How to implement the Repository design pattern in Laravel

In this article, I will show you how to implement the repository design pattern from scratch in Laravel. I will be using Laravel version 5.8.3, but Laravel version is not the most important. Before you start writing code, you need to know some information about repository design patterns.
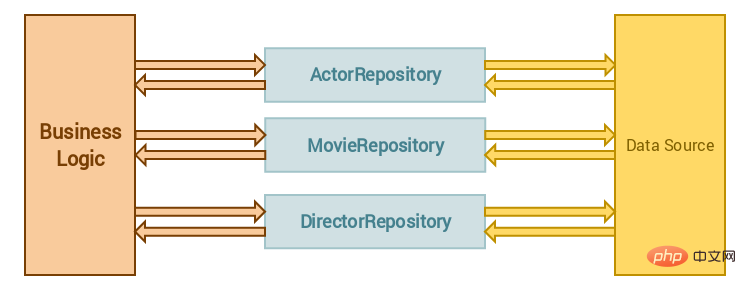
repository Design patterns allow you to work with objects without knowing how those objects are persisted. Essentially, it is an abstraction of the data layer.
This means that your business logic does not need to know how to retrieve the data or what the data source is, the business logic relies on the repository to retrieve the correct data.
Regarding this pattern, I have seen some misunderstanding it as repository being used to create or update data. This is not what repository is supposed to do, repository is not supposed to create or update data, only to retrieve it.
Do you understand? Let’s write the code together
Since we are starting from scratch, let’s create a new Laravel project:
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel repository
For this tutorial, we will build a small blogging application. Now that we have created a new Laravel project, we should create a controller and model for it.
php artisan make:controller BlogController
This will create the BlogController in the app/Http/Controllers directory.
php artisan make:model Models/Blog -m
Tip: The -m option will create a corresponding database migration. You can find the generated migration in the *database/migrations directory. *
Now you should be able to find the newly generated model Blog in the app/Models directory. This is just a way I like to store my models.
Now that we have our controller and model, it’s time to look at the migration file we created. In addition to the default Laravel timestamp fields, our blog only requires the Title, Content, and UserID fields.
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateBlogsTable extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('blogs', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->string('title');
$table->text('content');
$table->integer('user_id');
$table->timestamps();
$table->foreign('user_id')
->references('id')
->on('users');
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('blogs');
}
} Tips:
If you are using an old version below Laravel 5.8, please replace
$table->bigIncrements('id');
with:
$table->increments('id');
Setting up the database
I will use the MySQL database as an example, the first step is to create a new database.
mysql -u root -p create database laravel_repository;
The above command will create a new database called laravel_repository. Next we need to add database information to the .env file in the Laravel root directory.
DB_DATABASE=laravel_repositoryDB_USERNAME=rootDB_PASSWORD=secret
We need to clear the cache after you update the .env file:
php artisan config:clear
Run migration
Now that we have the database set up, we can start running the migration:
php artisan migrate
This will create the blogs table, containing the title# we declared in the migration ## , content and user_id fields.
##Implementationrepository Design patternEverything is ready, we can now start to implement the
repositorydesign Styled. We will create the Repositories directory inside the app directory. The second directory we will create is the Interfaces directory, which is located within the Repositories directory. In the
Interfacesfile we will create a BlogRepositoryInterface interface that contains two methods.
- Returns the
- all
method of all blog posts
Returns the - getByUser## of all the blog posts of a specific user # Method The last class we need to create is
<?php namespace App\Repositories\Interfaces; use App\User; interface BlogRepositoryInterface { public function all(); public function getByUser(User $user); }Copy after loginBlogRepository
BlogRepositoryInterface, we will write the simplest implementation .
<?php
namespace App\Repositories;
use App\Models\Blog;
use App\User;
use App\Repositories\Interfaces\BlogRepositoryInterface;
class BlogRepository implements BlogRepositoryInterface
{
public function all()
{
return Blog::all();
}
public function getByUser(User $user)
{
return Blog::where('user_id',$user->id)->get();
}
}app/└── Repositories/
├── BlogRepository.php
└── Interfaces/
└── BlogRepositoryInterface.phprepository.
