 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 A brief introduction to the Python genetic algorithm Geatpy toolbox
A brief introduction to the Python genetic algorithm Geatpy toolbox
A brief introduction to the Python genetic algorithm Geatpy toolbox
[Related recommendations: Python3 video tutorial]
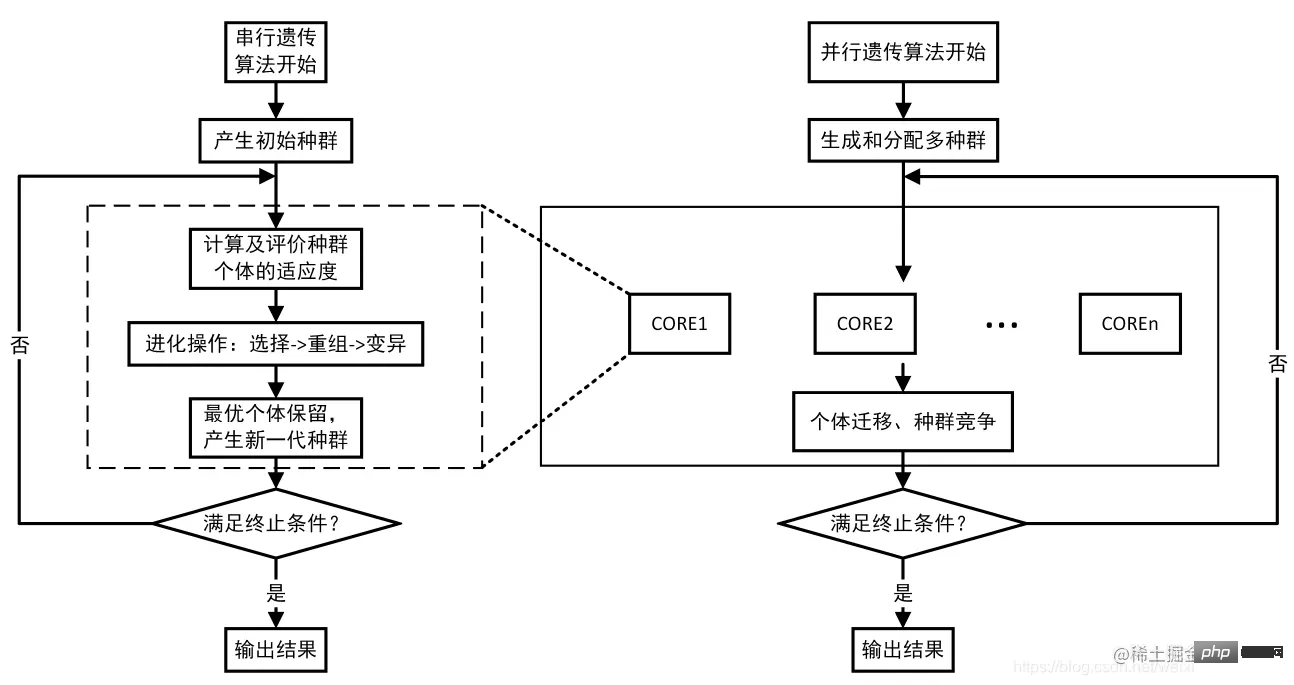
1. What is a genetic algorithm?
Genetic algorithm is a type of search algorithm constructed artificially by simulating the mechanism of biological genetics and natural selection. To a certain extent, genetic algorithm is a mathematical simulation of the biological evolution process. The survival process of biological populations generally follows Darwinian evolution principles. Individuals in the population are selected or eliminated by nature based on their ability to adapt to the environment. The result of the evolutionary process is reflected in the structure of the individual. Its chromosome contains several genes. The corresponding connection between phenotype and genotype reflects the logical relationship between the external characteristics and internal mechanism of the individual. Adapt to the natural environment through crossover and mutation between individuals. Biological chromosomes are represented mathematically or computerically as a string of numbers, still called chromosomes, sometimes also called individuals; adaptability is measured by a numerical value corresponding to a chromosome; the selection or elimination of chromosomes is based on the problem faced. Find the maximum or minimum.
2. Genetic Algorithm Library Geatpy
2.1 Introduction to Genetic Algorithm Toolbox Geatpy Parameters
API official reference document
population parameter[Important attributes: Chrom, Phen, Objv, CV, FitnV]
- sizes: int - population size, that is, population number of individuals.
