Summary of five methods for implementing distributed locks in Redis
Recommended learning: Redis video tutorial
In a single application, if we do not lock the shared data, Data consistency problems will arise, and our solution is usually to lock them.
In the distributed architecture, we will also encounter data sharing operation problems. This article uses Redis to solve the data consistency problem in the distributed architecture.
1. Single-machine data consistency
The single-machine data consistency architecture is shown in the figure below: multiple clients can access the same server and connect to the same database.
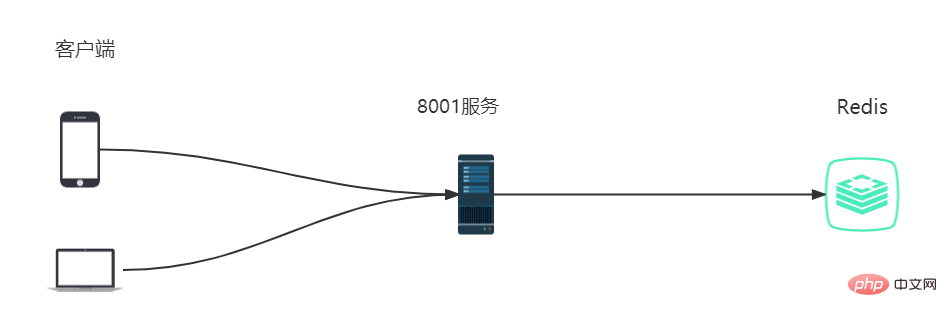
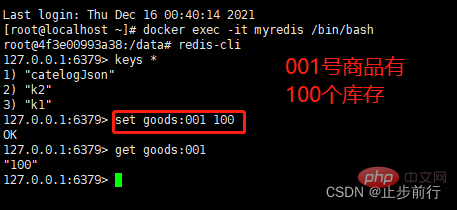
Scene description: The client simulates the process of purchasing goods, and sets the total inventory in Redis to leave 100, multiple Clients make concurrent purchases at the same time.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
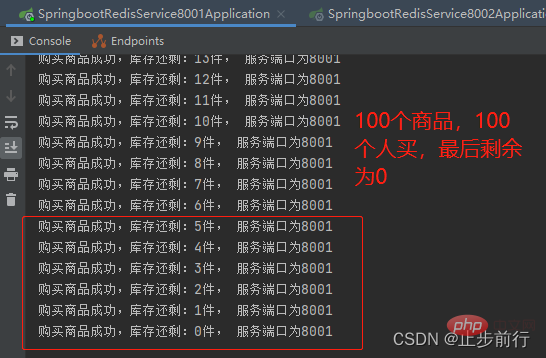
Use Jmeter to simulate high concurrency scenarios. The test results are as follows:
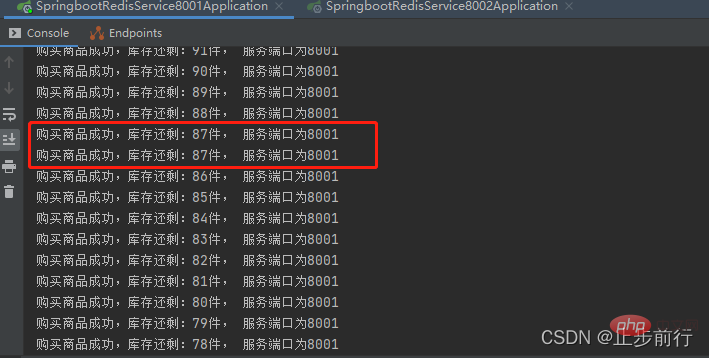
Test results Multiple users purchased the same product, and data inconsistency occurred!