##UsingRepository in a ControllerTo start using BlogRepository, we first need to Inject it into
BlogController. Thanks to Laravel's dependency injection, we can easily replace it with another one. This is what our controller looks like: <?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Repositories\Interfaces\BlogRepositoryInterface;
use App\User;
class BlogController extends Controller
{
private $blogRepository;
public function __construct(BlogRepositoryInterface $blogRepository)
{
$this->blogRepository = $blogRepository;
}
public function index()
{
$blogs = $this->blogRepository->all();
return view('blog')->withBlogs($blogs);
}
public function detail($id)
{
$user = User::find($id);
$blogs = $this->blogRepository->getByUser($user);
return view('blog')->withBlogs($blogs);
}
}
methods are easily reusable. repository 设计模式也使更改数据源变得更加容易。在这个例子中,我们使用 MySQL 数据库来检索我们的博客内容。我们使用 Eloquent 来完成查询数据库操作。但是假设我们在某个网站上看到了一个很棒的博客 API,我们想使用这个 API 作为数据源,我们所要做的就是重写 BlogRepository 来调用这个 API 替换 Eloquent 。 我们将注入 BlogController 中的 BlogRepository ,而不是注入 BlogController 中的 BlogRepositoryInterface ,然后让服务容器决定将使用哪个存储库。这将在 AppServiceProvider 的 boot 方法中实现,但我更喜欢为此创建一个新的 provider 来保持整洁。 我们为此创建一个新的 provider 的原因是,当您的项目开始发展为大型项目时,结构会变得非常凌乱。设想一下,一个拥有 10 个以上模型的项目,每个模型都有自己的 repository ,你的 AppServiceProvider 可读性将会大大降低。 我们的 RepositoryServiceProvider 会像下面这样: 留意用另一个 repository 替代 BlogRepository 是多么容易! 不要忘记添加 RepositoryServiceProvider 到 config/app.php 文件的 providers 列表中。完成了这些后我们需要清空缓存: 现在你已经成功实现了 repository 设计模式,不是很难吧? 你可以选择增加一些路由和视图来拓展代码,但本文将在这里结束,因为本文主要是介绍 repository 设计模式的。 如果你喜欢这篇文章,或者它帮助你实现了 repository 设计模式,请确保你也查看了我的其他文章。如果你有任何反馈、疑问,或希望我撰写另一个有关 Laravel 的主题,请随时发表评论。 原文地址:https://itnext.io/repository-design-pattern-done-right-in-laravel-d177b5fa75d4 译文地址:https://learnku.com/laravel/t/31798 【相关推荐:laravel视频教程】 The above is the detailed content of How to implement the Repository design pattern in Laravel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!RepositoryServiceProvider
php artisan make:provider RepositoryServiceProvider
<?php
namespace App\Providers;
use App\Repositories\BlogRepository;
use App\Repositories\Interfaces\BlogRepositoryInterface;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class RepositoryServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register()
{
$this->app->bind(
BlogRepositoryInterface::class,
BlogRepository::class
);
}
}'providers' => [
\App\Providers\RepositoryServiceProvider::class
],
php artisan config:clear
就是这样

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
LaravelEloquent Model Retrieval: Easily obtaining database data EloquentORM provides a concise and easy-to-understand way to operate the database. This article will introduce various Eloquent model search techniques in detail to help you obtain data from the database efficiently. 1. Get all records. Use the all() method to get all records in the database table: useApp\Models\Post;$posts=Post::all(); This will return a collection. You can access data using foreach loop or other collection methods: foreach($postsas$post){echo$post->
 The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, containerization and microservice architectures, supporting Docker and Kubernetes; 2) introducing JIT compilers and enumeration types to improve performance and data processing efficiency; 3) Continuously optimize performance and promote best practices.
 Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Efficiently process 7 million records and create interactive maps with geospatial technology. This article explores how to efficiently process over 7 million records using Laravel and MySQL and convert them into interactive map visualizations. Initial challenge project requirements: Extract valuable insights using 7 million records in MySQL database. Many people first consider programming languages, but ignore the database itself: Can it meet the needs? Is data migration or structural adjustment required? Can MySQL withstand such a large data load? Preliminary analysis: Key filters and properties need to be identified. After analysis, it was found that only a few attributes were related to the solution. We verified the feasibility of the filter and set some restrictions to optimize the search. Map search based on city
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
How does Laravel play a role in backend logic? It simplifies and enhances backend development through routing systems, EloquentORM, authentication and authorization, event and listeners, and performance optimization. 1. The routing system allows the definition of URL structure and request processing logic. 2.EloquentORM simplifies database interaction. 3. The authentication and authorization system is convenient for user management. 4. The event and listener implement loosely coupled code structure. 5. Performance optimization improves application efficiency through caching and queueing.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




