Organize and summarize basic SQL statements based on examples
This article brings you relevant knowledge about SQL, which mainly introduces the organization of basic SQL statements, including DDL, DML, DQL, etc. Let’s take a look at it together ,I hope everyone has to help.

Recommended study: "SQL Tutorial"
1. DDL (Data Definition Language)
Data definition language, used to define database objects (databases, tables, fields)
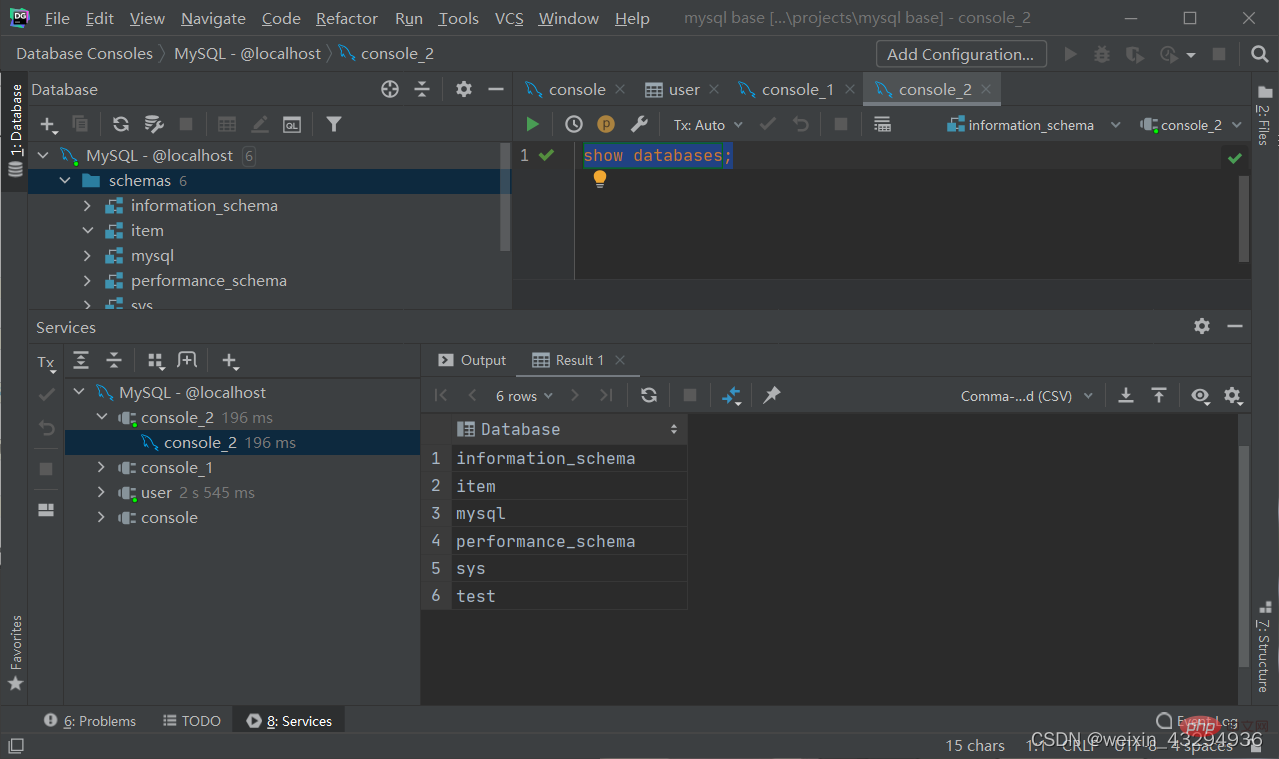
Query
