What does edr mean in network security?
In network security, EDR refers to "Endpoint Detection and Response". It is a proactive endpoint security solution that includes real-time monitoring and the use of automatic threat response mechanisms to collect endpoint security data; by recording terminals and networks Events, store this information locally on the endpoint or centrally in the database. EDR will collect known attack indicators, behavioral analysis databases to continuously search data and machine learning technology to monitor any possible security threats and respond quickly to these security threats.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) is a proactive endpoint security solution that records terminal and network events and stores this information locally on the endpoint or centrally in a database. EDR will collect known attack indicators, behavioral analysis database to continuously search the data and machine learning technology to monitor any possible security threats and respond quickly to these security threats. It also helps to quickly investigate the scope of the attack and provide response capabilities.
Capability
Prediction: risk assessment; anticipate threats; baseline security posture (Baseline Security Posture).
Protection: harden systems (strengthen the system); isolate system (isolate system); prevent attacks (prevent attacks).
Detection: detect incidents; confirm and prioritize risk. contain incidents.
Response: remediate; design policy change; investigate incidents.
Security model
Compared with static defense technology that uses preset security policies for endpoint security protection, EDR The threat detection and response forensics capabilities have been strengthened to quickly detect, identify, monitor and process endpoint events, thereby detecting and blocking threats before they cause harm, and helping protected networks to protect against zero-day threats and various emerging threats. The security model is as shown in the figure:
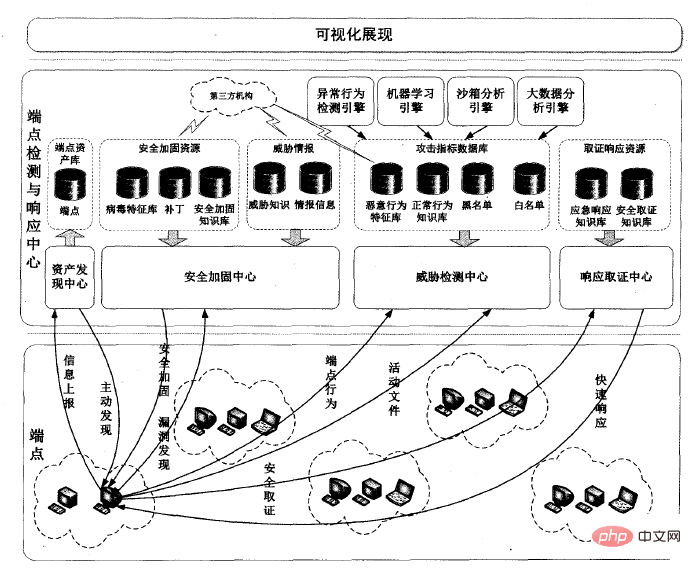
1. Asset discovery
is regularly collected through active scanning, passive discovery, manual entry and manual inspection. All software and hardware assets in the current network, including all endpoint assets in the entire network and the names and versions of software in use, ensure that there are no security blind spots in the entire network.
2. System reinforcement
Needs regular vulnerability scanning, patching, updating and further refinement of security policies, whitelisting currently unauthorized software to run, and restricting through firewalls to Open server ports and services when authorized. It is best to regularly check, modify and clean up internal personnel's account numbers, passwords and authorization information.
3. Threat detection
Carry out abnormal behavior analysis through the local host intrusion detection of the endpoint, and make corresponding protection and protection measures for various security threats before, during and after their occurrence. Detect behavior.
4. Response forensics
Visually display the security threats of the entire network, automatically isolate, repair and rescue threats, and lower the threshold of incident response and forensics, so that there is no need to rely on Emergency response and forensic analysis can be completed using external experts.
Function
Investigate security incidents;
Repair the endpoint It is in the pre-infection state;
detects security events;
contains terminal events;
##How it works
Once EDR technology is installed, EDR will use advanced algorithms to analyze the behavior of individual users on the system and remember and connect their activities. Sensing the abnormal behavior of a certain or specific user in the system, the data will be filtered to prevent signs of malicious behavior. These signs will trigger alarms and then we will determine whether the attack is true or false. If malicious activity is detected, the algorithm traces the attack path and builds it back to the entry point. (Correlation Tracking) The technology then consolidates all data points into narrow categories called Malicious Operations (MalOps), making them easier for analysts to view. In the event of a true attack, customers are notified and given actionable response steps and recommendations for further investigation and advanced forensics. If it is a false alarm, the alarm will be closed, only the investigation record will be added, and the customer will not be notifiedSystem Framework
The core of EDR is: On the one hand, it uses existing blacklists and endpoint static defense technologies based on virus signatures to block known threats. On the other hand, various security threats from the outside or inside can be proactively discovered through cloud threat intelligence, machine learning, abnormal behavior analysis, attack indicators, etc. At the same time, comprehensive detection and response are performed based on the background data of the endpoint, malware behavior, and the overall life cycle of advanced threats, and automated blocking, forensics, remediation, and traceability are performed to effectively protect endpoints.
