Understand the windowing function in SQL in one article
This article brings you relevant knowledge about SQL server. There are two types of windowing functions, also called analytic functions, one is the aggregation windowing function, and the other is the sorting windowing function. , The following article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about windowing functions in SQL. The article introduces it in detail through example code. Friends who need it can refer to it.

Recommended study: "SQL Tutorial"
Definition of OVER
OVER is used to define a row Window, which operates on a set of values, does not require the use of a GROUP BY clause to group data, and is able to return both base row columns and aggregate columns in the same row.
OVER syntax
OVER ( [ PARTITION BY column ] [ ORDER BY culumn ] )
PARTITION BY clause for grouping;
ORDER BY clause to sort.
Window function OVER() specifies a set of rows, and the windowing function calculates the value of each row in the result set output from the window function.
The windowing function can group data without using GROUP BY, and can also return the columns of the base row and the aggregated column at the same time.
Usage of OVER
OVER window function must be used together with aggregate function or sorting function. Aggregation function generally refers to SUM(), MAX(), MIN, COUNT(), AVG() and other common functions. Sorting functions generally refer to RANK(), ROW_NUMBER(), DENSE_RANK(), NTILE(), etc.
Examples of using OVER in aggregate functions
We use the SUM and COUNT functions as examples to demonstrate to you.
--建立测试表和测试数据
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(20),
GroupName VARCHAR(20),
Salary INT
)
INSERT INTO Employee
VALUES(1,'小明','开发部',8000),
(4,'小张','开发部',7600),
(5,'小白','开发部',7000),
(8,'小王','财务部',5000),
(9, null,'财务部',NULL),
(15,'小刘','财务部',6000),
(16,'小高','行政部',4500),
(18,'小王','行政部',4000),
(23,'小李','行政部',4500),
(29,'小吴','行政部',4700);Windowing function after SUM
SELECT *,
SUM(Salary) OVER(PARTITION BY Groupname) 每个组的总工资,
SUM(Salary) OVER(PARTITION BY groupname ORDER BY ID) 每个组的累计总工资,
SUM(Salary) OVER(ORDER BY ID) 累计工资,
SUM(Salary) OVER() 总工资
from Employee(Tip: You can slide the code left and right)
The results are as follows:
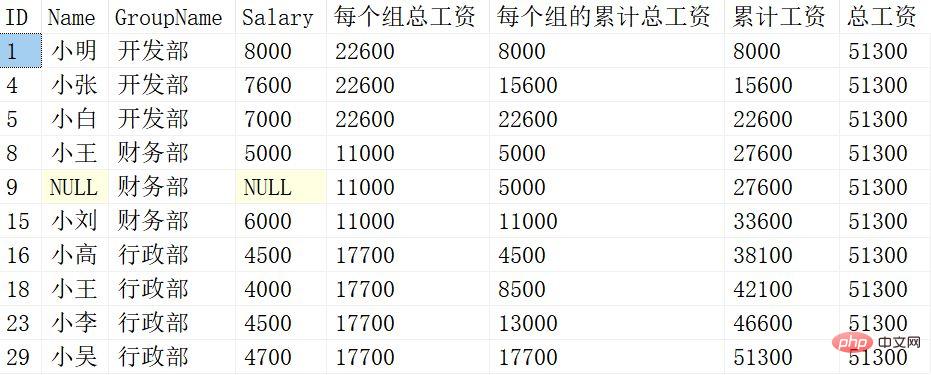
The meaning of each windowing function is different, let’s explain it in detail:
SUM(Salary) OVER (PARTITION BY Groupname)
Only for PARTITION BY The following column Groupname is grouped, and the sum of Salary is calculated after grouping.
SUM(Salary) OVER (PARTITION BY Groupname ORDER BY ID)
For the column Groupname after PARTITION BY Group, then sort by the ID after ORDER BY, and then accumulate Salary within the group.
SUM(Salary) OVER (ORDER BY ID)
ORDER BY only Sort the ID content after sorting, and accumulate the sorted Salary.