Query all databases
show databases;
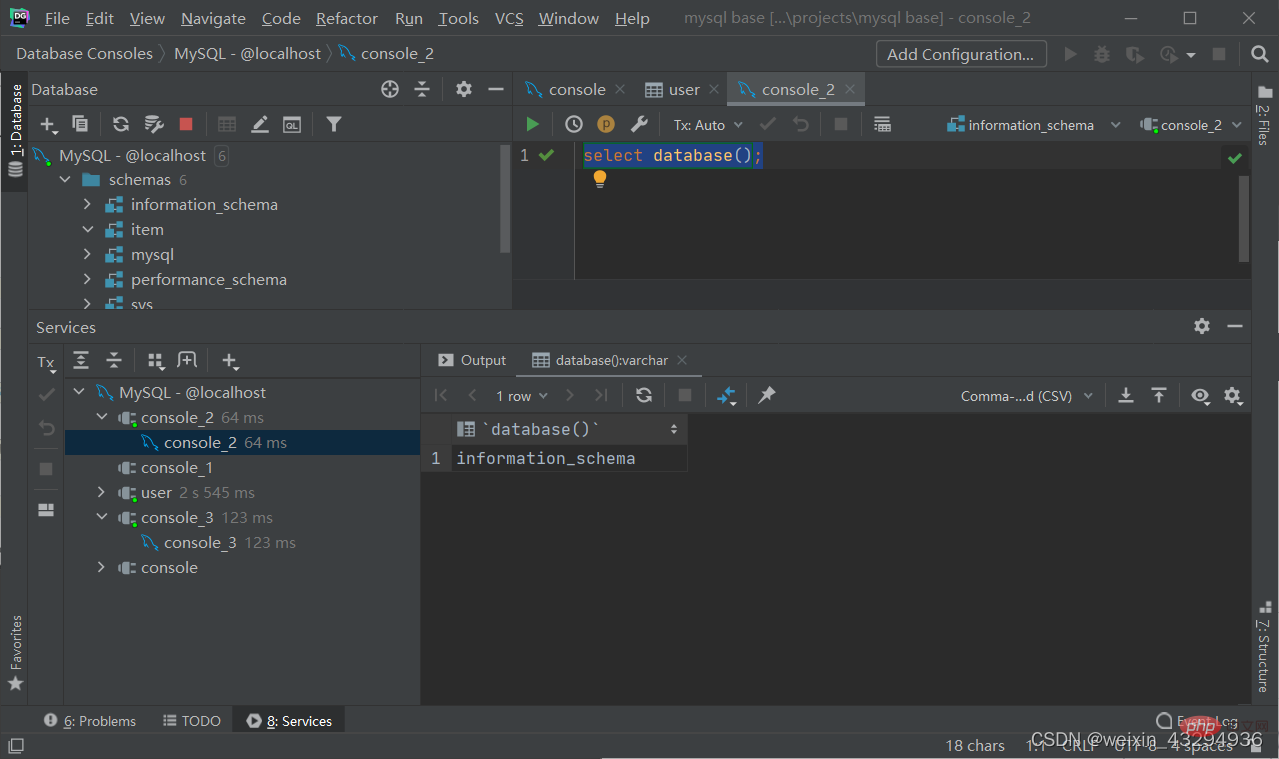
Query the current database
select database();
Create
create database [if not exists] 数据库名 [default charset 字符集][collate 排序规则]; #中括号里的可加可不加,具体情况而定 #第一个是如果不存在相同名称的数据库则创建 #第二个是设置字符的字符集和排序规则