EDR includes: Endpoint, endpoint detection and response center, and visual display three parts. The system framework is as shown in the figure:

##Endpoint: In EDR, the endpoint only has basic functions such as information reporting, security reinforcement, behavior monitoring, active file monitoring, rapid response, and security forensics. It is responsible for reporting the endpoint's operating information to the endpoint detection and response center. , and execute issued security policies, responses, evidence collection instructions, etc. at the same time.
Endpoint Detection and Response Center: is composed of asset discovery, security reinforcement, threat detection, response forensics and other centers.
Visualization: Provides real-time visibility and controllability for various endpoint security threats, reduces the complexity of discovering and handling security threats, and assists users to respond more quickly and intelligently security threats.
Detect threat types
- Malware (crimeware, ransomware, etc.)
- Fileless attacks
- Abuse of legitimate applications
- Suspicious user activity and behavior
Feature Types and Collection Types
- EDR is unique because its algorithms not only detect and combat threats, It also simplifies the management of alert and attack data. Using behavioral analytics to analyze user activity in real-time allows for immediate detection of potential threats without disrupting endpoints. It enhances the capabilities of forensic analysis by merging attack data into events that can be analyzed, working with antivirus and other tools to give you a secure network.
- Endpoint detection and response runs through sensors installed on the endpoint without requiring a reboot. All this data is stitched together to form a complete picture of endpoint activity, regardless of where the device is located.
Main technology
Intelligent sandbox technology
Aiming at suspicious The key technology for code dynamic behavior analysis is to create a strictly controlled and highly isolated program running environment by simulating various virtual resources, run and extract behavioral information during the running of suspicious code, and achieve rapid identification of unknown malicious code.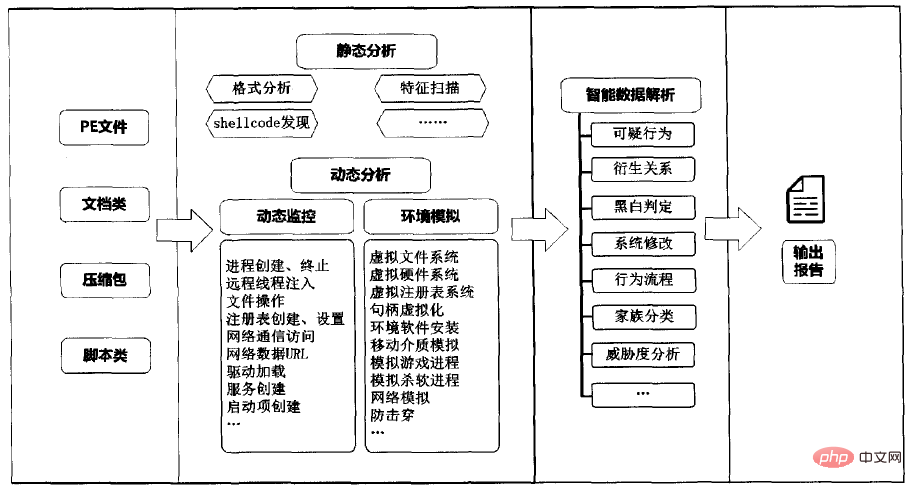
Machine learning technology
is a multi-disciplinary interdisciplinary knowledge, the core of the field of artificial intelligence, specializing in how computers simulate Realize human learning behavior, reorganize the existing knowledge system by acquiring new skills and knowledge, and continuously improve its own performance. In large-scale data mining processing, patterns can be obtained through automatic analysis, and then these patterns can be used to predict unknown data.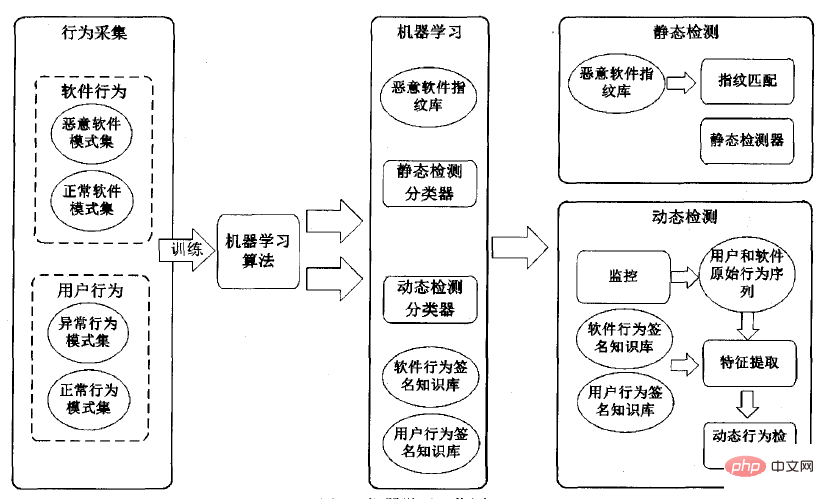
Digital forensics technology
Digital forensics refers to the detection of sufficiently reliable and convincing information that exists on computers, networks, The process of identifying, protecting, extracting and archiving digital evidence in digital devices such as electronic devices. In EDR, digital forensics must overcome key technologies such as cloud computing environment forensics, smart terminal forensics, and big data forensics, automatically locate and collect endpoint intrusion electronic evidence, lower the technical threshold of forensic analysis, and improve the efficiency of forensics and the accuracy of analysis results. It provides technical support for investigating endpoint security incidents and combating cybercrime.EDR Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- EDR has accurate identification The inherent advantage of attacking. Endpoints are the main battlefield for offensive and defensive confrontations. Implementing defense on endpoints through EDR can more comprehensively collect security data, accurately identify security threats, accurately determine whether security attacks are successful, and accurately restore the occurrence process of security incidents.
