Let's talk about interceptors (Gates) in Laravel

Laravel Gates (interceptors) allow you to authorize users to access certain areas of your application. You can easily define interceptors in your application and then use them to allow or deny access.
Simple example
Suppose in the user table, there is a column named admin, depending on whether the user is an administrator, it can be 1 or 0. We can easily secure a module that is part of the application with a simple check like this:
Route::get('administration', function(){
if(auth()->check() && auth()->user()->admin){
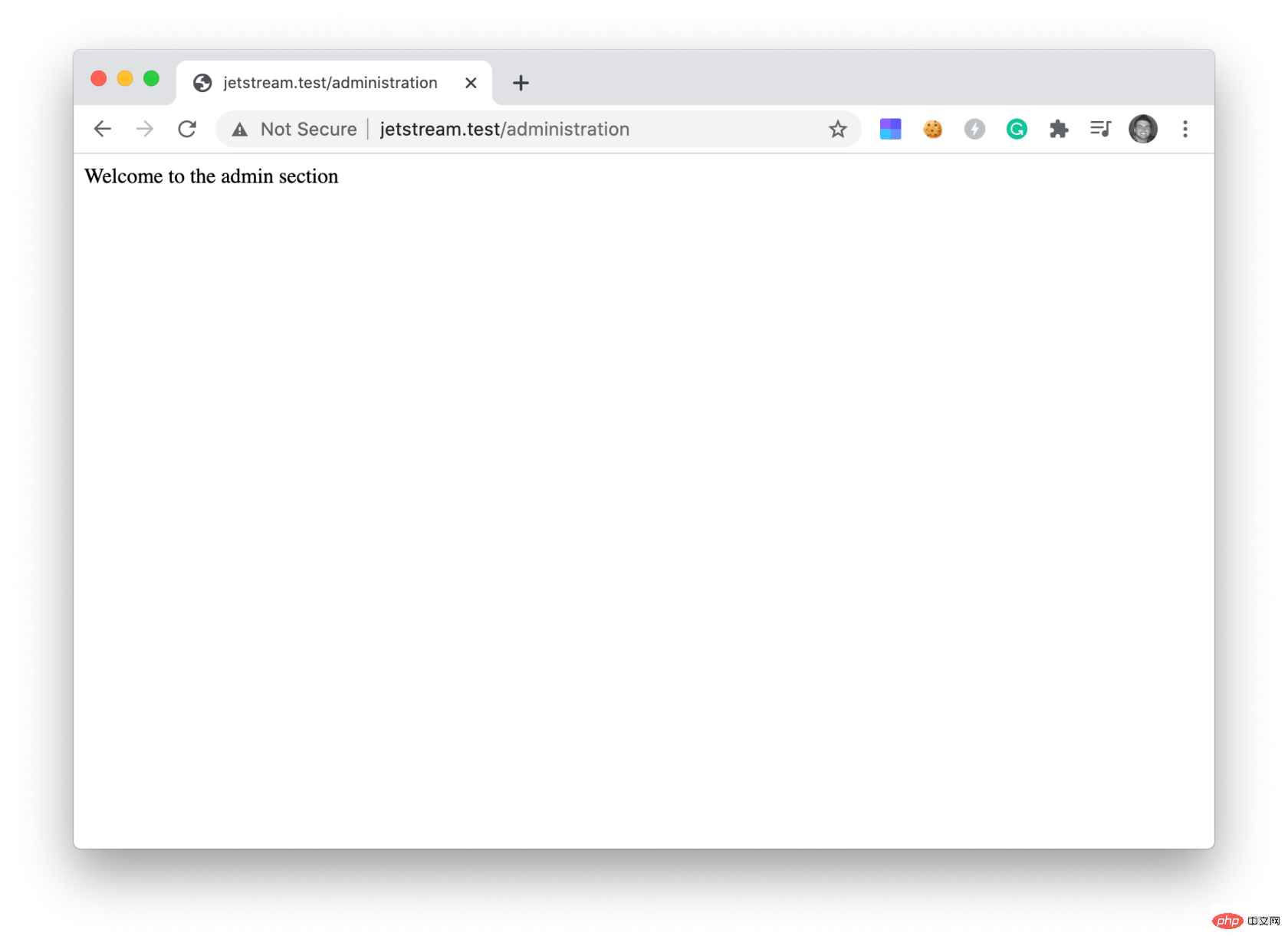
echo 'Welcome to the admin section';
} else {
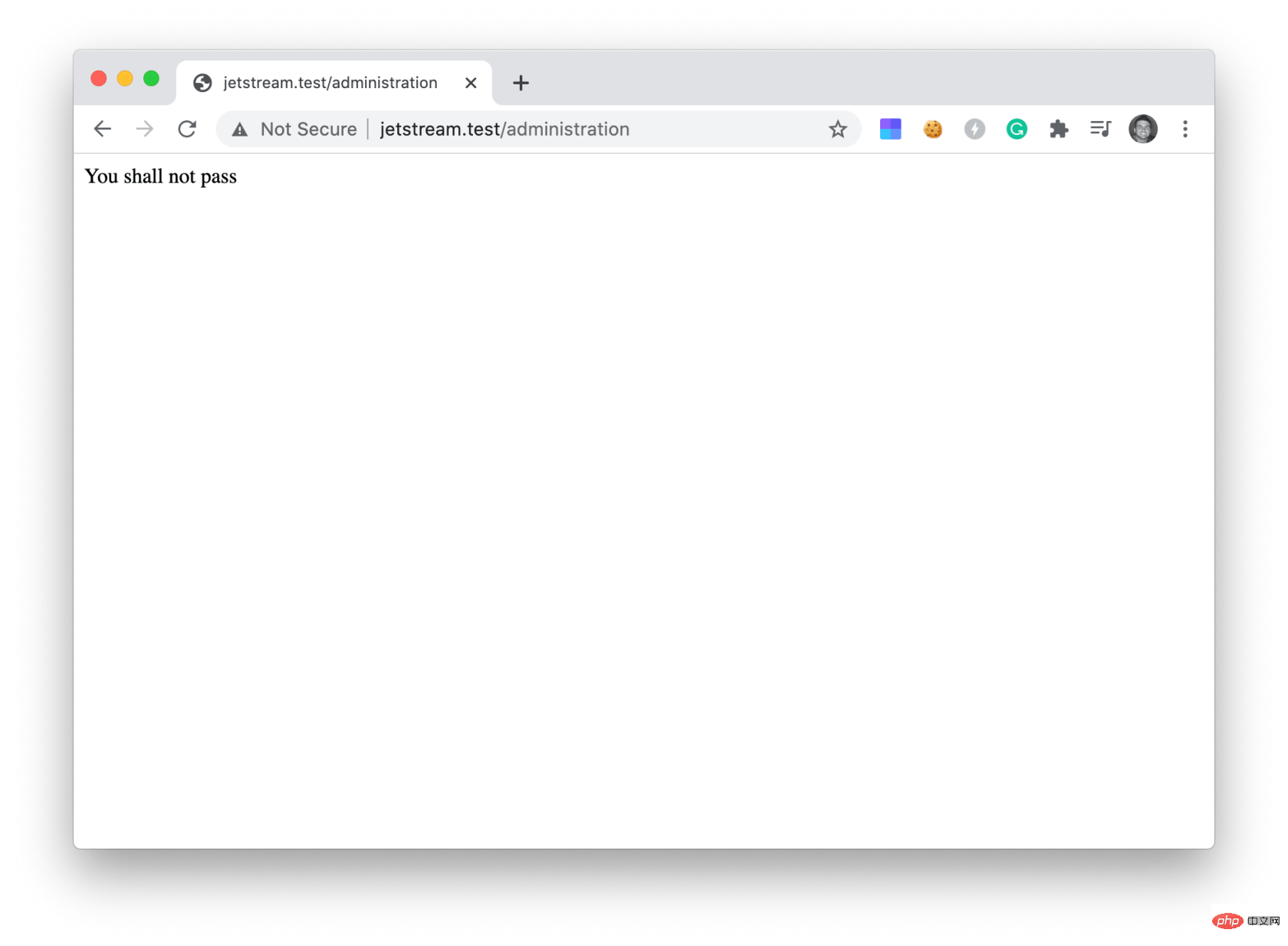
echo 'You shall not pass';
}
}); If a specific user has their admin line set to 1, they will see the following output.
Otherwise, they will see the following:
This looks great right! We have an easy way to allow or deny access to specific parts of our application. However, the problem is: what if there are a large number of places throughout the application where user access permissions need to be checked and modified. We would have to search the code globally and modify this logic everywhere. Not very efficient.
For this, we can define a Gate (interceptor) and use it throughout the application.
Define the interceptor
To define the interceptor, you can open the App\Providers\AuthServiceProvider.php file and in our boot () Add the following content to the method:
public function boot()
{
$this->registerPolicies();
Gate::define('access-admin', function ($user) {
return $user->admin;
});
}We can use this interceptor anywhere in the entire application where we want to authenticate the administrator user. In the next section you'll see how we use this new interceptor.
Using interceptors
To use interceptors, we can call Gate::allows() or Gate::denies( ) method, as shown below:
Route::get('administration', function(){
if (Gate::allows('access-admin')) {
echo 'Welcome to the admin section';
} else {
echo 'You shall not pass';
}
});Please note:
Gate::denies()method will doGate::allows()The benefit of performing a reverse check
interceptor is that we can now change our definition at any time and the authorization logic will be changed synchronously throughout the application.
