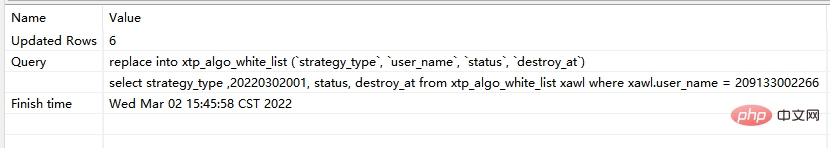
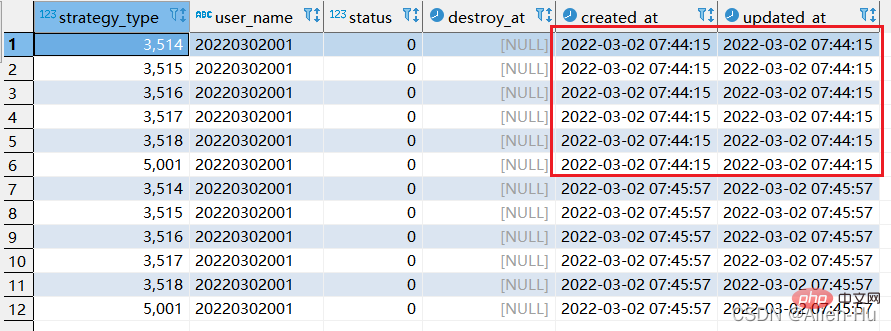
最终发现,没有唯一索引的时候,replace into 与replace 居然一摸一样的效果,都是继续增加数据。
通过以上分析,没看出replace into 与replace 具体有啥区别????有谁知道呢?
4.replace的用法
- 单独replace的作用是替换字段中某数值的显示效果。可以数值中的部分替换、也可以全部替换。
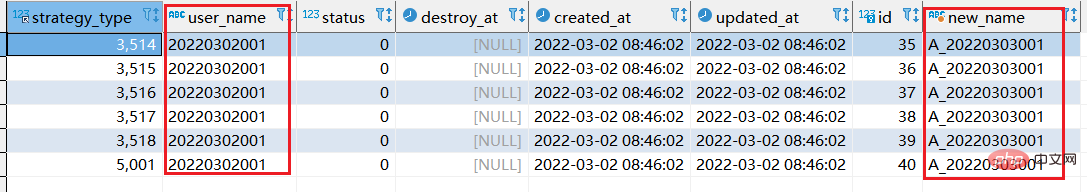
- 如下表格,将user_name的字段,20220302改为"A_20220303"显示,并且新字段叫做new_name显示
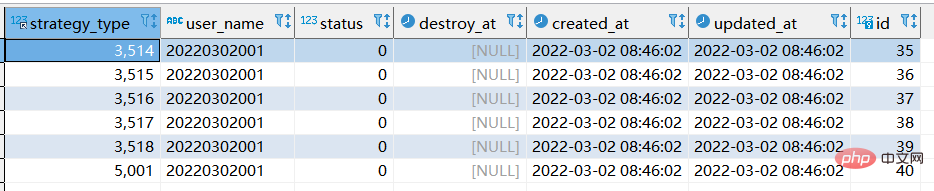
select *, replace(user_name,20220302,'A_20220303') as "new_name" from xtp_algo_white_list where user_name = 20220302001;
推荐学习:mysql视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Let's analyze the difference between replace into and replace in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP's big data structure processing skills
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
PHP's big data structure processing skills
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
Big data structure processing skills: Chunking: Break down the data set and process it in chunks to reduce memory consumption. Generator: Generate data items one by one without loading the entire data set, suitable for unlimited data sets. Streaming: Read files or query results line by line, suitable for large files or remote data. External storage: For very large data sets, store the data in a database or NoSQL.
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle database and MySQL are both databases based on the relational model, but Oracle is superior in terms of compatibility, scalability, data types and security; while MySQL focuses on speed and flexibility and is more suitable for small to medium-sized data sets. . ① Oracle provides a wide range of data types, ② provides advanced security features, ③ is suitable for enterprise-level applications; ① MySQL supports NoSQL data types, ② has fewer security measures, and ③ is suitable for small to medium-sized applications.