Solution: In the case of a single application, perform locking operations on concurrent operations to ensure that data operations are atomic
synchronizedReentrantLock
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
|
2. Distributed data consistency
The above solves the problem of single application data consistency problem, but if it is a distributed architecture deployment, the architecture is as follows:
provides two services, the ports are 8001, 8002, and the connection is the same A Redis service, in front of the service there is a Nginx as a load balancer
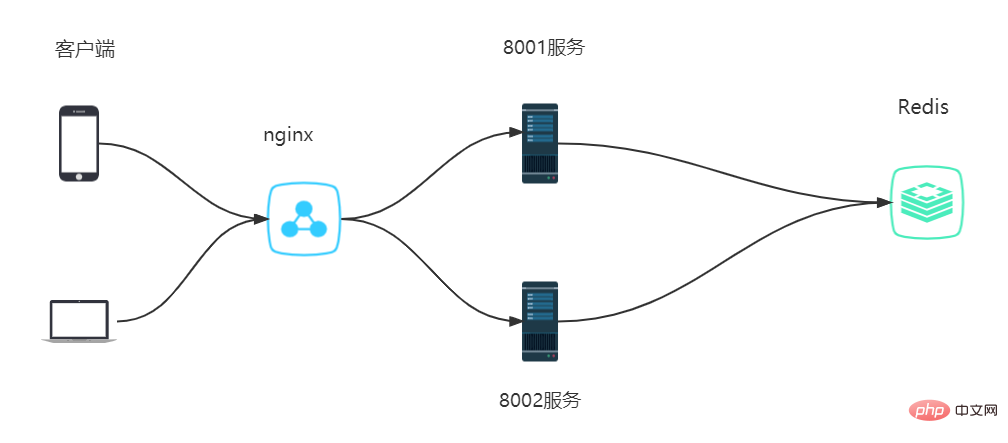
The two service codes are the same, but the ports are different
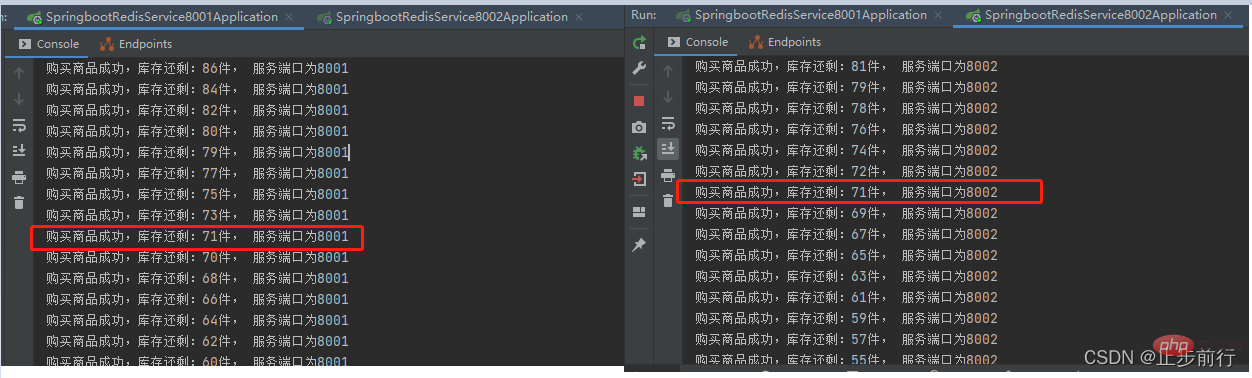
Start the two services 8001 and 8002. Each service is still locked with ReentrantLock and done with Jmeter Concurrency testing found that data consistency issues may occur!
3. Redis implements distributed lock
3.1 Method 1
Cancel the stand-alone lock, use redis below setCommand to implement distributed locking
SET KEY VALUE [EX seconds] [PX milliseconds] [NX|XX]
- EX seconds settings specified The expiration time (in seconds)
- PX milliseconds Sets the specified expiration time (in milliseconds)
- NX Sets the key only if the key does not exist
- XX is only set when the key already exists.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
|
The above code can solve the problem of data consistency in distributed architecture. But if you think about it more carefully, there will still be problems. Let’s make improvements below.
3.2 Method 2 (Improved Method 1)
In the above code, if the machine where the microservice jar package is deployed suddenly hangs during the running of the program, The code level has not reached the finally code block at all, which means that the lock has not been deleted before the shutdown. In this case, there is no way to guarantee unlocking
So, here is what is needed Add an expiration time to this key. There are two ways to set the expiration time in Redis:
template.expire(REDIS_LOCK,10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)template.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value,10L,TimeUnit.SECONDS)
The first method It requires a separate line of code, and it is not placed in the same step as locking, so it is not atomic and will cause problems.
The second method sets the expiration time at the same time as locking. There is no problem. Here we use this method
Adjust the code and set the expiration time while locking:
1 2 |
|
This method solves the problem of being unable to release the lock due to sudden service downtime. The problem. But if you think about it more carefully, there will still be problems. Let’s make improvements below.
3.3 Method three (improved method two)
Method two sets the expiration time of key, which solves the problem that key cannot be deleted, but The problem is here again
上面设置了key的过期时间为10秒,如果业务逻辑比较复杂,需要调用其他微服务,处理时间需要15秒(模拟场
景,别较真),而当10秒钟过去之后,这个key就过期了,其他请求就又可以设置这个key,此时如果耗时15秒
的请求处理完了,回来继续执行程序,就会把别人设置的key给删除了,这是个很严重的问题!
所以,谁上的锁,谁才能删除
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
|
这种方式解决了因服务处理时间太长而释放了别人锁的问题。这样就没问题了吗?
3.4 方式四(改进方式三)
在上面方式三下,规定了谁上的锁,谁才能删除,但finally快的判断和del删除操作不是原子操作,并发的时候也会出问题,并发嘛,就是要保证数据的一致性,保证数据的一致性,最好要保证对数据的操作具有原子性。
在Redis的set命令介绍中,最后推荐Lua脚本进行锁的删除,地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 |
|
3.5 方式五(改进方式四)
在方式四下,规定了谁上的锁,谁才能删除,并且解决了删除操作没有原子性问题。但还没有考虑缓存续命,以及Redis集群部署下,异步复制造成的锁丢失:主节点没来得及把刚刚set进来这条数据给从节点,就挂了。所以直接上RedLock的Redisson落地实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
|
推荐学习:Redis视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Summary of five methods for implementing distributed locks in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)





