What protocol does ip belong to in computer network architecture?
ip belongs to the "network layer" protocol of the computer network architecture. IP refers to the Internet Interconnection Protocol, which is a network layer protocol in the TCP/IP system. It can provide information of various protocols to the transport layer, such as TCP, UDP, etc.; IP information packets can be placed in the link layer through Various technologies such as Ethernet and Token Ring network are used for transmission.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
ip belongs to the "network layer" protocol of the computer network architecture.
IP protocol brief description
IP refers to the Internet Protocol, the abbreviation of Internet Protocol, IP is the entire TCP/IP protocol The core of the family and the foundation of the Internet. IP is located in the network layer of the TCP/IP model (equivalent to the network layer of the OSI model). It can provide various protocol information to the transport layer, such as TCP, UDP, etc.; IP information packets can be placed in the link layer. Transmitted through various technologies such as Ethernet and Token Ring networks.
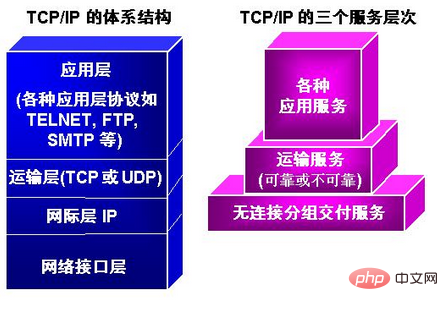
The purpose of designing IP is to improve the scalability of the network: first, to solve Internet problems and achieve interconnection of large-scale, heterogeneous networks; second, to segment top-level network applications and the underlying network technology to facilitate the independent development of both. According to the end-to-end design principle, IP only provides a connectionless, unreliable, best-effort packet transmission service to the host.
Although IPV4 will eventually be replaced by IPV6, IPV4 is still the mainstream version of the IP protocol, so we will focus on the IPV4 version. When learning TCP protocol and socket programming, we know that if we want to accurately locate a host in the shared network of the Internet, we must need the IP address of the host. The host has an IP address, but cannot perform routing control (Routing, which means forwarding and grouping data packets). A device such as a router has an IP address and can also perform routing control; we can connect the host to the Internet and routers are called nodes.
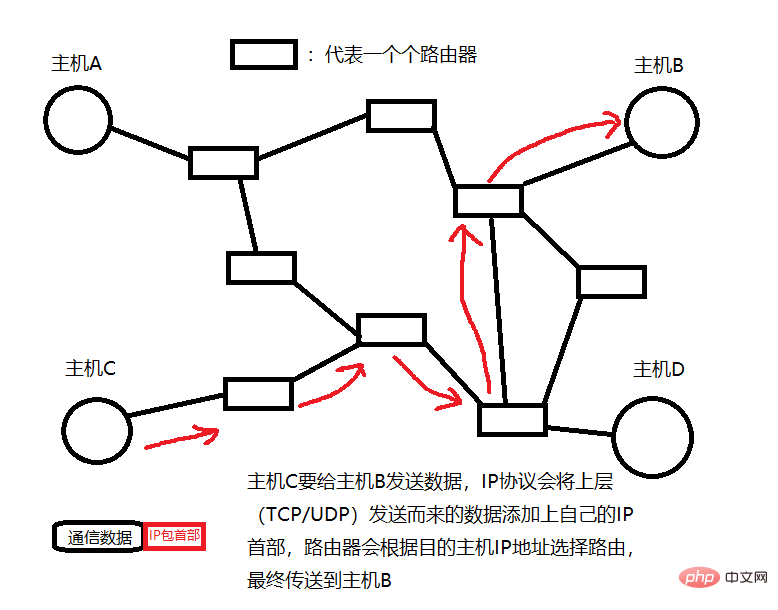
For example, we ordinary people only have our own address. If we want to send express delivery to a friend or receive express delivery from someone else, we can only provide the postman with the other party’s address or our own address, that is, we only have the address. logo, but we cannot send express delivery; and the courier is like a router, he also has his own address, and can also receive his private express, but he can also choose different express delivery according to the destination. lines for transportation. The following figure can clearly express the role of the IP protocol in the network environment.