Another purpose of using interceptors is to check permissions related to data. Taking a blog as an example, we can grant users editing permissions on posts they create.
We can pass data to the interceptor to check if the user has permission to perform an action.
Passing data like an interceptor
Suppose our application has a Post table with a column user_id, It contains the ID of the user who created it. We can define a Gate (interceptor) to determine if a user can edit a specific post like this:
Gate::define('edit-post', function ($user, $post) {
return $user->id === $post->user_id;
});Two parameters are passed to our interceptor definition. The first is the $user object, which contains the authenticated user, and the second parameter is our $post object.
Tips: If there is no authenticated user, the interceptor will return false.
The interceptor will allow access if the authenticated user is the original author; otherwise it will deny access.
Here's a quick example of how we can use the new edit-post interceptor.
Route::get('edit/{id}', function($id){
$post = \App\Model\Post::find($id);
if( Gate::allows('edit-post', $post) ){
echo 'You can edit this post';
} else {
echo 'You shall not pass';
}
});Above, we used Route Closures in the example, but we may want to map this route to a controller. This will also let us use the new Authorize function.
Authorize Authorization Helper Function
In addition to efficiency, another reason to use interceptors is the helper function.
Assume we map the route to the controller:
Route::get('edit/{id}', 'PostController@edit'); We can use the authorize() helper to check if the authenticated user has permission to edit the post:
<?php namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Post;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class PostController extends Controller
{
public function edit($id){
$post = Post::find($id);
$this->authorize('edit-post', $post);
}
}If the controller inherits from the App\Http\Controllers\Controller base class, you can use the function just like the Gate::allow() function authorize() Helper function.
Finally, what if we want to check authorization in the view? We can do this using the @can Blade function helper.
Authentication at the view layer
Assume that the Blade view is as follows:
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<meta>
<title>{{ $post->title }}</title>
<h1 id="post-gt-title">{{ $post->title }}</h1>
<p>{!! $post->body !!}</p>
We can use the Blade helper function@can Check if the current user is allowed to edit this post:
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<meta>
<title>{{ $post->title }}</title>
<h1 id="post-gt-title">{{ $post->title }}</h1>
<p>{!! $post->body !!}</p>
@can('edit-post', $post)
id }}">Edit Post
@endcan
If the authenticated user is the original author of the post, they will see an Edit Post button.
Using the @can helper function can make our code easier to read and manage. You can also use @cannot to reverse the operation.
Summary
This is the basics of using Gates (interceptors) in Laravel applications. Interceptors allow us to easily authorize specific users to access areas of our application. This may also be called an Access Control List (ACL), a list of permissions associated with an object. But we shouldn't overcomplicate things... In the simplest scenario, Interceptors are used to allow or deny access. Users can either be allowed authorization or be denied authorization. Since this tutorial is about getting the user through and not through... it makes sense to send you out with this image of Gandalf from Lord of the Rings (manual dog head). To learn more about Laravel Gates (interceptors), be sure to visit the Larav authorization documentation. English original address: https://devdojo.com/tnylea/laravel-gates Translation address: https://learnku.com/laravel/t/67585 [Related recommendations: laravel video tutorial]
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about interceptors (Gates) in Laravel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
LaravelEloquent Model Retrieval: Easily obtaining database data EloquentORM provides a concise and easy-to-understand way to operate the database. This article will introduce various Eloquent model search techniques in detail to help you obtain data from the database efficiently. 1. Get all records. Use the all() method to get all records in the database table: useApp\Models\Post;$posts=Post::all(); This will return a collection. You can access data using foreach loop or other collection methods: foreach($postsas$post){echo$post->
 The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, containerization and microservice architectures, supporting Docker and Kubernetes; 2) introducing JIT compilers and enumeration types to improve performance and data processing efficiency; 3) Continuously optimize performance and promote best practices.
 Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Efficiently process 7 million records and create interactive maps with geospatial technology. This article explores how to efficiently process over 7 million records using Laravel and MySQL and convert them into interactive map visualizations. Initial challenge project requirements: Extract valuable insights using 7 million records in MySQL database. Many people first consider programming languages, but ignore the database itself: Can it meet the needs? Is data migration or structural adjustment required? Can MySQL withstand such a large data load? Preliminary analysis: Key filters and properties need to be identified. After analysis, it was found that only a few attributes were related to the solution. We verified the feasibility of the filter and set some restrictions to optimize the search. Map search based on city
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
How does Laravel play a role in backend logic? It simplifies and enhances backend development through routing systems, EloquentORM, authentication and authorization, event and listeners, and performance optimization. 1. The routing system allows the definition of URL structure and request processing logic. 2.EloquentORM simplifies database interaction. 3. The authentication and authorization system is convenient for user management. 4. The event and listener implement loosely coupled code structure. 5. Performance optimization improves application efficiency through caching and queueing.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