SUM(Salary) OVER ()
Summary processing of Salary
After COUNT The result returned by the windowing function
SELECT *,
COUNT(*) OVER(PARTITION BY Groupname ) 每个组的个数,
COUNT(*) OVER(PARTITION BY Groupname ORDER BY ID) 每个组的累积个数,
COUNT(*) OVER(ORDER BY ID) 累积个数 ,
COUNT(*) OVER() 总个数
from Employeeis as follows:
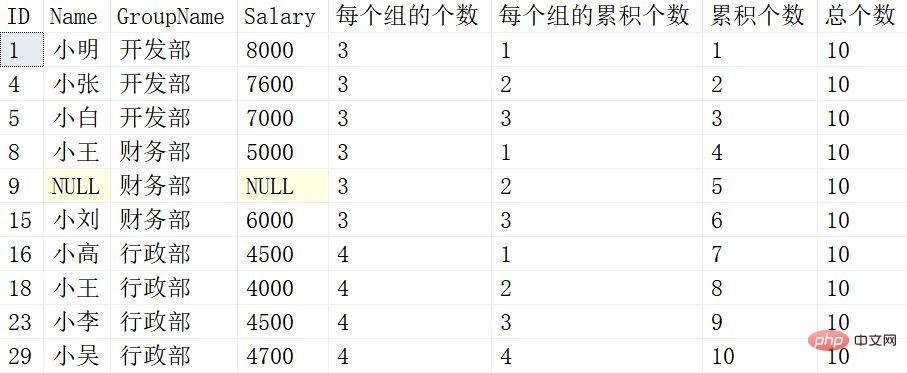
Each subsequent windowing function will no longer be interpreted one by one. You can refer to the above The windowing functions after SUM are compared one by one.
Examples of using OVER in sorting functions
We demonstrate the four sorting functions one by one
--先建立测试表和测试数据 WITH t AS (SELECT 1 StuID,'一班' ClassName,70 Score UNION ALL SELECT 2,'一班',85 UNION ALL SELECT 3,'一班',85 UNION ALL SELECT 4,'二班',80 UNION ALL SELECT 5,'二班',74 UNION ALL SELECT 6,'二班',80 ) SELECT * INTO Scores FROM t; SELECT * FROM Scores
ROW_NUMBER()
Definition : The function of the ROW_NUMBER() function is to sort the data queried by SELECT. Each piece of data is added with a serial number. It cannot be used for ranking students' grades. It is generally used for paging queries, such as querying the top 10 queries 10- 100 students. ROW_NUMBER() must be used together with ORDER BY, otherwise an error will be reported.
Sort student scores
SELECT *, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY ClassName ORDER BY SCORE DESC) 班内排序, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS 总排序 FROM Scores;
The results are as follows:
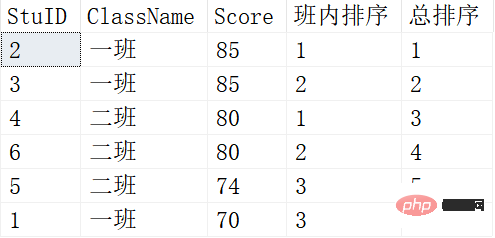
The functions of PARTITION BY and ORDER BY here are the same as what we saw above The aggregate functions have the same function and are used for grouping and sorting.
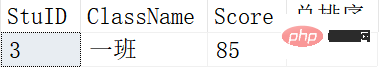
In addition, the ROW_NUMBER() function can also take data in a specified order.
SELECT * FROM ( SELECT *, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS 总排序 FROM Scores ) t WHERE t.总排序=2;
The results are as follows:
RANK()
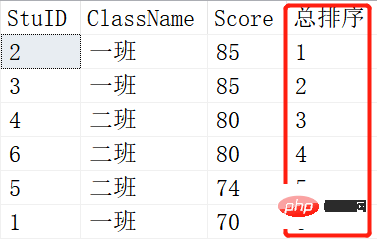
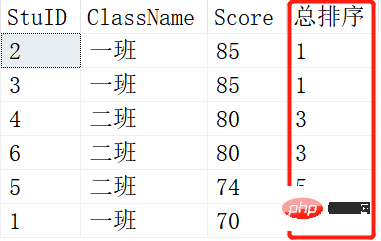
Definition: RANK() function, as the name suggests, a ranking function that can rank a certain field Ranking, what is the difference between this and ROW_NUMBER()? ROW_NUMBER() is sorting. When there are students with the same grades, ROW_NUMBER() will sort them in sequence. Their serial numbers are different, but Rank() is different. If they appear the same, their rankings are the same. Look at the example below:
Example
SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS [RANK],* FROM Scores; SELECT RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS [RANK],* FROM Scores;
Result:
DENSE_RANK()
定义:DENSE_RANK()函数也是排名函数,和RANK()功能相似,也是对字段进行排名,那它和RANK()到底有什么不同那?特别是对于有成绩相同的情况,DENSE_RANK()排名是连续的,RANK()是跳跃的排名,一般情况下用的排名函数就是RANK() 我们看例子:
示例
SELECT RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS [RANK],* FROM Scores; SELECT DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS [RANK],* FROM Scores;
结果如下:

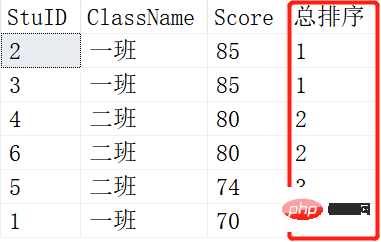
上面是RANK()的结果,下面是DENSE_RANK()的结果
NTILE()
定义:NTILE()函数是将有序分区中的行分发到指定数目的组中,各个组有编号,编号从1开始,就像我们说的'分区'一样 ,分为几个区,一个区会有多少个。
SELECT *,NTILE(1) OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS 分区后排序 FROM Scores; SELECT *,NTILE(2) OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS 分区后排序 FROM Scores; SELECT *,NTILE(3) OVER (ORDER BY SCORE DESC) AS 分区后排序 FROM Scores;
结果如下:
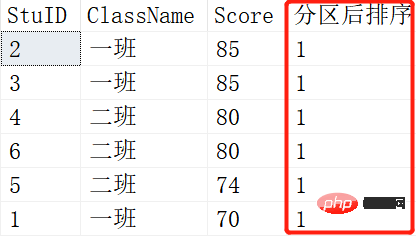
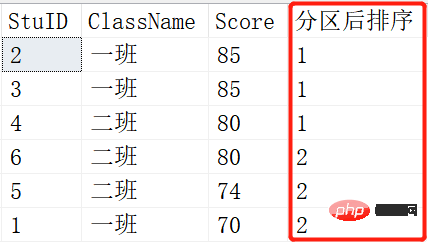
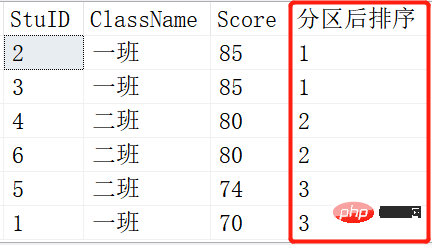
就是将查询出来的记录根据NTILE函数里的参数进行平分分区。
总结
OVER开窗函数是我们工作中经常要使用到的,特别是在做数据分析计算的时候,经常要对数据进行分组排序。上面我们额外介绍了聚合函数和排序函数的与OVER结合的使用方法,此外还有很多与OVER一起使用的函数,比如LEAD函数,LAG函数,STRING_AGG函数等等都会使用到开窗函数OVER,其使用方法也要务必掌握。
推荐学习:《SQL教程》
The above is the detailed content of Understand the windowing function in SQL in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
