What does win7x86 mean?
The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, Dell G3 computer.
win7x86 means the 32-bit windows7 operating system.
Windows7 systems are divided into 32-bit and 64-bit systems, and X86 is another name for 32-bit systems.
X86 actually means 32bit, which is a 32-bit mirroring system. Then X64 means 64bit, which refers to a 64-bit operating system. We can open "Control Panel" - "System and Security" - "System" - "System Type" in order. On the page, we can see whether our computer is an X86 or X64 system.
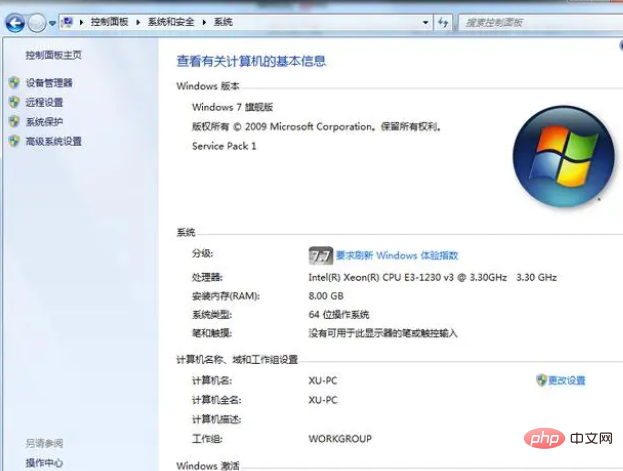

Computer digit description
The computer uses binary encoding to represent numbers, characters, instructions and other control information. When a computer is storing, transmitting or operating, a set of binary codes as a unit is called a word, and the number of binary bits in a word is called the word length.
The word length is one of the main technical indicators of the CPU. It refers to the number of binary digits that the CPU can process in parallel at one time. The word length is always an integer multiple of 8. Usually the word length of the PC is 32 bits, 64 Bit.
32-bit and 64-bit represent the maximum number of bits that the CPU can process at one time. The CPU of a 32-bit computer can process up to 32 bits of data at a time, which is 4 bytes of data, while a 64-bit CPU can process 64 bits of data at a time, which is 8 bytes of data.
Comparison of 64-bit and 32-bit
The change from 32-bit to 64-bit architecture is a fundamental change, because most operating systems must be completely modified, to gain the advantages of the new architecture. Other software must also be ported to take advantage of the new capabilities; older software is typically supported through hardware compatibility mode (new processors support older 32-bit versions of the instruction set) or software emulation. Or implement a 32-bit processor core directly in a 64-bit processor (like Intel's Itanium processor, which contains an x86 processor core to execute 32-bit x86 applications). Operating systems that support 64-bit architecture generally support both 32-bit and 64-bit applications.
The obvious exception is the AS/400, whose software executes on a virtual instruction set architecture called TIMI (Technology Independent Machine Interface), which converts low-level software into native machine code before execution. Low-level software must be completely rewritten to move the entire OS and all software to the new platform. For example, when IBM moved the older 32/48-bit "IMPI" instruction set to 64-bit PowerPC (IMPI is not at all like 32-bit PowerPC, so it's much better than moving from a 32-bit version of the instruction set to a 64-bit version of the same instruction set The scale is even larger).
The 64-bit architecture can undoubtedly be used in applications that need to process large amounts of data, such as digital video, scientific computing, and early large databases. There has been much debate over whether its 32-bit compatibility mode will be faster than equivalent 32-bit systems in other tasks. In x86-64 architecture (AMD64 and Intel 64), major 32-bit operating systems and applications can run smoothly on 64-bit hardware.
Sun's 64-bit Java virtual machine starts slower than 32-bit virtual machines because Sun still assumes that all 64-bit machines are servers and only implements "server" compilers for 64-bit platforms (C2). The "client" compiler (C1) produces slower code, but compiles faster. So although a Java program on a 64-bit JVM will perform better over a long period of time (typically long-running "server" applications), its startup time may be longer. For short-lived applications (such as the Java compiler javac), increasing the startup time can control the execution time and make the 64-bit JVM slower overall.
