 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How does Python's built-in module OS create a SHELL-side file processor?
How does Python's built-in module OS create a SHELL-side file processor?
How does Python's built-in module OS create a SHELL-side file processor?
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Python, which mainly introduces the relevant content about how the built-in module OS builds a SHELL-side file processor. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it will be helpful to you. Everyone is helpful.

[Related recommendations: Python3 video tutorial]
OS module
When explaining the package module, we mentioned To check the global package path and registration through the sys module, today we try to understand the OS module. The main function of this module is to open up the communication between the program and the system.
Through help('modules') we can find that OS appears as a built-in module of python.
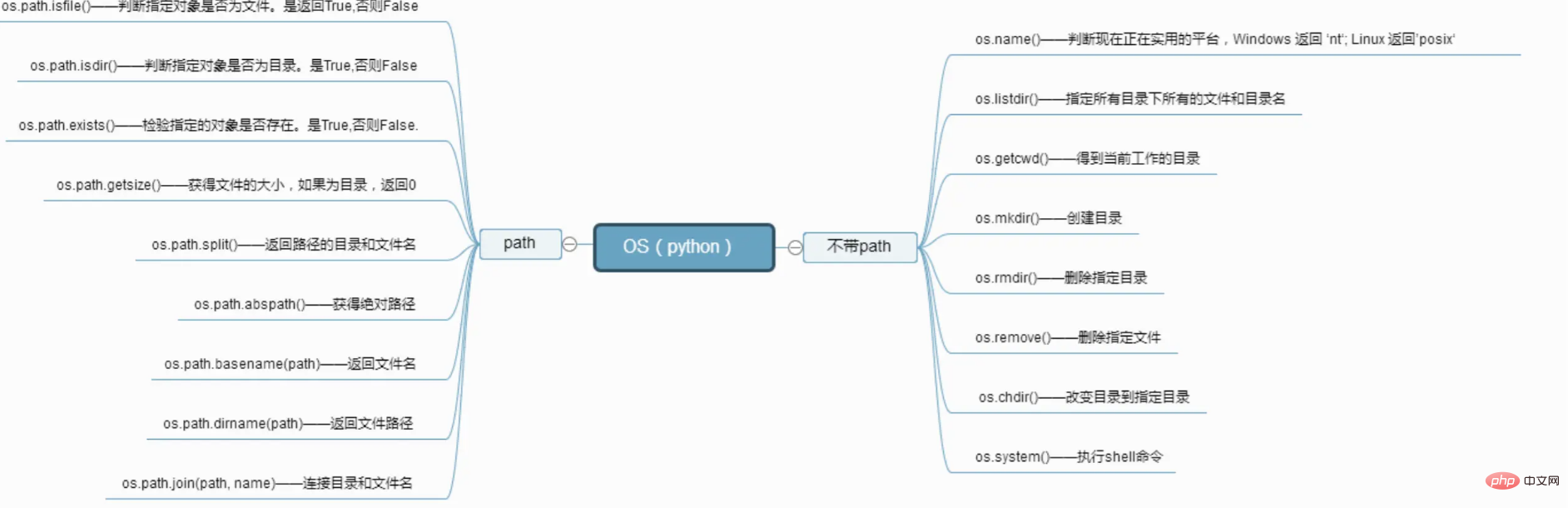
With path
Judge the file
import os print(os.path.isfile('demo.txt'))
If it is a file, return True Otherwise returns False.
Judge the folder
import os print(os.path.isdir('../os'))
We pass a path as the parameter. If it is a folder, it returns True, otherwise it returns False.
Determine whether the file exists
This should be an operation we often use in scripts. If it exists, we will use it. If it does not exist, we need to create the file. Populate default content.
import os print(os.path.exists('ttttt.txt'))
Similarly returns True if it exists and False otherwise.
Get the file size
We often view file information through ls -al on the server, including the file size attribute, as python The built-in modules must also have related attribute acquisition functions.
import os print(os.path.getsize('demo.txt'))
Getting the path and file

#In the past, when operating Java, we often needed to get the directory where the file is located. At that time, it was all obtained through Java object attributes, and Python China Automated took care of it for us.
Get the absolute path
I wonder if you have noticed that when we get the directory where the script is located above, we use ../os and other methods, including the path and file chapter where we manually type out the file. The full path is actually provided by python.
import os print(os.path.abspath('practice.py'))

Return file name
import os print(os.path.basename('practice.py'))