- ChromNum: int - The number of chromosomes, that is, how many chromosomes each individual has.
- Encoding: str - chromosome encoding method, 'BG': binary/Gray encoding; 'RI': real integer encoding, that is, a mixed encoding of real numbers and integers; 'P': permutation encoding
- Field : array - decoding matrix
- Chrom : array - population chromosome matrix, each row corresponds to a chromosome of an individual.
- Lind : int - population chromosome length.
- ObjV: array - population objective function value matrix, each row corresponds to an individual's objective function value, each column corresponds to a target
- FitnV: array - population individual fitness column vector, each The element corresponds to the fitness of an individual, and the minimum fitness is 0
- CV: array - CV (Constraint Violation Value) is a matrix used to quantitatively describe the degree of violation of constraint conditions. Each row corresponds to an individual, and each column corresponds to A constraint
- Phen: array - the population phenotype matrix (that is, the matrix composed of the decision variables represented by each chromosome of the population after decoding).
- If constraints are set based on the feasibility rule through the CV matrix, then the inequality constraints need to be ≤, and the equality constraints need to be passed into abs() (because it follows the principle that the larger the value, the smaller the fitness)


- lbin and ubin (decision variable range) in ea.Problem.init() Boundary matrix) represents the opening and closing of the range interval, 1 closed 0 open interval
Geatpy result parameter introduction
success: True or False, indicates whether the algorithm was successfully solved.
stopMsg: A string that stores the reason for stopping the algorithm.
optPop: Population object that stores the algorithm solution results. If there is no feasible solution, optPop.sizes=0. optPop.Phen is the decision variable matrix, optPop.ObjV is the objective function value matrix.
lastPop: The last generation population object after the algorithm evolution is completed.
Vars: equal to optPop.Phen, here is the optimal solution. If there is no feasible solution, Vars=None.
ObjV: equal to optPop.ObjV, here is the objective function value corresponding to the optimal solution. If there is no feasible solution, ObjV=None.
