 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Let's talk about how to use Node's built-in module zlib for gzip compression
Let's talk about how to use Node's built-in module zlib for gzip compression
Let's talk about how to use Node's built-in module zlib for gzip compression
How to perform gzip compression in Node? The following article introduces how the built-in module zlib of Node performs gzip compression. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

Any server-side development is indispensable for performance optimization operations. When using the HTTP interface (API) for data transfer at the front and back ends, if the amount of data transferred is too large, it will inevitably cause The request timed out or failed.
nodejs provides us with a zlib built-in module, we can use its gzip method to compress the passed data, Thereby improving data transmission efficiency. [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial]
What is gzip?
GZIP encoding over the HTTP protocol is a technique used to improve the performance of WEB applications
This generally refers to a function installed in the server. When someone visits the website in this server, this function in the server compresses the web content and transmits it to the visiting computer browser for display. , Generally, plain text content can be compressed to 40% of the original size
This waytransmission is faster. The effect is that the data will be displayed quickly after you click the URL, improving the user experience. Of course, this will also increase the load on the server. Generally, this functional module is installed in the server
Reducing the file size has two obvious benefits:
- First, it can reduce storage space
- Secondly, when transferring files through the network, it can reduce the transmission time
When we transfer local data, if a file is too large We often use file compression technology (zip or rar, etc.) to compress large files into small files for delivery, and the recipient can then decompress them, because the compression speed is generally relatively fast, so It can reduce the time during the file transfer process, thereby improving efficiency
Simply put,gzip is actually a method used on the server (back-end) and client (front-end) ) A method of compressing data
What is the relationship between gzip and zlib?
zlib is the implementation library of the DEFLATE algorithm. Its API supports both the gzip file format and A simplified data flow format
DEFLATEuses both theLZ77 algorithmandHuffman coding (Huffman Coding)A lossless data compression algorithm
gzip in HTTP compression, a method of accelerating transmission on the World Wide Web HTML and other content technology
So it can be said that zlib adds some content based on gzip, which is whynodeThe gzip method is in the zlib built-in module because
ordinary data transmission
us Use node to build a server to demonstrate the common way we pass data:
server.js
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf-8",
});
const readStream = fs.createReadStream("./index.html");
// res本质就是一个可写流
readStream.pipe(res);
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("服务器启动啦!");
});This is a simple node server, after the browser accesses it, it will return us an index.html. You can write whatever you want in this index.html, the more you write. The better
The stream stream in the built-in module fs that we talked about in the previous section is also used here. It should be noted that , The res parameter in the node server is essentially a writable stream, so we can directly use res in the pipe pipeline
