This article will help you understand Vuex thoroughly

1. What is Vuex? Why use it?
vuex official explanation
Vuex is a state management mode library developed specifically for Vue.js applications. It uses centralized storage to manage the state of all components of the application, and uses corresponding rules to ensure that the state changes in a predictable way. (Learning video sharing: vue video tutorial)
You can think about it, what are the values transmitted between components? There is communication between father and son, communication between sibling components...but parameter passing is very cumbersome for multi-layer nesting, and code maintenance will also be very troublesome. Therefore, vuex extracts the shared state of components and manages them in a global singleton mode, and puts the shared data functions into vuex so that any component can use them.
2. When should we use it?
Vuex can help us manage shared state and comes with more concepts and frameworks. This requires weighing short- and long-term benefits.
If you don't plan to develop a large single-page application, using Vuex may be cumbersome and redundant. It's true - if your app is simple enough, you're probably better off not using Vuex. A simple store mode is enough for what you need. However, if you need to build a medium to large single page application, you will most likely be thinking about how to better manage state outside the components, and Vuex will be a natural choice.
3. Installation
Method 1:
Check the option system of vuex when creating the project on the scaffolding It will be created automatically
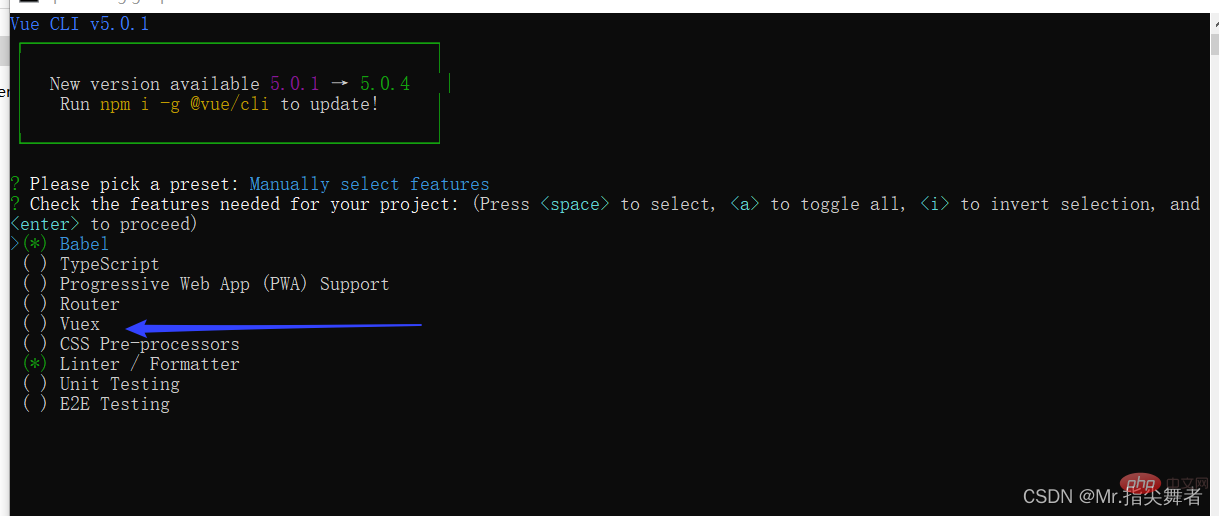
Method 2: npm or Yarn installation
npm install vuex@next --save
Four. Configuration
If you use scaffolding to create it, no operation is required and you can ignore this step.
Create a new store file ->index.js, perform the following configuration, in main. Import into js
yarn add vuex@next --save
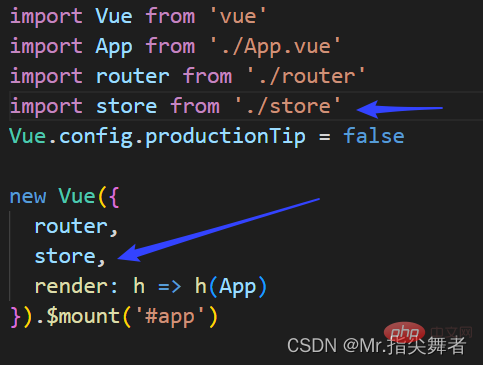
In main.js
5. Core concepts
There are five states in vuex State Getter Mutation Action Module The following will be explained in detail
5.1 State
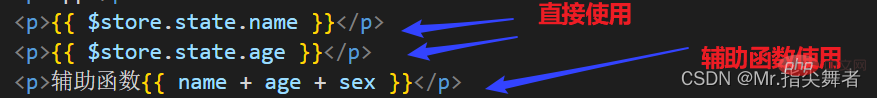
Provides the only public data source. All shared data is stored in the state of the store. It is similar to data
. Data is defined in the state in vuex and can be used in any component. Call
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
},
getters: {
},
//里面定义方法,操作state方发