IP protocol header format (IPV4)
Same as learning TCP and UDP protocols before, let’s first introduce the IP protocol header format
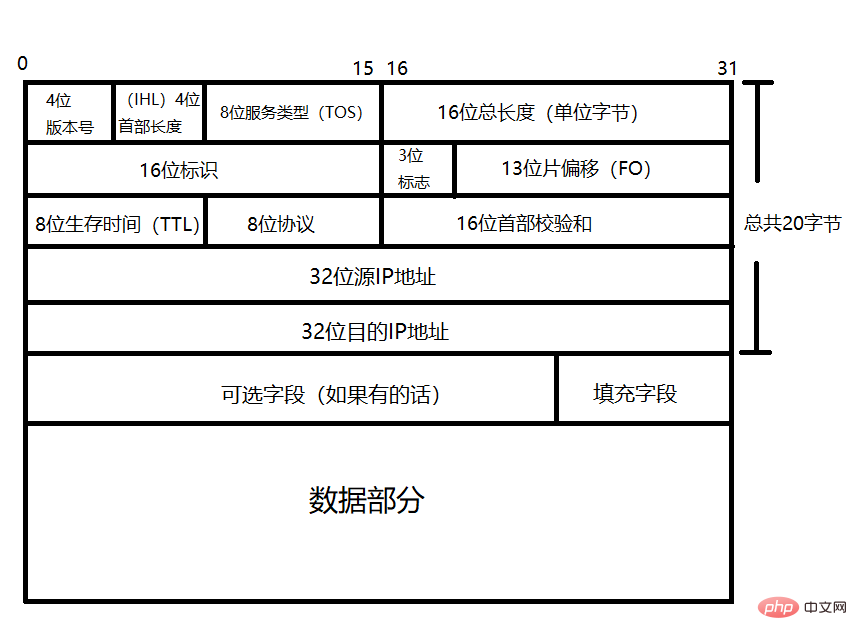
We can find that the IP protocol header is very similar to the TCP protocol header. Unless there are special circumstances, both are 20 bytes, so we often put the two together and call them TCP. /IP protocol. Below is a detailed introduction to each field in the IP protocol header:
- 4-digit version number (Version): used to specify the version of the IP protocol. The version number of IPV4 is 4. If the IP message is the IPV4 version, then the value of this field is 4. Use 4 digits to The logo is 0100. The version number of IPv6 is 6.
- 4-digit header length (Internet Header Length): Indicates the size of the IP header, The unit is 4 bytes, length * 4 bytes, because this field has a total of 4 bits, so the maximum value of this field is 2^4 - 1, which is 15, so the maximum length of the IP header is 15 * 4, which is 60 bytes; by default, this field is set to 5, so the default IP header is 20 words Festival.
- 8-digit Type of Service: The first three digits represent priority (deprecated), the 4th digit represents minimum latency, the 5th digit represents maximum throughput, and the 6th digit represents maximum reliability. The 7th digit represents the minimum cost. These four digits conflict with each other and only one can be chosen. It needs to be selected according to different situations. If it is a remote login such as SSH/TELNET, then the minimum delay should be selected. If it is an FTP type program, the maximum throughput should be selected; the 8th bit is a reserved bit and is not currently used. , must be filled in with 0.
- 16-bit total length (Total Length): Indicates the total number of bytes in the IP header and the data part carried behind it. This field has 16 bits, so the overall maximum length of the IP datagram is 65535 bytes.
- 16-bit identification (ID): uniquely identifies the message sent by the host. If an IP message is fragmented at the data link layer, then this field in each fragment should have the same value. Help the peer host perform fragmentation and reassembly after reception.
- 3-bit flag (Flag): The first bit is reserved (reserved means not used now, but will be used in the future if necessary), and must be filled with 0; the second bit is used to indicate whether sharding can be performed, if If it is 0, it can be fragmented. If it is 1, it cannot be fragmented. If an IP packet is prohibited from fragmentation and its length is greater than the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit, described in detail later), the packet can only be discarded; If the packet is fragmented, if the third bit is 1, it means that it is a packet in the middle of the fragmentation, that is, there will be fragmented packets in the future. If the third bit is 0, it means that this is the last fragment.
