What is the difference between docker and virtual machine
The difference between docker and virtual machines: 1. Docker starts quickly at the second level, while virtual machines usually take several minutes to start; 2. Different performance losses, docker requires fewer resources; 3. Different isolation , docker belongs to the isolation between processes, and the isolation is weak, while virtual machines can achieve system-level isolation.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, docker version 19.03, Dell G3 computer.
What is the difference between docker and virtual machine
Virtual machine: The virtual machine virtualizes the network card, cpu, and memory through the Hypervisor (virtual machine management system, common ones include VMWare workstation, VirtualBox) Wait for the virtual hardware and then build a virtual machine on it. Each virtual machine is an independent operating system and has its own system kernel.
Containers: Containers use namespace to isolate file systems, processes, networks, devices and other resources, and use cgroups to limit permissions and CPU resources. Ultimately, containers do not affect each other and containers cannot affect the host. .
Advantages of docker
Docker programs running on containers directly use the hardware resources of the host machine, so in terms of CPU, memory, and utilization, , Docker will have greater advantages in efficiency
Docker directly uses the system kernel of the host, avoiding the system boot time required when the virtual machine starts and the resource consumption of the operating system running. Using Docker can Starting a large number of containers within a few seconds is something that a virtual machine cannot do. The advantages of quick startup and low resource consumption make Docker a good application scenario in the automatic operation and maintenance system of elastic cloud platforms.
The startup time of the container is seconds, which saves a lot of time in development, testing, and deployment. Another very critical point is that Docker can be deployed and expanded efficiently. Docker containers can run on almost any platform, including virtual machines, physical machines, public clouds, private clouds, personal computers, servers, etc. This compatibility , which allows users to directly migrate an application from one platform to another.
However, the security of virtual machines is better than that of containers. Docker shares resources such as the kernel and file system with the host, and is more likely to affect other containers and hosts.
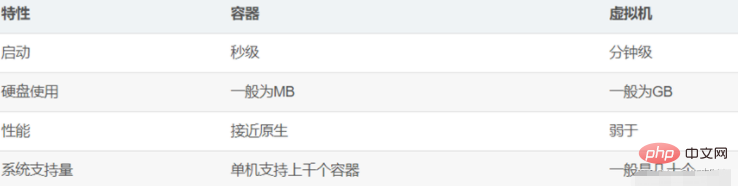
Difference
##1. Different startup speed
docker starts quickly within seconds. Virtual machines usually take several minutes to start.2. Different performance losses
Docker requires fewer resources. Docker virtualizes at the operating system level. Docker containers interact with the kernel, and there is almost no performance loss. Performance is better than virtualization through the hypervisor layer and kernel layer.3. Different system utilization rates
docker is more lightweight. The docker architecture can share a kernel and a shared application library, occupying very little memory. In the same hardware environment, Docker runs far more images than virtual machines, and the system utilization is very high.4. Different isolation properties
Compared with virtual machines, docker isolation is weaker. Docker belongs to the isolation between processes, and virtual machines can achieve system-level isolation. .5. Different security
Docker’s security is also weaker. The tenant root of Docker is the same as the host root. Once the user in the container is upgraded from ordinary user rights to root rights, it directly has the root rights of the host and can perform unlimited operations. The virtual machine tenant root permissions are separated from the host's root virtual machine permissions, and the virtual machines utilize ring-1 hardware isolation technology such as Intel's VT-d and VT-x. This isolation technology can prevent virtual machines from breaking through and interacting with each other. interactions, and containers do not yet have any form of hardware isolation, which makes containers vulnerable to attacks.6. Different manageability
Docker’s centralized management tool is not yet mature. Various virtualization technologies have mature management tools. For example, VMware vCenter provides complete virtual machine management capabilities.7. Availability and recoverability are different
docker’s high-availability support for business is achieved through rapid redeployment. Virtualization has mature guarantee mechanisms such as load balancing, high availability, fault tolerance, migration and data protection that have been tested in production practice. VMware can promise 99.999% high availability of virtual machines to ensure business continuity.8. Creation and deletion speeds are different
Virtualization creation takes minutes, while Docker container creation takes seconds. The rapid iteration of Docker determines whether It can save a lot of time in development, testing, and deployment.9. Delivery and deployment speeds are different
Virtual machines can achieve consistent environment delivery through images, but image distribution cannot be systematic; Docker records this in the Dockerfile The container building process can achieve rapid distribution and rapid deployment in the cluster; Recommended learning: "docker video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between docker and virtual machine. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
To save the image in Docker, you can use the docker commit command to create a new image, containing the current state of the specified container, syntax: docker commit [Options] Container ID Image name. To save the image to the repository, you can use the docker push command, syntax: docker push image name [: tag]. To import saved images, you can use the docker pull command, syntax: docker pull image name [: tag].