mutations: {
},
// 操作异步操作mutation
actions: {
},
modules: {
},
})Call:
Method 1:
Use
directly in the tag 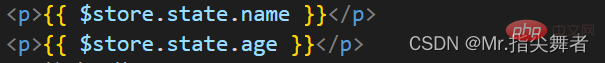
Method 2:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
name:"张三",
age:12,
count:0
},
})Method 3:
Import mapstate on demand from vuex Function
this.$store.state.全局数据名称
Note: Global data required by the current component is mapped to the current componentcomputedProperties
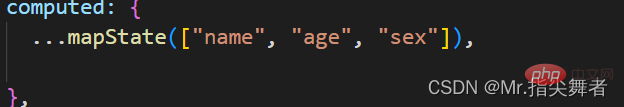
##5.2 Mutation
The only way to change the state in the Vuex store is to submit a mutation. Mutation in Vuex is very similar to events: each mutation has a stringevent type (type) and a callback function (handler). This callback function is where we actually make the state changes, and it accepts state as the first parameter:
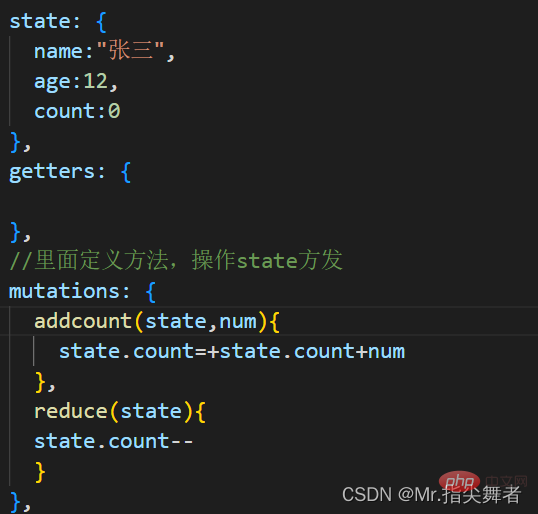
在vuex中定义:
其中参数state参数是必须的,也可以自己传递一个参数,如下代码,进行计数器的加减操作,加法操作时可以根据所传递参数大小进行相加,减法操作没有传参每次减一
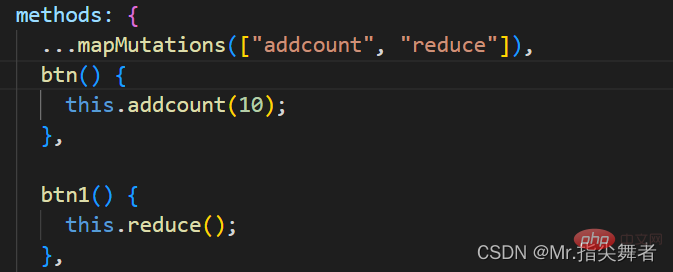
在组件中使用:
定义两个按钮进行加减操作

方法一:
注意:使用commit触发Mutation操作
methods:{
//加法
btn(){
this.$store.commit("addcount",10) //每次加十
}
//减法
btn1(){
this.$store.commit("reduce")
}
}方法二:
使用辅助函数进行操作,具体方法同上
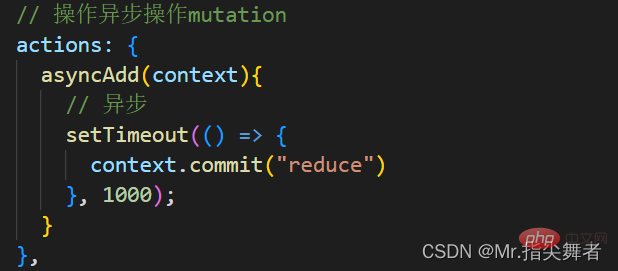
5.3 Action ——进行异步操作
Action和Mutation相似,Mutation 不能进行异步操作,若要进行异步操作,就得使用Action
在vuex中定义:
将上面的减法操作改为异步操作
在组件中使用:
方法一:
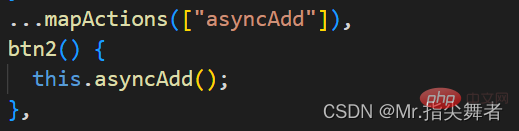
直接使用 dispatch触发Action函数
this.$store.dispatch("reduce")方法二:
使用辅助函数
5.4 Getter
类似于vue中的computed,进行缓存,对于Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据
具体操作类似于前几种,这里不做具体说明
5.5 Modules
当遇见大型项目时,数据量大,store就会显得很臃肿
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
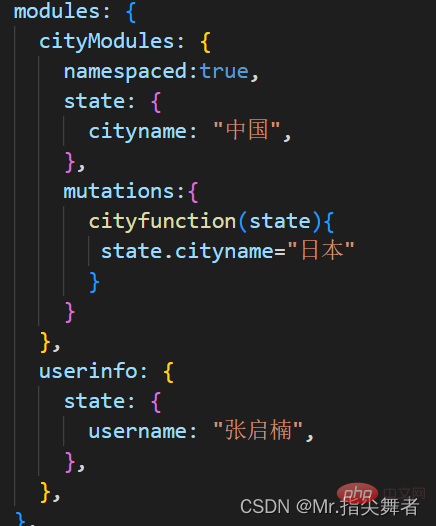
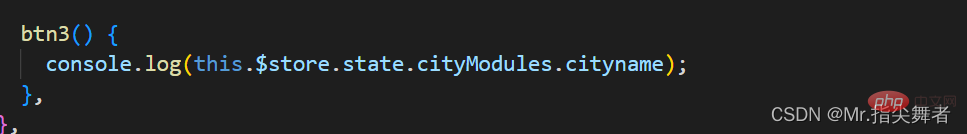
默认情况下,模块内部的 action 和 mutation 仍然是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一个 action 或 mutation 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
The above is the detailed content of This article will help you understand Vuex thoroughly. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Implement marquee/text scrolling effects in Vue, using CSS animations or third-party libraries. This article introduces how to use CSS animation: create scroll text and wrap text with <div>. Define CSS animations and set overflow: hidden, width, and animation. Define keyframes, set transform: translateX() at the beginning and end of the animation. Adjust animation properties such as duration, scroll speed, and direction.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.