- 13-bit fragment offset (Fragment Offset): This field indicates the offset of the fragment relative to the beginning of the original IP message , which actually means that the current fragment is in the original message At the location, the corresponding value of the first fragment is 0. Since this field has a total of 13 bits, it can represent up to 2^13 or 8192 relative positions. The unit is 8 bytes, so the maximum position can be represented by 8192 * 8 = 65536 bytes.
- 8-bit Time To Live: The maximum number of message hops for a datagram to reach its destination (Hop, refers to an interval in the network, and IP data packets are forwarded between hops in the network) , usually 64, each time it passes through a route, TTL–, if it has not reached the destination when TTL == 0, then the packet will be discarded. This field is mainly used to prevent routing loops. Data packets are forwarded in a loop, which wastes network resources.
- 8-bit protocol (Protocol): Indicates what protocol is the upper layer of IP. The well-known TCP, UDP, ICMP, etc. are all in the upper layer of IP.
- 16-bit header checksum (Header Checksum): Use CRC for verification to identify whether the IP header is damaged. If it is damaged, it will be discarded directly. It only verifies the IP header and does not verify the following content. , because the verification of the content part needs to be considered by the upper transport layer (TCP), and the IP protocol will directly discard the message as long as it finds a problem with the header.
- 32-bit source IP address (Source Address): Indicates the IP of the sender.
- 32-bit destination IP address (Destination Address): Indicates the IP of the receiving end.
- Options field (Options): variable length, up to 40 bytes.
Supplement: Fragmentation and Assembly
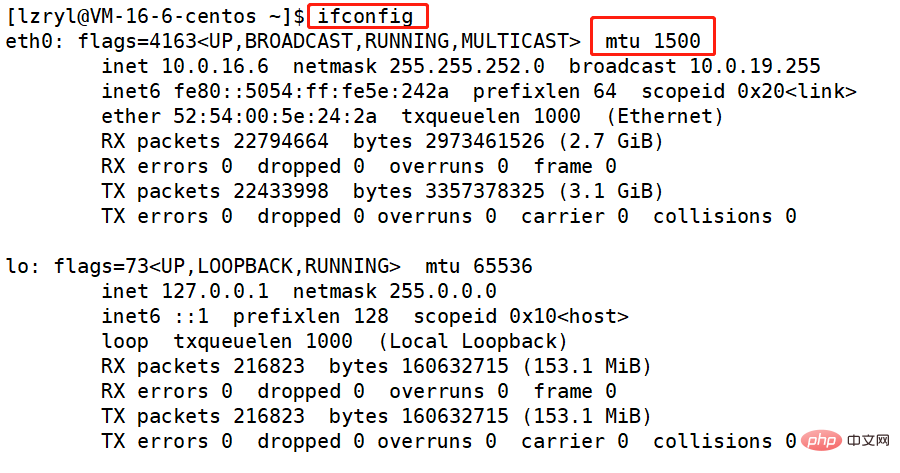
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is a concept in the MAC protocol below the IP layer. We can understand the MAC protocol as a physical Some protocols of the layer, which are located in the lower layer of the IP protocol, then when sending data, it is equivalent to User data application layer protocol header (such as HTTP request header) is handed over to the transport layer (such as TCP protocol) as the payload. The TCP protocol then delivers the data transmitted from the application layer of the TCP header to the IP layer, and the IP layer then delivers the TCP message transmitted from the TCP layer in the IP protocol header to the MAC frame. Therefore, each MAC frame is actually the payload of the IP layer in the IP protocol header. The MAC frame has a length limit, so the IP datagram is not required to be sent as long as you want when it is delivered downwards. If the MAC frame requires an MTU of 1500 bytes, and the total length of the IP datagram is 2000 words section, then it is necessary to fragment the original IP data packet into two pieces and send them in sequence. After the peer host receives it, the peer IP layer completes the assembly. We can use the ifconfig command to view the MTU in the Linux environment.