It should be noted that speed is not the only consideration when it comes to 32-bit and 64-bit processors. Applications such as multitasking, stress testing, and clustering (for HPC) may be better suited for 64-bit architecture to be deployed correctly. For the above reasons, 64-bit clusters have been widely deployed in large organizations such as IBM, Vodafone, HP, Microsoft.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What does win7x86 mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Can I install mysql on Windows 7
Apr 08, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
Can I install mysql on Windows 7
Apr 08, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
Yes, MySQL can be installed on Windows 7, and although Microsoft has stopped supporting Windows 7, MySQL is still compatible with it. However, the following points should be noted during the installation process: Download the MySQL installer for Windows. Select the appropriate version of MySQL (community or enterprise). Select the appropriate installation directory and character set during the installation process. Set the root user password and keep it properly. Connect to the database for testing. Note the compatibility and security issues on Windows 7, and it is recommended to upgrade to a supported operating system.
 How to speed up the loading speed of PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
How to speed up the loading speed of PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
Solving the problem of slow Photoshop startup requires a multi-pronged approach, including: upgrading hardware (memory, solid-state drive, CPU); uninstalling outdated or incompatible plug-ins; cleaning up system garbage and excessive background programs regularly; closing irrelevant programs with caution; avoiding opening a large number of files during startup.
 In front-end development, how to use CSS and JavaScript to achieve searchlight effects similar to Windows 10 settings interface?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
In front-end development, how to use CSS and JavaScript to achieve searchlight effects similar to Windows 10 settings interface?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement Windows-like in front-end development...
 How to pull the vertical reference line of PS
Apr 06, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to pull the vertical reference line of PS
Apr 06, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Pull vertical guides in Photoshop: Enable ruler view (View > ruler). Hover the mouse over the vertical edge of the ruler, and then the cursor becomes a vertical line with double arrows and hold and drag the mouse to pull out the reference line. Click Delete by dragging the guide, or hovering it into a cross.
 Solutions to the errors reported by MySQL on a specific system version
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:54 AM
Solutions to the errors reported by MySQL on a specific system version
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:54 AM
The solution to MySQL installation error is: 1. Carefully check the system environment to ensure that the MySQL dependency library requirements are met. Different operating systems and version requirements are different; 2. Carefully read the error message and take corresponding measures according to prompts (such as missing library files or insufficient permissions), such as installing dependencies or using sudo commands; 3. If necessary, try to install the source code and carefully check the compilation log, but this requires a certain amount of Linux knowledge and experience. The key to ultimately solving the problem is to carefully check the system environment and error information, and refer to the official documents.
 Unable to access mysql from terminal
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:57 PM
Unable to access mysql from terminal
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:57 PM
Unable to access MySQL from the terminal may be due to: MySQL service not running; connection command error; insufficient permissions; firewall blocks connection; MySQL configuration file error.
 How to solve mysql cannot connect to local host
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
How to solve mysql cannot connect to local host
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
The MySQL connection may be due to the following reasons: MySQL service is not started, the firewall intercepts the connection, the port number is incorrect, the user name or password is incorrect, the listening address in my.cnf is improperly configured, etc. The troubleshooting steps include: 1. Check whether the MySQL service is running; 2. Adjust the firewall settings to allow MySQL to listen to port 3306; 3. Confirm that the port number is consistent with the actual port number; 4. Check whether the user name and password are correct; 5. Make sure the bind-address settings in my.cnf are correct.
 MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The main reasons for MySQL installation failure are: 1. Permission issues, you need to run as an administrator or use the sudo command; 2. Dependencies are missing, and you need to install relevant development packages; 3. Port conflicts, you need to close the program that occupies port 3306 or modify the configuration file; 4. The installation package is corrupt, you need to download and verify the integrity; 5. The environment variable is incorrectly configured, and the environment variables must be correctly configured according to the operating system. Solve these problems and carefully check each step to successfully install MySQL.