If you don’t know much about
nodebuilding a server or thestreamstream of the built-in modulefs, you can read my previous article :Node.js | Build a back-end server (including the use of the built-in module http | url | querystring)Node.js | Operate local files - play with fs built-in module
Run the server.js file and use the browser to access the node server:
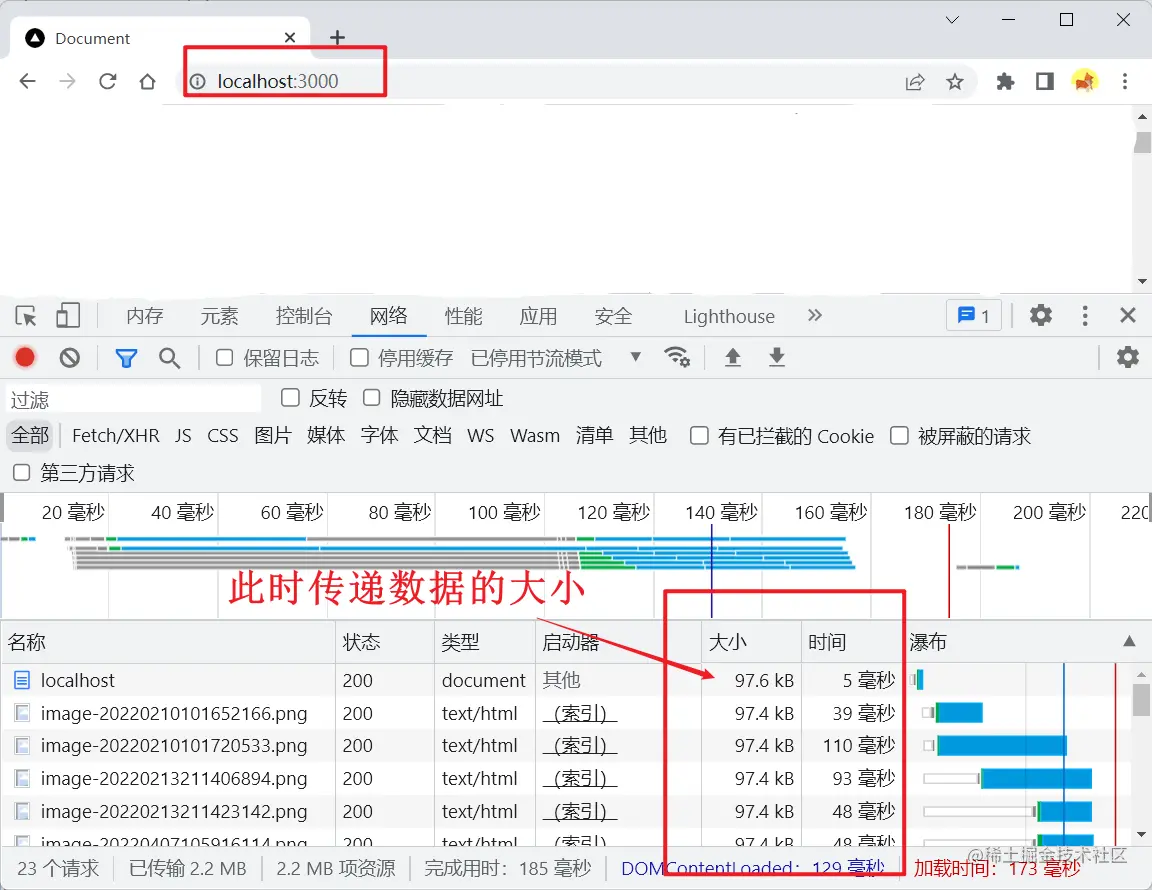
You can see me here The size of the data transferred is 97.6kb (this depends on the contents of your index.html)
gzip compressed data transfer
We use gzip to transform the above example of ordinary data transmission:
server.js
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
// 导入内置模块zlib
const zlib = require("zlib");
// 获取gzip方法
const gzip = zlib.createGzip();
http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf-8",
"Content-Encoding": "gzip", // 告诉浏览器我们是通过gzip压缩的
});
const readStream = fs.createReadStream("./index.html");
// res本质就是一个可写流
// 在数据返回之前使用gzip压缩数据
readStream.pipe(gzip).pipe(res);
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("服务器启动啦!");
});先引入zlib内置模块,再使用zlib.createGzip()获取gzip方法,这个gzip方法实际也是一种数据流的格式,与node服务器中的res参数一样,这也是pipe管道中能直接使用gzip的原因
我们在将数据传递给res参数(客户端)之前,通过pipe管道的链式调用,将gzip加上
这样readStream(服务端)的数据会先经过gzip压缩,之后才会传递给res参数(客户端)
❗️ 需要注意的是:
http数据压缩的方式不止有gzip,还有其它的压缩方式,只不过gzip是最常见最常用的一种方式
所以我们服务端使用gzip将数据压缩后传递给浏览器时,浏览器并不知道我们是使用哪种方式压缩的数据,于是就不知道该以哪种方式进行解压,所以我们需要手动明确的告诉浏览器我们使用的是gzip,服务端加上以下响应头即可:
"Content-Encoding": "gzip", // 告诉浏览器我们是通过gzip压缩的
这样浏览器就能够正确解压我们传递的数据了,运行上面的server.js,打开浏览器访问我们的node服务器:
可以看到使用gzip压缩后我这里传递的数据大小只有27.5kb(这取决于你的index.html的内容),这与之前的97.6kb相比,数据传输速率大幅提升,这就是我们使用gzip的意义!
结语
这篇文章讲了node的一个非常实用的小模块zlib,zlib大家可能之前没听过,但gzip应该都曾听过,gzip是请求数据传输性能优化的一种很好的方式,看完本篇文章,相信你会对gzip有了更深的理解
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about how to use Node's built-in module zlib for gzip compression. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node with nvm: 1. Download "nvm-setup.zip" and install it on the C drive; 2. Configure environment variables and check the version number through the "nvm -v" command; 3. Use the "nvm install" command Install node; 4. Delete the installed node through the "nvm uninstall" command.
 How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to handle file upload? The following article will introduce to you how to use express to handle file uploads in the node project. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will share with you Node's process management tool "pm2", and talk about why pm2 is needed, how to install and use pm2, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
npm node gyp fails because "node-gyp.js" does not match the version of "Node.js". The solution is: 1. Clear the node cache through "npm cache clean -f"; 2. Through "npm install -g n" Install the n module; 3. Install the "node v12.21.0" version through the "n v12.21.0" command.
 What is a single sign-on system? How to implement it using nodejs?
Feb 24, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
What is a single sign-on system? How to implement it using nodejs?
Feb 24, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
What is a single sign-on system? How to implement it using nodejs? The following article will introduce to you how to use node to implement a single sign-on system. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to