EDR completely covers the entire life cycle of endpoint security defense. For various security threat events, EDR can carry out corresponding security detection and response actions before, during and after their occurrence. Before a security incident occurs, proactively collect client security data in real time and perform targeted security reinforcement; when a security incident occurs, proactively discover and prevent security threats through various security engines such as abnormal behavior detection and intelligent sandbox analysis; after a security incident occurs , trace the origin through endpoint data.
EDR is compatible with various network architectures. EDR can be widely adapted to various network architectures such as traditional computer networks, cloud computing, and edge computing. It can be applied to various types of endpoints and is not affected by network and data encryption.
EDR assists administrators in intelligently responding to security threats. EDR can automatically complete a series of tasks such as the discovery, isolation, repair, remediation, investigation, analysis and forensics of security threats, which greatly reduces the complexity of discovering and handling security threats, and can assist users to respond to security threats more quickly and intelligently. .
Disadvantages
The limitation of EDR is that it cannot completely replace existing endpoint security defense technologies. EDR has a complementary relationship with traditional endpoint security defense technologies such as anti-virus, host firewall, host intrusion detection, patch reinforcement, peripheral control, and software whitelisting, and is not a substitute.
Technical Prerequisite
If you want to use or better understand EDR, you need to have some knowledge. Only in this way can we better use and understand the principles and usage of EDR.
Familiar with Linux environment, python or shell, Java;
Familiar with hadoop, spark and other big data components;
Familiar with data mining and analysis (such as risk level classification), data statistics technology (such as some confidence calculations), machine learning technology (classification detection, etc.), deep learning technology, big data analysis technology (mainly Correlation analysis), funnel analysis method, etc.
Familiar with mysql or nosql database, centralized storage database, distributed storage database.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What does edr mean in network security?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 What does edr mean in network security?
Aug 29, 2022 pm 02:25 PM
What does edr mean in network security?
Aug 29, 2022 pm 02:25 PM
In network security, EDR refers to "Endpoint Detection and Response". It is a proactive endpoint security solution that includes real-time monitoring and the use of automatic threat response mechanisms to collect endpoint security data; by recording terminal and network events, this information is stored locally. stored on endpoints or centrally in a database. EDR will collect known attack indicators, behavioral analysis databases to continuously search data and machine learning technology to monitor any possible security threats and respond quickly to these security threats.
 What level of information is transmitted using an encrypted fax machine?