Fragmentation and assembly are transparent to the upper layer TCP/UDP and the lower layer MAC, that is, neither the upper layer nor the lower layer knows that the IP layer has fragmented the data packet, so the fragmentation and assembly operations will be performed by the sender IP layer and receiver IP layer are completed automatically. However, fragmentation means that one piece of data needs to be converted into multiple groups of data for transmission, and assembly needs to be performed at the opposite end. This will greatly reduce the network transmission efficiency and increase the risk of errors. Therefore, fragmentation should be avoided during the transmission process, that is, Try not to send IP datagrams that exceed the MTU length.
IP address
Definition of IP address:
In IPV4, we use a 32-bit positive integer to represent the IP address. The computer will store the IP address directly in binary, but People are not good at memorizing binary integers, so we use dotted decimal system to record IP addresses: that is, the 32-bit IP address is divided into 4 groups of 8 digits, separated by '.' between groups, and then each group is converted to decimal .
So we can directly calculate that there are up to 2 ^ 32 = 4292967296 IP addresses under the IPV4 standard, but the number that can be used by people is far less than this number. (For example, some IP addresses are reserved for special purposes, and some devices such as routers will occupy multiple IP addresses)
The composition of the IP address:
The IP address consists of The network identifier (network address) and the host identifier (host address) are composed of two parts .
The process of finding an IP address is like traveling to a certain place. For example, if we want to go to Tiananmen Square, it is impossible to take the high-speed train directly to Tiananmen Square. We must first arrive in Beijing (destination network ), and then arrive at Tiananmen (destination host) through transportation in Beijing. Therefore, when we select routing, we should first find the LAN where the target host is located, and then find the target host in the LAN. This method can quickly help us locate the target LAN. Searching for the target host in the LAN is much faster than finding a host in the vast network.
Network ID: Ensure that the two network segments connected to each other have different identities.
Host ID: Ensure that two hosts in the same network segment have different identities.
Division of IP addresses:
IP addresses are divided into five levels, namely Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D and Class E (which have never been used), so currently The only IP addresses we can see are A, B, C, and D. The basis for division is the bits from the 1st to the 4th bit of the IP address.
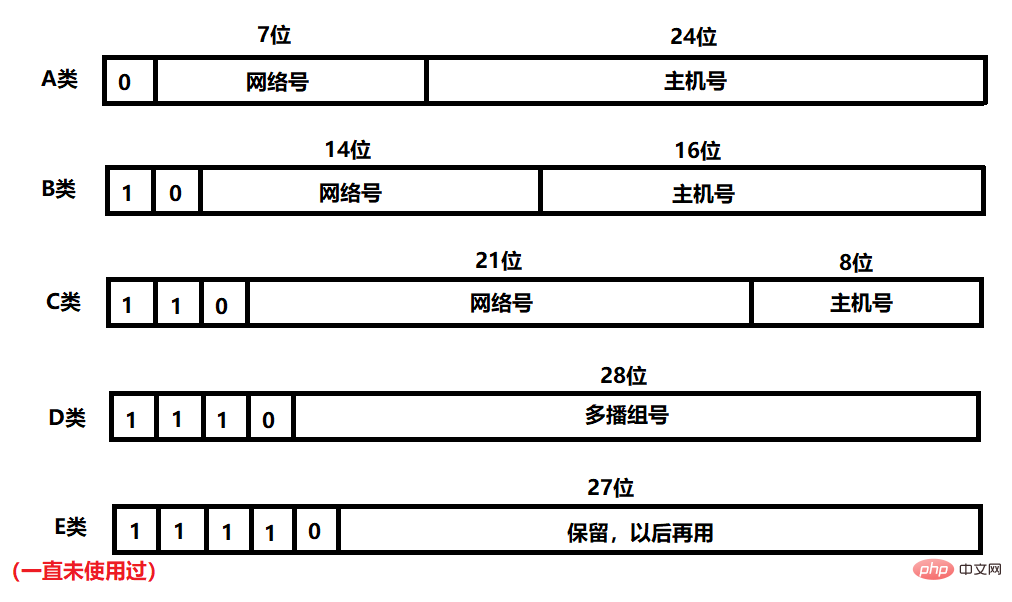
- Class A address: 0.0.0.0 ~ 127.255.255.255
- Class B address: 128.0.0.0 ~ 191.255.255.255
- Class C address: 192.0.0.0 ~ 223.255.255.255
- Class D address: 224.0.0.0 ~ 239.255.255.255
- Class E address: 240.0.0.0 ~ 247.255.255.255
people have proposed a new division scheme: CIDR (Classless Interdomain Routing)
- Introducing the subnet mask to distinguish the network number and the host number
- The subnet mask is also a 32-bit positive integer, but it usually ends with a string of 0
- The IP address and subnet mask are
- &
operated, and the result is the network numberThe division of the network number and the host number has nothing to do with whether the IP address is Class A, Class B or Class C
| Binary expression | |
|---|---|
| 1000 1100 1111 1100 0001 0100 0100 0100 |
| Binary expression | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary expression | |