CV: equal to optPop.CV, here is the constraint violation degree matrix corresponding to the optimal solution. If there is no feasible solution, CV=None.
startTime: Program execution start time.
endTime: Program execution end time.
executeTime: The time taken by the algorithm.
nfev: Number of algorithm evaluations
gd: (Available only when multi-objective optimization is given and the theoretical optimal solution is given) GD index value .
igd: (Available only when multi-objective optimization is given and the theoretical optimal solution is given) IGD indicator value.
hv: (only for multi-objective optimization) HV indicator value.
spacing: (only for multi-objective optimization) Spacing indicator value.
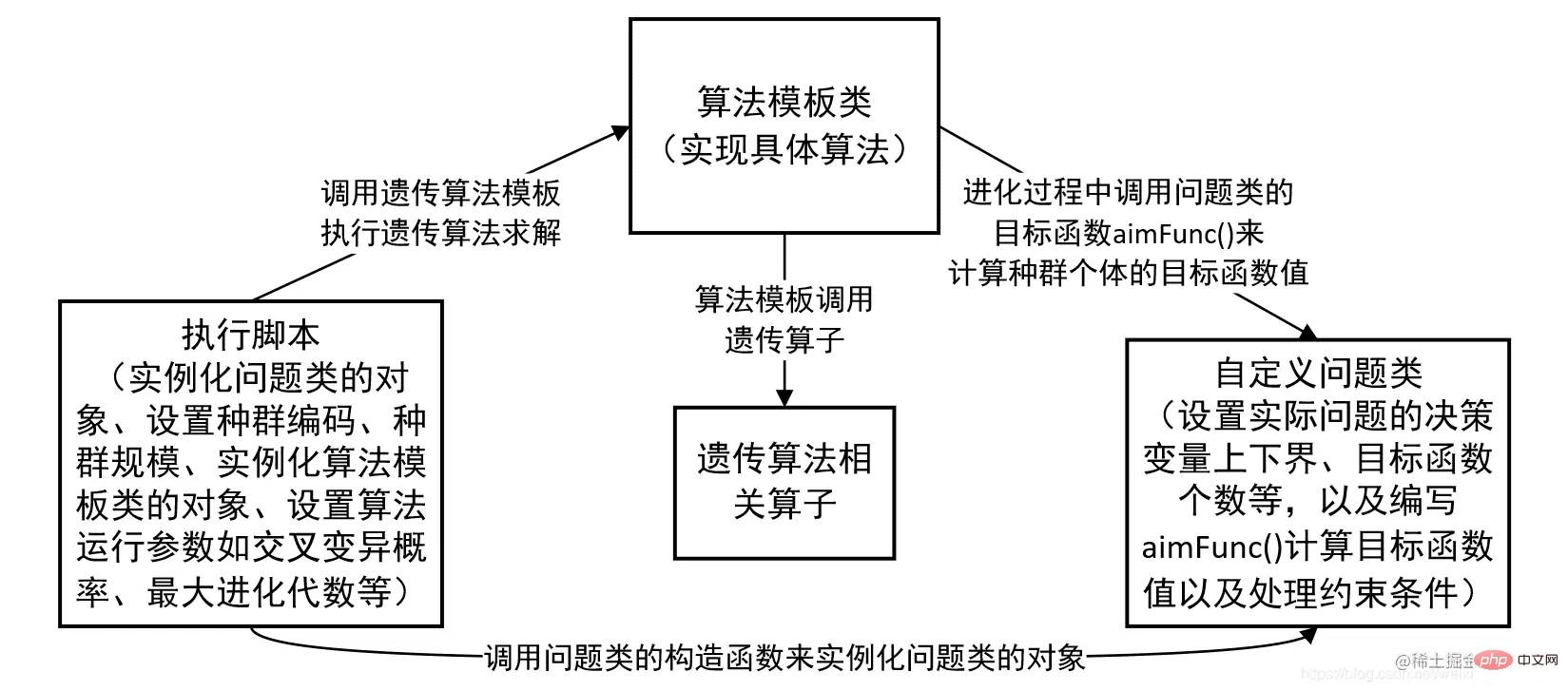
3. Best Practices
3.1 Code Example|Parameter Template

Solution Set:
header_regex = '|'.join(['{}'] * len(headers))
header_str = header_regex.format(*[str(key).center(width) for key, width in zip(headers, widths)])
print("=" * len(header_str))
print(header_str)
print("-" * len(header_str))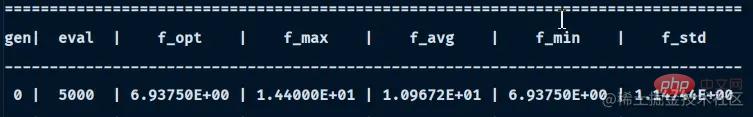
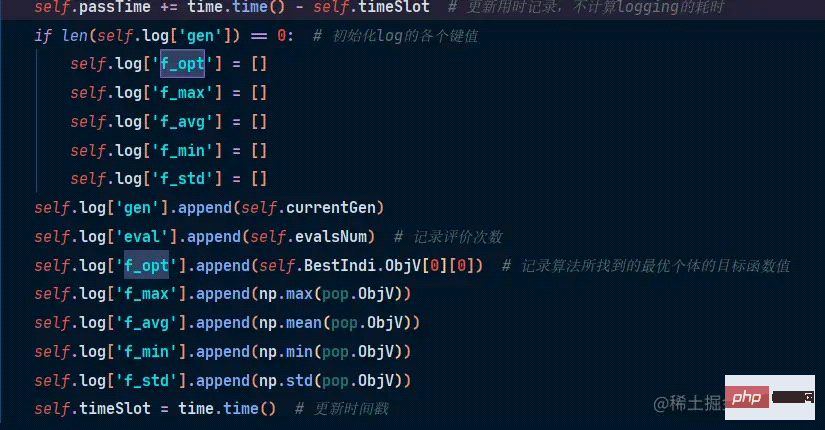
3.2 Best Practicegen: evolutionary algebra
eval: record number of evaluations
f\_opt: objective function value of the contemporary optimal individual
f \_max=Maximum function value of the contemporary population
f\_min Minimum f\_avg : average
 Use the geatpy library to solve the shortest path of a directed acyclic graph
Use the geatpy library to solve the shortest path of a directed acyclic graph
Code [Shortest Path] 1: Use the geatpy library
import numpy as np
import geatpy as ea
class MyProblem(ea.Problem): # 继承Problem父类
def __init__(self):
name = 'Shortest_Path' # 初始化name(函数名称,可以随意设置)
M = 1 # 初始化M(目标维数)
maxormins = [1] # 初始化maxormins(目标最小最大化标记列表,1:最小化该目标;-1:最大化该目标)
Dim = 10 # 初始化Dim(决策变量维数)
varTypes = [1] * Dim # 初始化varTypes(决策变量的类型,元素为0表示对应的变量是连续的;1表示是离散的)
lb = [0] * Dim # 决策变量下界
ub = [9] * Dim # 决策变量上界
lbin = [1] * Dim # 决策变量下边界 1表示闭合区间,0表示开区间
ubin = [1] * Dim # 决策变量上边界
# 调用父类构造方法完成实例化
ea.Problem.__init__(self, name, M, maxormins, Dim, varTypes, lb, ub, lbin, ubin)
# 设置每一个结点下一步可达的结点(结点从1开始数,因此列表nodes的第0号元素设为空列表表示无意义)
self.nodes = [[], [2, 3], [3, 4, 5], [5, 6], [7, 8], [4, 6], [7, 9], [8, 9], [9, 10], [10]]
# 设置有向图中各条边的权重
self.weights = {'(1, 2)': 36, '(1, 3)': 27, '(2, 4)': 18, '(2, 5)': 20, '(2, 3)': 13, '(3, 5)': 12,
'(3, 6)': 23,