Delete
drop database [if exists] 数据库名; #中括号是如果存在相同名称的数据库就删除
Using
use 数据库名;
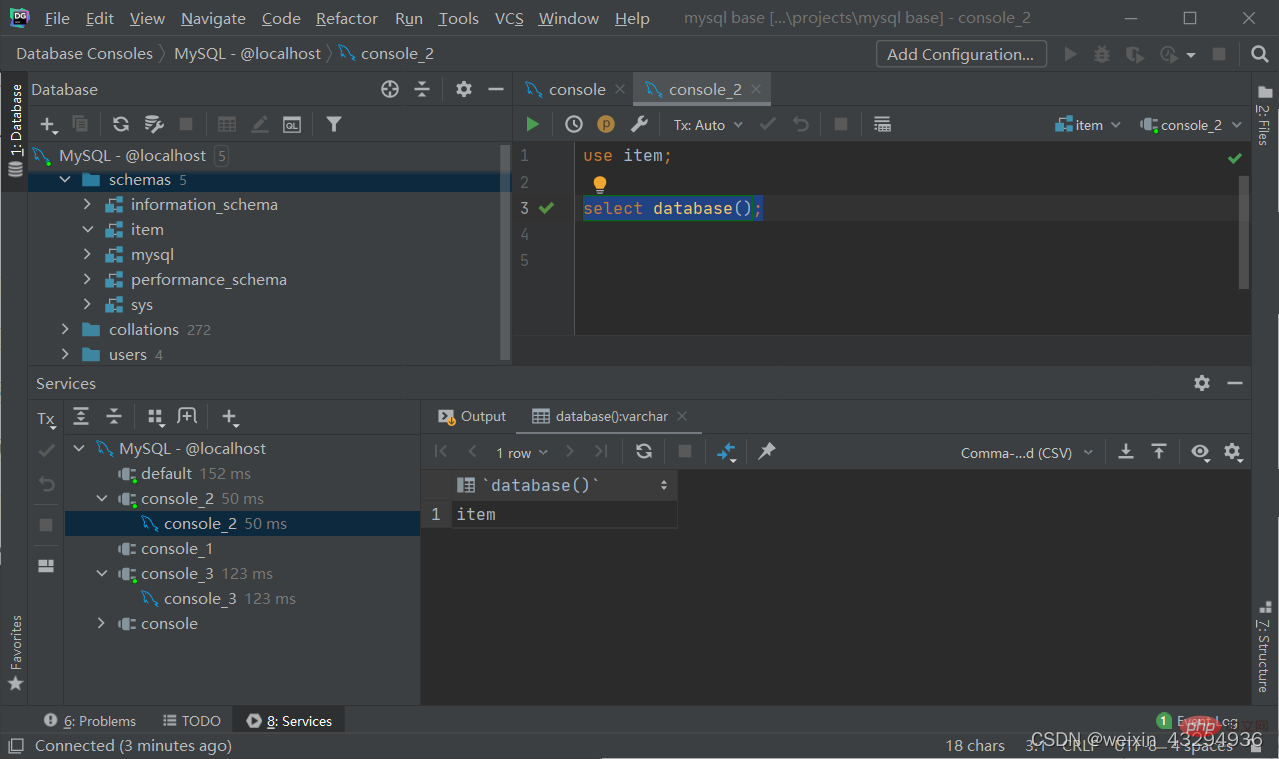
Table Operation-Create
create table 表名 ( 字段1 字段1类型[comment 字段1注释], 字段2 字段2类型[comment 字段2注释], 字段3 字段3类型[comment 字段3注释], ...... 