|---|---|
| 1000 1100 1111 1100 0001 0100 0100 0100 |
| Binary expression | |
|---|---|
140.252.20.64, and the last 4 bits of its subnet mask are 0. This subnet can represent 2 ^ 4 = 16 hosts, so the address of this subnet The range is 140.252.20.64 ~ 140.252.20.79Some special IP addresses
Set all the host addresses in the IP address to 0, that is, the LAN The network number, this IP address represents this LAN.
- Set all host addresses in the IP address to 1 to turn it into a broadcast address. This broadcast address can send data packets to all hosts connected to each other on the same link
- 127. *The IP address is used for local loopback testing, usually 127.0.0.1
- Private IP address and public IP address
10.* The first 8 digits are the network number, and there are 16,777,216 addresses in total
- 172.16.*~172.31.* Previous The 12 digits are the network number, with a total of 1,048,576 addresses
- 192.168.* The first 16 digits are the network number, with a total of 65,536 addresses
- The IP addresses in the above range are all private IPs. IPs not within the above range are global IP addresses (public IP addresses).
FAQ
column!The above is the detailed content of What protocol does ip belong to in computer network architecture?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to set Xiaohongshu not to display IP address? How does it change the id to locate the city?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
How to set Xiaohongshu not to display IP address? How does it change the id to locate the city?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Xiaohongshu is a popular social e-commerce platform where users can share their daily life and discover their favorite products. Some users are more sensitive to personal privacy and hope that their IP address will not be displayed on Xiaohongshu to protect their online privacy. So, how to set Xiaohongshu not to display the IP address? This article will answer this question in detail. 1. How to set Xiaohongshu not to display the IP address? 1. Modify Xiaohongshu settings: Open Xiaohongshu APP, click "Me" in the lower right corner to enter the personal center. Then click on the avatar to enter account settings. In the account settings, find "Privacy Settings" and click to enter. Here, you can find the setting options for IP address, just turn it off. 2. Clear cache: Sometimes, Xiaohongshu may display an error
 How to solve the problem that Windows 10 IP address cannot be saved after setting it
Jul 08, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
How to solve the problem that Windows 10 IP address cannot be saved after setting it
Jul 08, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
Sometimes everyone encounters the need to manually modify the IP address, but some Windows 10 customers report that the IP address cannot be saved after setting it. How to solve this situation? The IP address is stored basically because there is an error in filling in your IP address. You can check whether the subnet prefix has been written with the subnet mask. If so, change it back. After the change, you can save it normally. IP address. How to solve the problem that the Windows 10 IP address cannot be saved after it is set: The error picture is as follows: The prompt "Unable to save the IP setting, please check one or more settings and try" caused by filling in the error. This is the subnet prefix length, not the subnet mask. as the picture shows. As shown in the picture above, many users actually write out the subnet prefix as the subnet mask.
 Where is the IP address of Xiaomi mobile phone?
Feb 29, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
Where is the IP address of Xiaomi mobile phone?