'(4, 7)': 11, '(4, 8)': 32, '(5, 4)': 16, '(5, 6)': 30, '(6, 7)': 12, '(6, 9)': 38,
'(7, 8)': 20,
'(7, 9)': 32, '(8, 9)': 15, '(8, 10)': 24, '(9, 10)': 13}
def decode(self, priority): # 将优先级编码的染色体解码得到一条从节点1到节点10的可行路径
edges = [] # 存储边
path = [1] # 结点1是路径起点
while not path[-1] == 10: # 开始从起点走到终点
currentNode = path[-1] # 得到当前所在的结点编号
nextNodes = self.nodes[currentNode] # 获取下一步可达的结点组成的列表
chooseNode = nextNodes[np.argmax(
priority[np.array(nextNodes) - 1])] # 从NextNodes中选择优先级更高的结点作为下一步要访问的结点,因为结点从1数起,而下标从0数起,因此要减去1
path.append(chooseNode)
edges.append((currentNode, chooseNode))
return path, edges
def aimFunc(self, pop): # 目标函数
pop.ObjV = np.zeros((pop.sizes, 1)) # 初始化ObjV
for i in range(pop.sizes): # 遍历种群的每个个体,分别计算各个个体的目标函数值
priority = pop.Phen[i, :]
path, edges = self.decode(priority) # 将优先级编码的染色体解码得到访问路径及经过的边
pathLen = 0
for edge in edges:
key = str(edge) # 根据路径得到键值,以便根据键值找到路径对应的长度
if not key in self.weights:
raise RuntimeError("Error in aimFunc: The path is invalid. (当前路径是无效的。)", path)
pathLen += self.weights[key] # 将该段路径长度加入
pop.ObjV[i] = pathLen # 计算目标函数值,赋值给pop种群对象的ObjV属性
## 执行脚本
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 实例化问题对象
problem = MyProblem()
# 构建算法
algorithm = ea.soea_EGA_templet(problem,
ea.Population(Encoding='RI', NIND=4),
MAXGEN=10, # 最大进化代数
logTras=1) # 表示每隔多少代记录一次日志信息
# 求解
res = ea.optimize(algorithm, verbose=True, drawing=1, outputMsg=False, drawLog=False, saveFlag=True,
dirName='result')
print('最短路程为:%s' % (res['ObjV'][0][0]))
print('最佳路线为:')
best_journey, edges = problem.decode(res['Vars'][0])
for i in range(len(best_journey)):
print(int(best_journey[i]), end=' ')
print()Python3 video tutorial
]The above is the detailed content of A brief introduction to the Python genetic algorithm Geatpy toolbox. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
There is no APP that can convert all XML files into PDFs because the XML structure is flexible and diverse. The core of XML to PDF is to convert the data structure into a page layout, which requires parsing XML and generating PDF. Common methods include parsing XML using Python libraries such as ElementTree and generating PDFs using ReportLab library. For complex XML, it may be necessary to use XSLT transformation structures. When optimizing performance, consider using multithreaded or multiprocesses and select the appropriate library.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.