字段n 字段n类型[comment 字段n注释] )[comment 表注释];
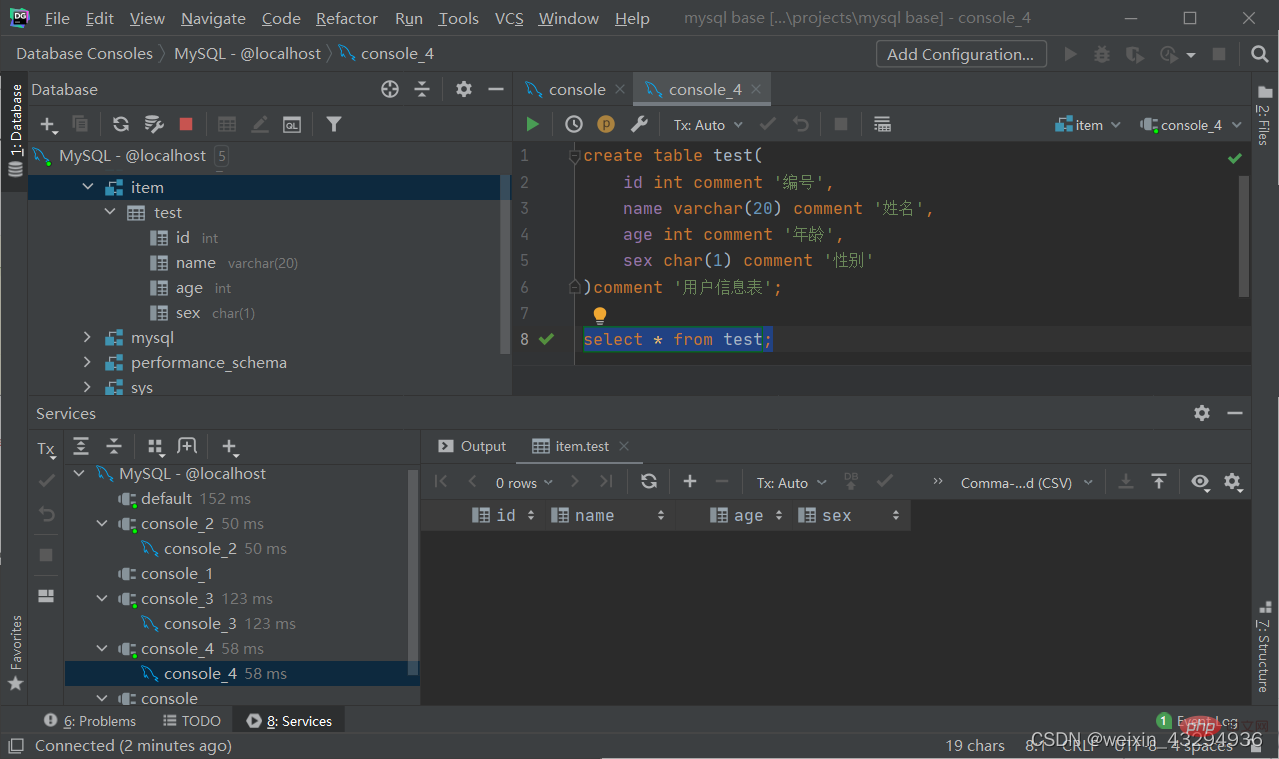
Note: [....] is an optional parameter, there is no comma after the last field
Table operation - modification
Add field
alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型(长度) [comment 注释][约束];
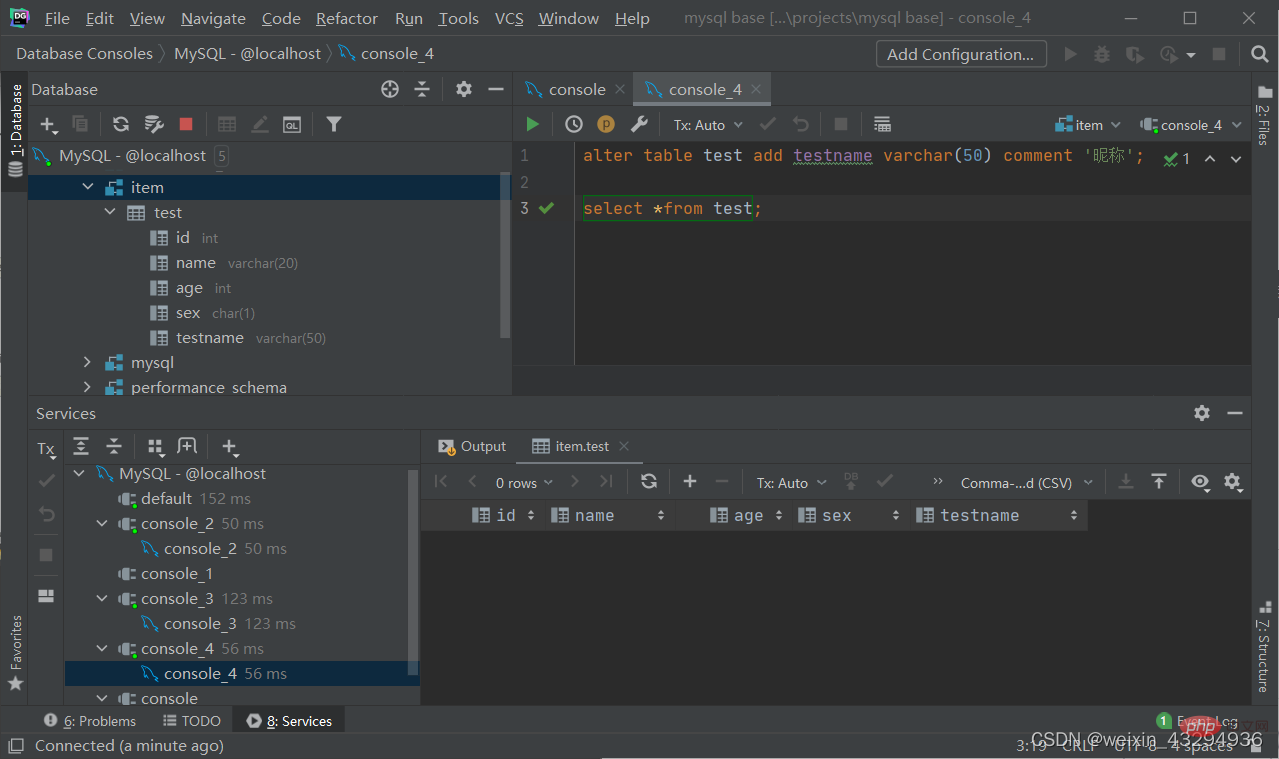
Modify data type
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 新数据类型(长度);
Modify field name and field type
alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 类型(长度)[comment 注释][约束];
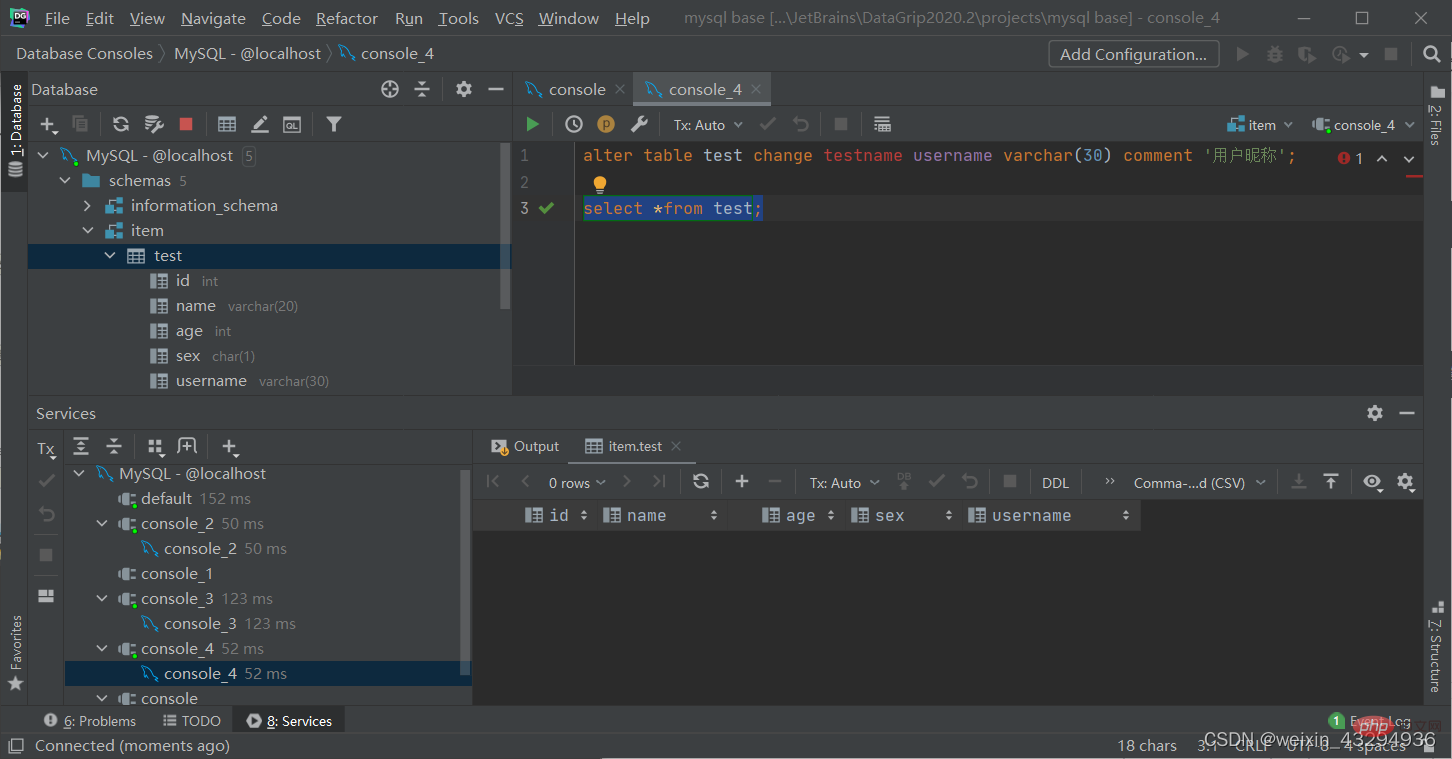
Delete field
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
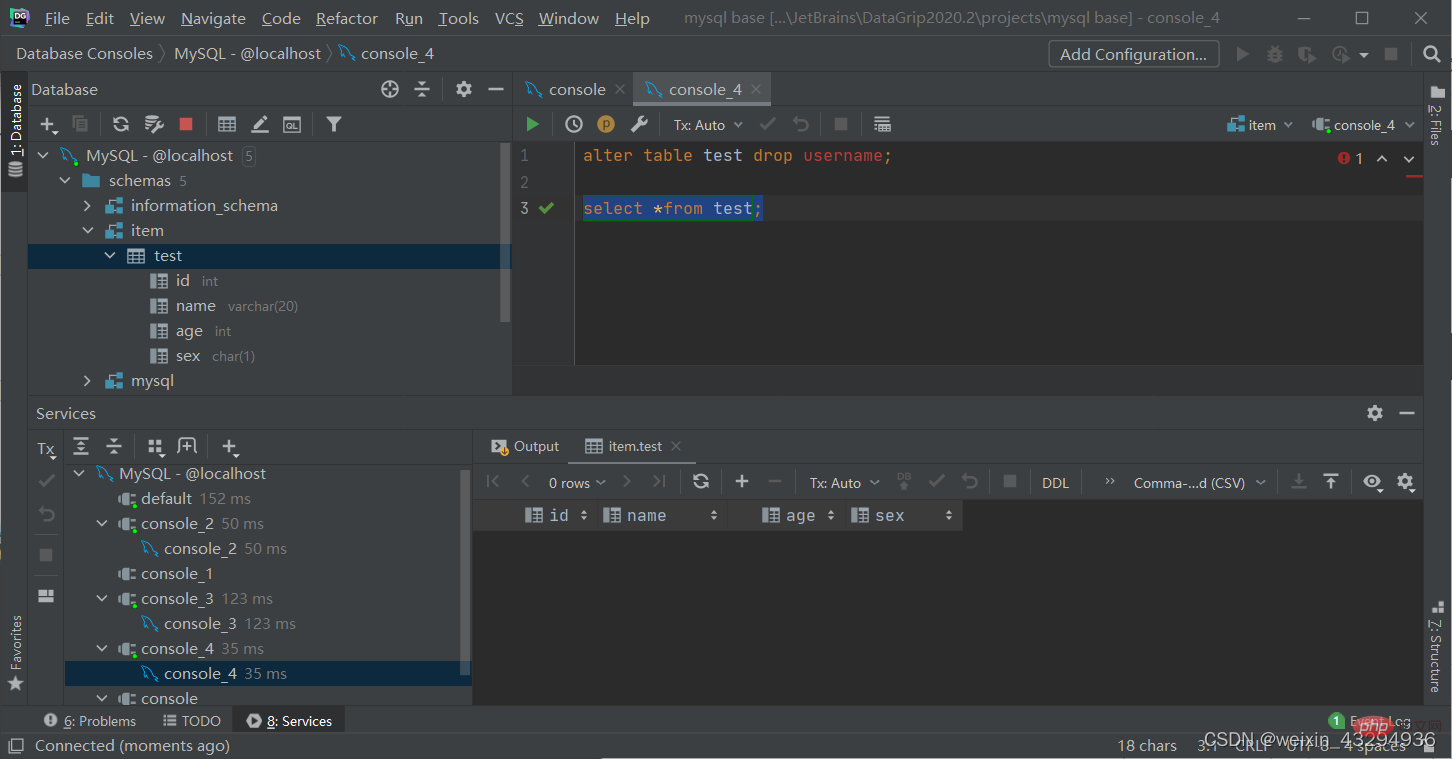
Modify table name