HQL and SQL are compared in the Hibernate framework: HQL (1. Object-oriented syntax, 2. Database-independent queries, 3. Type safety), while SQL directly operates the database (1. Database-independent standards, 2. Complex executable queries and data manipulation).
 Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
"Usage of Division Operation in OracleSQL" In OracleSQL, division operation is one of the common mathematical operations. During data query and processing, division operations can help us calculate the ratio between fields or derive the logical relationship between specific values. This article will introduce the usage of division operation in OracleSQL and provide specific code examples. 1. Two ways of division operations in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operations can be performed in two different ways.
 Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Oracle and DB2 are two commonly used relational database management systems, each of which has its own unique SQL syntax and characteristics. This article will compare and differ between the SQL syntax of Oracle and DB2, and provide specific code examples. Database connection In Oracle, use the following statement to connect to the database: CONNECTusername/password@database. In DB2, the statement to connect to the database is as follows: CONNECTTOdataba
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What is Identity in SQL? Specific code examples are needed. In SQL, Identity is a special data type used to generate auto-incrementing numbers. It is often used to uniquely identify each row of data in a table. The Identity column is often used in conjunction with the primary key column to ensure that each record has a unique identifier. This article will detail how to use Identity and some practical code examples. The basic way to use Identity is to use Identit when creating a table.
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
When Springboot+Mybatis-plus does not use SQL statements to perform multi-table adding operations, the problems I encountered are decomposed by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object with parameters to simulate passing parameters to the background. We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use tools such as Mybatis-plus-join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper.xml file and configure The smelly and long ResultMap, and then write the corresponding sql statement. Although this method seems cumbersome, it is highly flexible and allows us to
 How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Solution: 1. Check whether the logged-in user has sufficient permissions to access or operate the database, and ensure that the user has the correct permissions; 2. Check whether the account of the SQL Server service has permission to access the specified file or folder, and ensure that the account Have sufficient permissions to read and write the file or folder; 3. Check whether the specified database file has been opened or locked by other processes, try to close or release the file, and rerun the query; 4. Try as administrator Run Management Studio as etc.
 How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL?
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL?
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL? Data aggregation and statistics are very important steps when performing data analysis and statistics. As a powerful relational database management system, MySQL provides a wealth of aggregation and statistical functions, which can easily perform data aggregation and statistical operations. This article will introduce the method of using SQL statements to perform data aggregation and statistics in MySQL, and provide specific code examples. 1. Use the COUNT function for counting. The COUNT function is the most commonly used