Feb 29, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
Where is the IP address of Xiaomi mobile phone? You can check the IP address on Xiaomi mobile phone, but most users don’t know where to check the IP address. Next is the graphic tutorial on how to check the IP address of Xiaomi mobile phone brought by the editor. Interested users come and take a look! Where is the IP address of Xiaomi mobile phone? 1. First open the settings function in Xiaomi mobile phone, select [My Device] and click to enter; 2. Then on the My Device function page, click [All Parameters] service; 3. Then on the All Parameters page , slide to the bottom and select [Status Information]; 4. Finally, you can see the IP address in the status information interface.
 Where to change the IP address of Xianyu_Share how to change the IP address of Xianyu
Mar 20, 2024 pm 05:06 PM
Where to change the IP address of Xianyu_Share how to change the IP address of Xianyu
Mar 20, 2024 pm 05:06 PM
Xianyu is a very practical second-hand trading platform. Here we can buy many different products and sell our own idle items. What if we want to modify our address? Let’s take a look with the editor below! Share how to modify the Xianyu IP address. First, open the Xianyu software. After entering the homepage, you can see seafood market, recommendations, address and other options in the upper left corner. Click "Address". 2. Then on the address page, we click the [Down Arrow] next to the address; 3. After the final click, we click on the city on the city selection page;
 What to do if win10 computer automatically configures ipv4 address 169_How to turn off automatic configuration of ipv4 address on win10 computer
Mar 27, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
What to do if win10 computer automatically configures ipv4 address 169_How to turn off automatic configuration of ipv4 address on win10 computer
Mar 27, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
1. Open Cortana search, enter cmd, then select Command Prompt, right-click and run as administrator. 2. Enter: netshwinsockresetcatalog and press Enter. 3. Then enter: netshintipresetreset.log and press Enter. 4. Restart the computer, then enter the IP, DNS and other information you want to enter in the IP settings, and confirm.
 How to change the location of Douyin IP address? Why does the IP address change location?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
How to change the location of Douyin IP address? Why does the IP address change location?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Users share their lives, show off their talents, and interact with netizens across the country and even the world through Douyin. Some users wish to change their IP addresses on Douyin due to reasons such as privacy protection or geographical restrictions. So, how does the Douyin IP address change its location? 1. How to change the location of Douyin IP address? A proxy server is an intermediary service used to forward user requests to the Internet and return responses. By configuring a proxy server, users can hide their real IP addresses and change their IP addresses. This approach helps protect user privacy and improves network security. Proxy servers can also be used to access restricted content or bypass geolocation restrictions. Overall, using a proxy server is a practical network tool that can help users browse the Internet more safely and freely.
 Bitcoin transaction IP address (Is the Bitcoin transaction IP address public?)
Feb 06, 2024 am 10:03 AM
Bitcoin transaction IP address (Is the Bitcoin transaction IP address public?)
Feb 06, 2024 am 10:03 AM
Bitcoin transaction IP address Bitcoin transaction IP address is an indispensable and important component of the Bitcoin transaction system. It is the core of the Bitcoin trading platform through which Bitcoin traders can conduct Bitcoin transactions. The Bitcoin transaction IP address is the basis of the Bitcoin transaction system and the basis on which Bitcoin traders can conduct Bitcoin transactions. The Bitcoin trading IP address is a global network address used to locate the Bitcoin trading system’s servers and traders’ devices. By querying the Bitcoin transaction IP address, you can obtain transaction status and related information. In addition, Bitcoin trading IP addresses can also be used to connect clients to the Bitcoin trading system and traders’ devices. Are Bitcoin transaction IP addresses public? Bitcoin transaction IP addresses will not be made public
 Go Regular Expression Guide: How to Match IP Addresses
Jul 12, 2023 am 11:09 AM
Go Regular Expression Guide: How to Match IP Addresses
Jul 12, 2023 am 11:09 AM
Go Regular Expressions Guide: How to Match IP Addresses Introduction: Regular expressions are a powerful tool for matching and searching for specific patterns in strings. In the Go language, you can use the built-in regexp package to implement regular expression operations. This article will introduce how to use regular expressions in Go language to match IP addresses. IP address format: An IP address is an address composed of 32-bit binary numbers, usually represented by four separated decimal numbers. Each decimal number ranges from 0 to 255, for example:



