Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript
This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript
This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript

There are many articles about deep copying on the Internet, but the quality varies, many of them are not well thought out, and the writing methods are relatively crude and unsatisfactory. This article aims to complete a perfect deep copy. If you have any questions after reading it, please feel free to add and improve it.
To evaluate whether a deep copy is complete, please check whether the following questions have been implemented:
Can basic type databe copied?Keys and values are both basic types
Ordinary This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptectsCan they be copied?SymbolCan the key of an This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect be copied? CanDateandRegExpThis article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect types be copied? CanMapandSetThis article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect types be copied?FunctionCan the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect type be copied? (We generally don’t use deep copying for functions)Can the
prototypeof an This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect be copied?Non-enumerable propertiesCan it be copied?Circular referenceCan it be copied?
how? Is the deep copy you wrote perfect enough?
The final implementation of deep copy
The final code version is given directly here for the convenience of those who want to know quickly. Of course, if you want to understand step by step, you can continue to view the rest of the article:
function deepClone(target) {
const map = new WeakMap()
function isObject(target) {
return (typeof target === 'This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect' && target ) || typeof target === 'function'
}
function clone(data) {
if (!isObject(data)) {
return data
}
if ([Date, RegExp].includes(data.constructor)) {
return new data.constructor(data)
}
if (typeof data === 'function') {
return new Function('return ' + data.toString())()
}
const exist = map.get(data)
if (exist) {
return exist
}
if (data instanceof Map) {
const result = new Map()
map.set(data, result)
data.forEach((val, key) => {
if (isObject(val)) {
result.set(key, clone(val))
} else {
result.set(key, val)
}
})
return result
}
if (data instanceof Set) {
const result = new Set()
map.set(data, result)
data.forEach(val => {
if (isObject(val)) {
result.add(clone(val))
} else {
result.add(val)
}
})
return result
}
const keys = Reflect.ownKeys(data)
const allDesc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(data)
const result = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(data), allDesc)
map.set(data, result)
keys.forEach(key => {
const val = data[key]
if (isObject(val)) {
result[key] = clone(val)
} else {
result[key] = val
}
})
return result
}
return clone(target)
}1. The copy principle of JavaScript data types
First look at the JS data type diagram ( Except Object, all others are basic types): 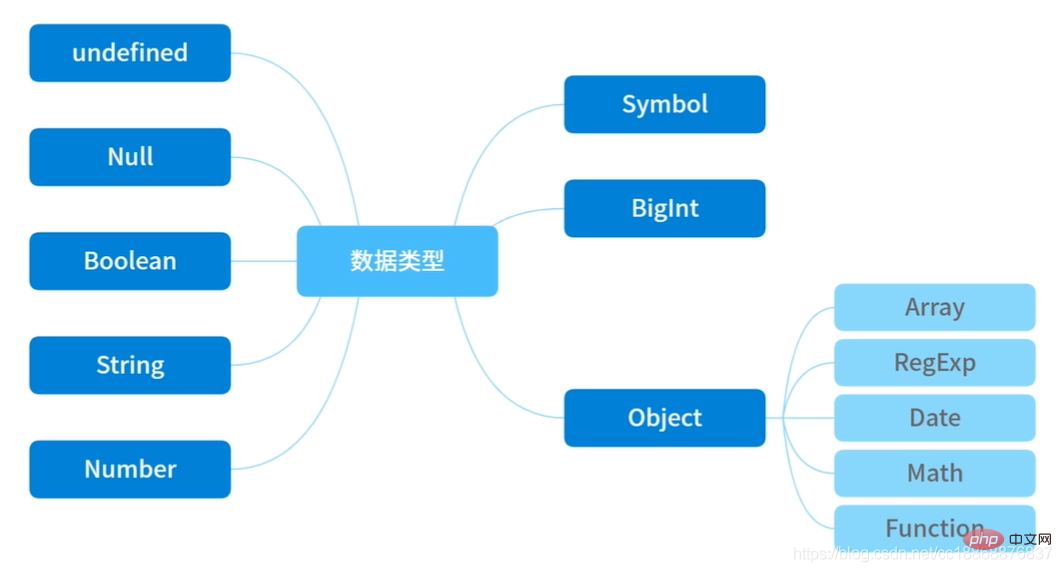
In JavaScript, the copying of basic type values is to directly copy a new and identical data. The two data are mutually exclusive. Independent and not affecting each other. The copying of reference type values (Object type) is to pass the reference of the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect (that is, the memory address where the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect is located, that is, the pointer to the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect), which is equivalent to multiple variables pointing to the same This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect. Then as long as one of the variables has a reference to the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect When modified, the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptects pointed to by other variables will also be modified (because they point to the same This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect). As shown below: 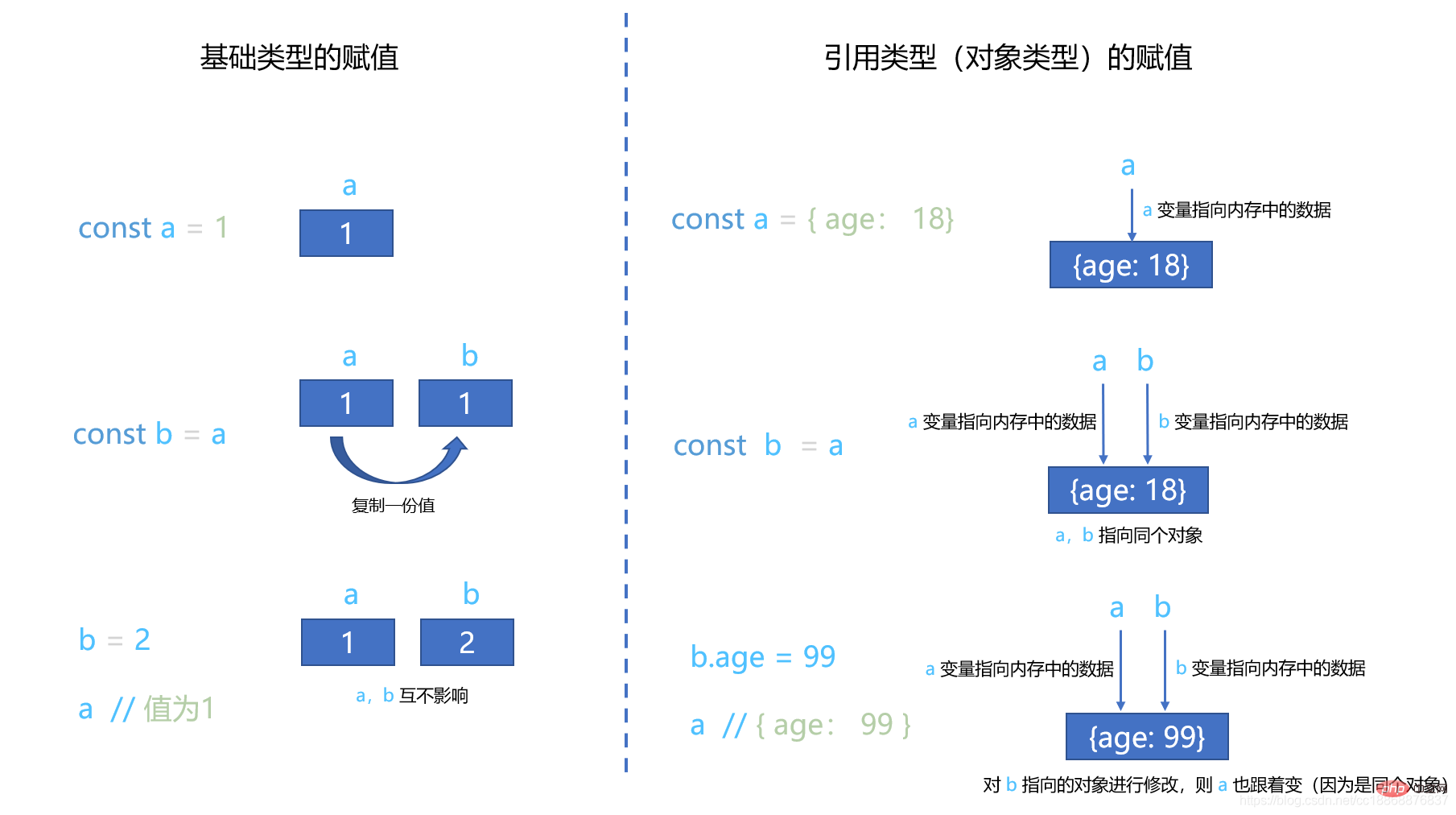
2. Dark and shallow copy
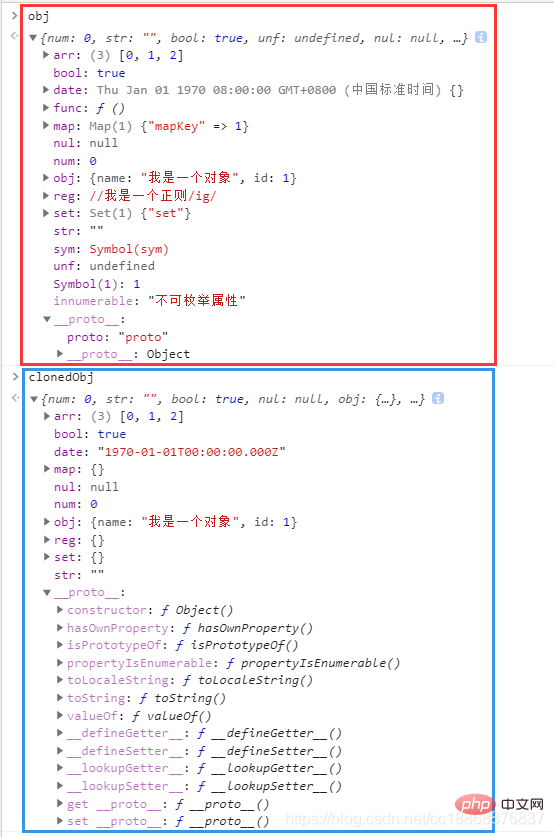
Deep and shallow copy mainly targets the Object type, and the value of the basic type itself is copied exactly the same One copy, no distinction between dark and light copies. Here we first give the copy This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect for testing. You can use this This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect to test whether the deep copy function you wrote is perfect:
// 测试的This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript对象
const This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript = {
// =========== 1.基础数据类型 ===========
num: 0, // number
str: '', // string
bool: true, // boolean
unf: undefined, // undefined
nul: null, // null
sym: Symbol('sym'), // symbol
bign: BigInt(1n), // bigint
// =========== 2.Object类型 ===========
// 普通对象
This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript: {
name: '我是一个对象',
id: 1
},
// 数组
arr: [0, 1, 2],
// 函数
func: function () {
console.log('我是一个函数')
},
// 日期
date: new Date(0),
// 正则
reg: new RegExp('/我是一个正则/ig'),
// Map
map: new Map().set('mapKey', 1),
// Set
set: new Set().add('set'),
// =========== 3.其他 ===========
[Symbol('1')]: 1 // Symbol作为key
};
// 4.添加不可枚举属性
Object.defineProperty(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript, 'innumerable', {
enumerable: false,
value: '不可枚举属性'
});
// 5.设置原型对象
Object.setPrototypeOf(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript, {
proto: 'proto'
})
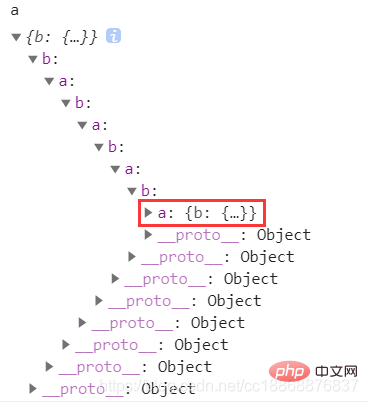
// 6.设置loop成循环引用的属性
This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript.loop = This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptThis article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript The This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect is in Result in Chrome:

##2.1 Shallow copy
Shallow copy: Create a new Object to accept the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect value that you want to re-copy or reference. If the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect attribute is a basic data type, the value of the basic type is copied to the new This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect; but if the attribute is a reference data type, the address in the memory is copied. If one of the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptects changes the address pointed to by the memory, Object will definitely affect another This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect.
First let’s take a look at some shallow copy methods (for details, click on the hyperlinks to the corresponding methods):| Use Method | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| Object.assign(target, ... sources) | Description: Used to assign the values of all enumerable properties from one or more source This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptects to the target This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect. It will return the target This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect. 1. The inherited properties of the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect will not be copied; | 2. The non-enumerable properties of the This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect will not be copied; 3. Symbol type properties can be copied. |
| let This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptClone = { ...This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript }; |
| Object.assign () Almost the same, but if the attributes are all basic type values, it will be more convenient to use the spread operator to perform shallow copy. |
| const new_array = old_array.concat(value1[, value2[, ...[, valueN] ]]) |
|
|
| arr.slice([begin[, end]]) |
|
| 存在的问题 | 改进方案 |
|---|---|
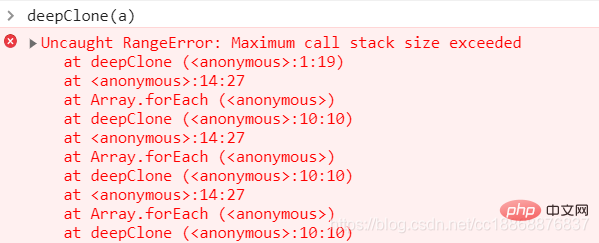
| 1. 不能处理循环引用 | 使用 WeakMap 作为一个Hash表来进行查询 |
2. 只考虑了Object对象 | 当参数为 Date、RegExp 、Function、Map、Set,则直接生成一个新的实例返回 |
3. 属性名为Symbol的属性4. 丢失了不可枚举的属性 | 针对能够遍历对象的不可枚举属性以及 Symbol 类型,我们可以使用 Reflect.ownKeys()注: Reflect.ownKeys(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript)相当于[...Object.getOwnPropertyNames(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript), ...Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript)] |
| 4. 原型上的属性 | Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()设置属性描述对象,以及Object.create()方式继承原型链 |
代码实现:
function deepClone(target) {
// WeakMap作为记录对象Hash表(用于防止循环引用)
const map = new WeakMap()
// 判断是否为This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect类型的辅助函数,减少重复代码
function isObject(target) {
return (typeof target === 'This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect' && target ) || typeof target === 'function'
}
function clone(data) {
// 基础类型直接返回值
if (!isObject(data)) {
return data
}
// 日期或者正则对象则直接构造一个新的对象返回
if ([Date, RegExp].includes(data.constructor)) {
return new data.constructor(data)
}
// 处理函数对象
if (typeof data === 'function') {
return new Function('return ' + data.toString())()
}
// 如果该对象已存在,则直接返回该对象
const exist = map.get(data)
if (exist) {
return exist
}
// 处理Map对象
if (data instanceof Map) {
const result = new Map()
map.set(data, result)
data.forEach((val, key) => {
// 注意:map中的值为This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect的话也得深拷贝
if (isObject(val)) {
result.set(key, clone(val))
} else {
result.set(key, val)
}
})
return result
}
// 处理Set对象
if (data instanceof Set) {
const result = new Set()
map.set(data, result)
data.forEach(val => {
// 注意:set中的值为This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScriptect的话也得深拷贝
if (isObject(val)) {
result.add(clone(val))
} else {
result.add(val)
}
})
return result
}
// 收集键名(考虑了以Symbol作为key以及不可枚举的属性)
const keys = Reflect.ownKeys(data)
// 利用 Object 的 getOwnPropertyDescriptors 方法可以获得对象的所有属性以及对应的属性描述
const allDesc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(data)
// 结合 Object 的 create 方法创建一个新对象,并继承传入原对象的原型链, 这里得到的result是对data的浅拷贝
const result = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(data), allDesc)
// 新对象加入到map中,进行记录
map.set(data, result)
// Object.create()是浅拷贝,所以要判断并递归执行深拷贝
keys.forEach(key => {
const val = data[key]
if (isObject(val)) {
// 属性值为 对象类型 或 函数对象 的话也需要进行深拷贝
result[key] = clone(val)
} else {
result[key] = val
}
})
return result
}
return clone(target)
}
// 测试
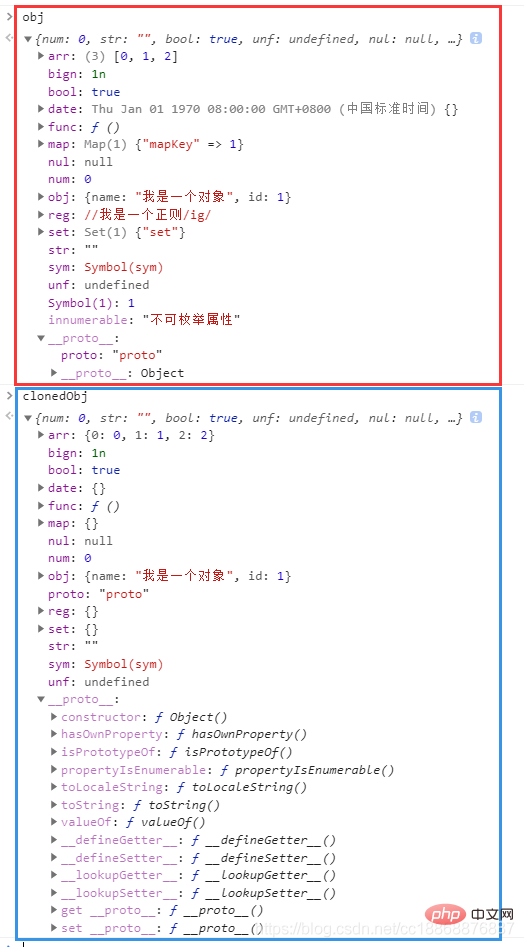
const clonedObj = deepClone(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript)
clonedObj === This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript // false,返回的是一个新对象
clonedObj.arr === This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript.arr // false,说明拷贝的不是引用
clonedObj.func === This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript.func // false,说明function也复制了一份
clonedObj.proto // proto,可以取到原型的属性详细的说明见代码中的注释,更多测试希望大家自己动手尝试验证一下以加深印象。
在遍历 Object 类型数据时,我们需要把 Symbol 类型的键名也考虑进来,所以不能通过 Object.keys 获取键名或 for...in 方式遍历,而是通过Reflect.ownKeys()获取所有自身的键名(getOwnPropertyNames 和 getOwnPropertySymbols 函数将键名组合成数组也行:[...Object.getOwnPropertyNames(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript), ...Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript)]),然后再遍历递归,最终实现拷贝。
浏览器执行结果:
可以发现我们的cloneObj对象和原来的This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript对象一模一样,并且修改cloneObj对象的各个属性都不会对This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript对象造成影响。其他的大家再多尝试体会哦!
【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、编程视频】
The above is the detailed content of This article will give you a detailed understanding of deep copying in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data