Aug 31, 2022 pm 02:31 PM
What level of information is transmitted using an encrypted fax machine?
Aug 31, 2022 pm 02:31 PM
"Confidential" and "Secret". Do not use ordinary telephones or fax machines to discuss or transmit confidential information. To fax confidential information, you must use an encrypted fax machine approved by the national cryptography management department. It is strictly forbidden to use an unencrypted fax machine to transmit state secrets. Encrypted fax machines can only transmit confidential and confidential information, and top-secret information should be sent to local confidential departments for translation.
 What is the difference between cybersecurity and information security?
Jun 11, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
What is the difference between cybersecurity and information security?
Jun 11, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
With the advent of the digital age, network security and information security have become indispensable topics. However, many people are not clear about the difference between these two concepts. This article will provide a detailed analysis in terms of definition, scope, threats, etc. 1. Definition and Category Differences Network security refers to a technology that protects the security of the network and the hardware, software, data and other resources involved in its operation. Specifically, network security includes the following aspects: network infrastructure, network application services, network data and information flow, network security management and monitoring, network protocols and transmission security.
 What are the five basic elements of information security?
Sep 13, 2023 pm 02:35 PM
What are the five basic elements of information security?
Sep 13, 2023 pm 02:35 PM
The five basic elements of information security are confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation and auditability. Detailed introduction: 1. Confidentiality is to ensure that information can only be accessed and used by authorized people or entities to prevent unauthorized disclosure or disclosure. In order to maintain confidentiality, encryption technology can be used to encrypt sensitive information and only authorized personnel To decrypt and access; 2. Integrity refers to ensuring the accuracy and integrity of information during storage, transmission and processing, and preventing information from being tampered with, modified or damaged. In order to maintain integrity, data integrity checks can be used, etc. .
 What are the characteristics of information security
Aug 15, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
What are the characteristics of information security
Aug 15, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
Characteristics of information security: 1. Confidentiality, information can only be accessed and used by authorized persons or entities, and cannot be obtained by unauthorized persons; 2. Integrity, information remains complete and accurate during transmission, storage and processing ; 3. Availability, the information is available and accessible when needed; 4. Credibility, the source and content of the information are trustworthy to prevent the spread of false or malicious information; 5. Non-repudiation, the sender of the information and the recipient cannot deny their behavior or communication; 6. Auditability, traceability and auditability of information security; 7. Privacy protection, etc.
 10 iPhone privacy settings to enhance security
Apr 23, 2023 pm 09:46 PM
10 iPhone privacy settings to enhance security
Apr 23, 2023 pm 09:46 PM
The iPhone is widely regarded as a ubiquitous smartphone that provides users with a host of computer-like features. However, cybercriminals often target smartphones, including iPhones, to extract sensitive data and personal information. Given the convenience of performing daily tasks on the go, the iPhone also poses a potential vulnerability to user privacy. Even tech-savvy people can be at risk if their device's security settings are not configured properly. Fortunately, users can take precautions to prevent unauthorized access to their iPhone. This guide outlines 10 important iPhone privacy settings that users should adjust to enhance the security of their device. Your iPhone is not what you think it is
 What are the elements of information security?
Aug 18, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
What are the elements of information security?
Aug 18, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
The elements of information security include confidentiality, integrity, availability, authenticity, non-repudiation, auditability and recoverability. Detailed introduction: 1. Confidentiality refers to ensuring that information can only be accessed and used by authorized people or entities, which means that information should be encrypted during transmission and storage, and only verified users can access the information; 2. Completeness Safety refers to ensuring that information is not tampered with or damaged during transmission and storage; 3. Availability refers to ensuring that information can be used timely and reliably when needed, which requires the use of data integrity checks and verification mechanisms, etc.
 Methodological analysis of enterprise information security management
Jun 11, 2023 am 11:39 AM
Methodological analysis of enterprise information security management
Jun 11, 2023 am 11:39 AM
With the rapid development of information technology, enterprises are facing more and more information security risks. Information security problems may come from internal sources, such as employee negligence, poor management, malicious operations, etc.; they may also come from external sources, such as hacker attacks, virus infections, phishing, etc. Ensuring corporate information security not only involves the economic interests of the company, but also involves customer trust and brand value. Therefore, enterprises should pay attention to information security management and adopt scientific and effective methods to conduct information security management. In this article, we will analyze enterprise information security from a methodological perspective.