Get file path

It only works if we pass in the full path of the file dirname, which feels a bit tasteless
Path splicing
We often have paths Address concatenation. Windows and Linux have different file delimiters. Java provides us with a variable to obtain the delimiter, but python directly ignores the delimiter and directly provides us with a splicing method.
import os print(os.path.join('parent','child'))

Without path
Get the platform
Sometimes we need To perform different operations according to different platforms, you need to obtain platform information at this time.
import os print(os.name)

Get all files
Since it is a module, our commonly used functions are definitely indispensable. As mentioned before, we often use the server Execute ls -al .
import os print(os.listdir)

Current working path
Many times we do not return directly Script path execution scripts are often executed through absolute paths or relative paths. Sometimes scripts will depend on certain files on the execution path, so it is important to obtain the execution script path.

Directory operations
I believe it is also important to create and delete files and directories. Let’s take a look at how to do it.
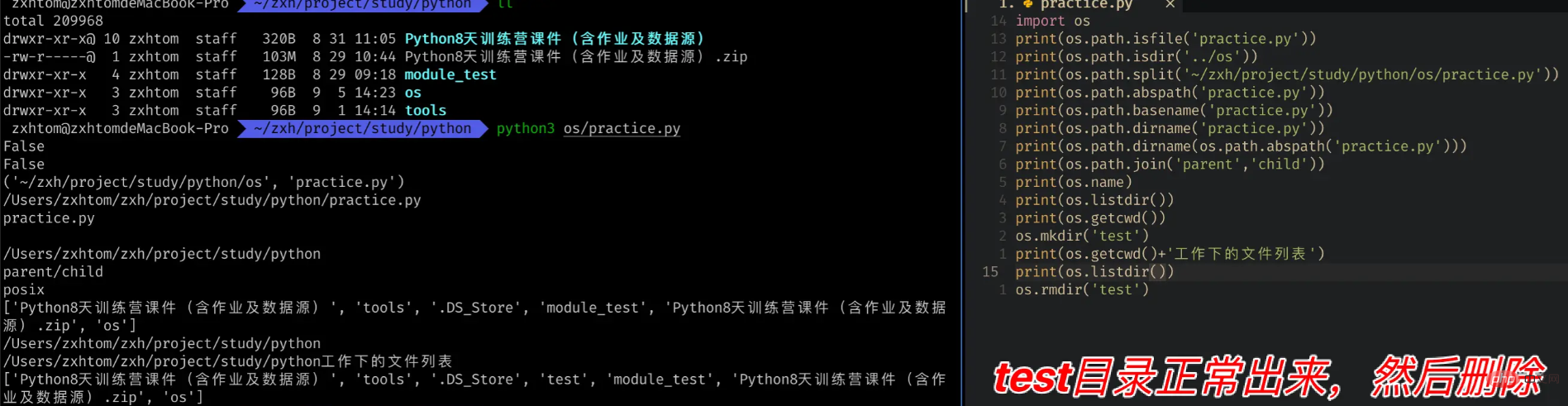
import os os.mkdir('test') print(os.getcwd()+'工作下的文件列表'+os.listdir()) os.rmdir('test')
Rename File
import os os.rename(old,new)
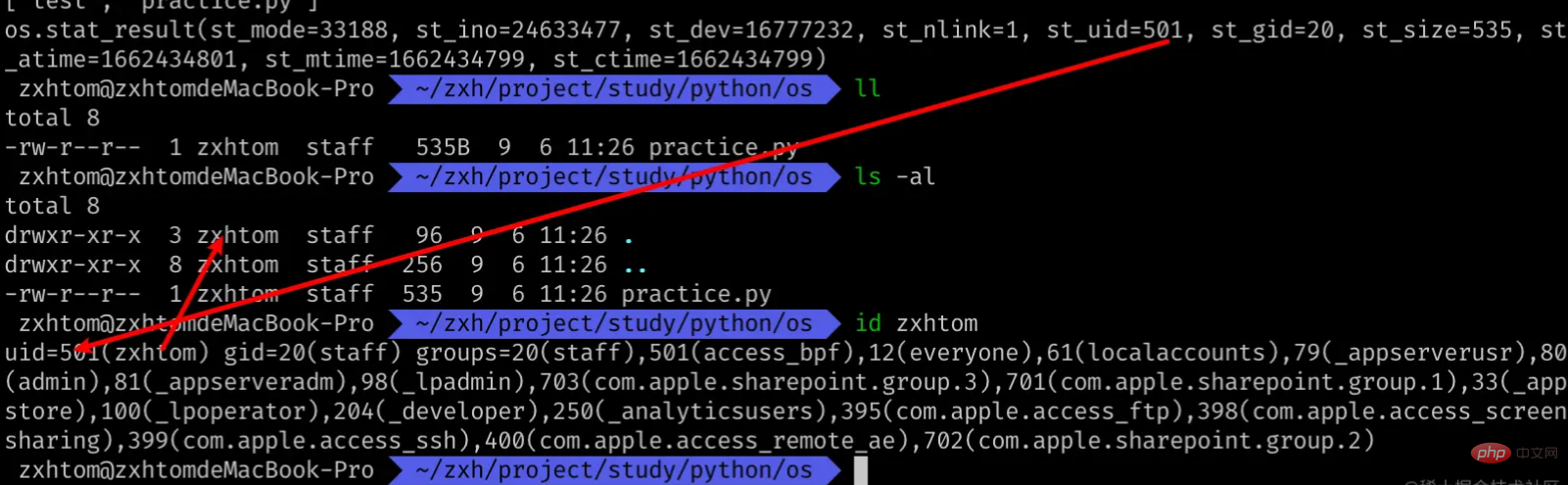
File Properties
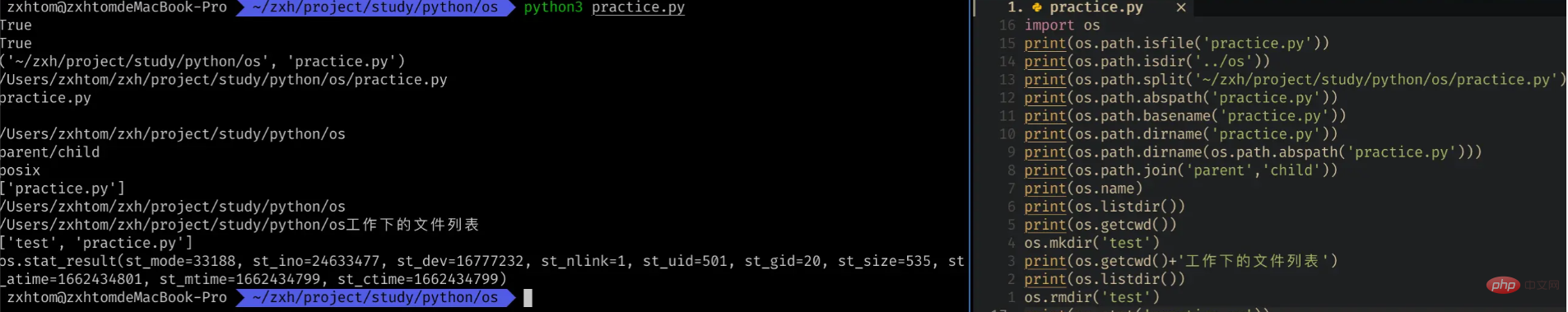
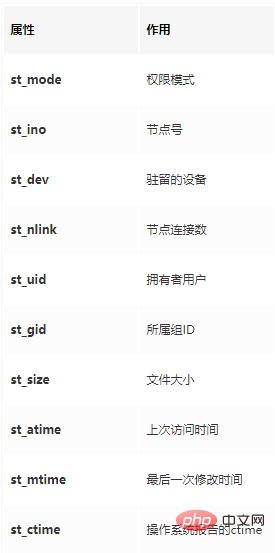
我们能够看到打印了很多属性。
修改权限杀死进程
os.chmod(file) os.get_terminal_size() os.kill(10884,signal.SIGKILL)
打通shell
作为一个shell爱好者,我还是很喜欢使用shell 来实现的,尤其是在做系统初始化的时候这个时候没有python ,而shell 是linux 系统自带的,所以shell 脚本的时候还是很有必要的,我个人也是shell+python 相互辅佐的存在。我们知道shell 中直接 python xxx.py。 但是python 如何执行shell 呢?
import os name=os.system('ls -al')
上面我们提到获取平台信息 os.name ,我们可以根据这个命令来通过 os.system('cmd') 指定不同系统的cmd 命令。
【相关推荐:Python3视频教程 】
The above is the detailed content of How does Python's built-in module OS create a SHELL-side file processor?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.