alter table 表名 rename to 新表名;
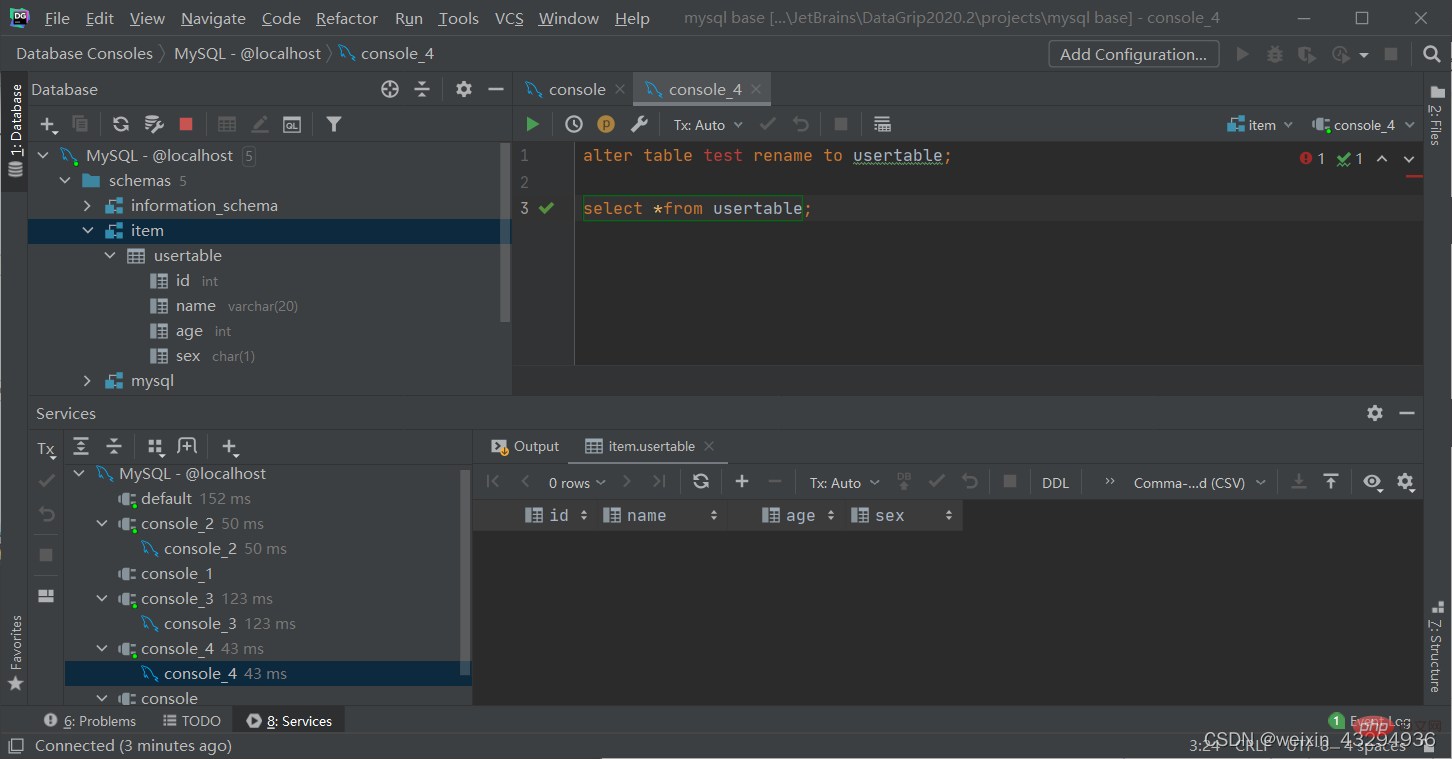
Table operation - delete
Delete table (make the specified table disappear from the database)
drop table [if exists] 表名;
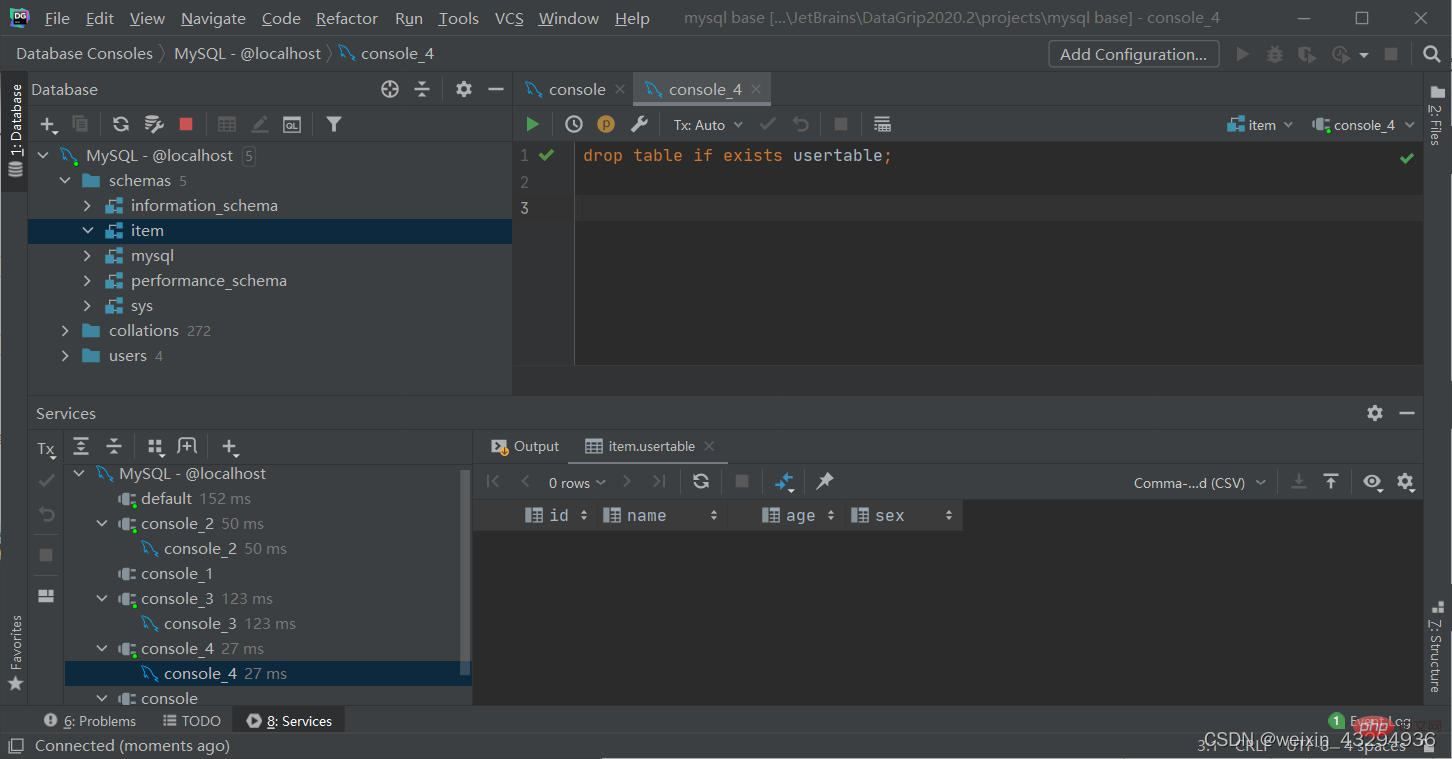
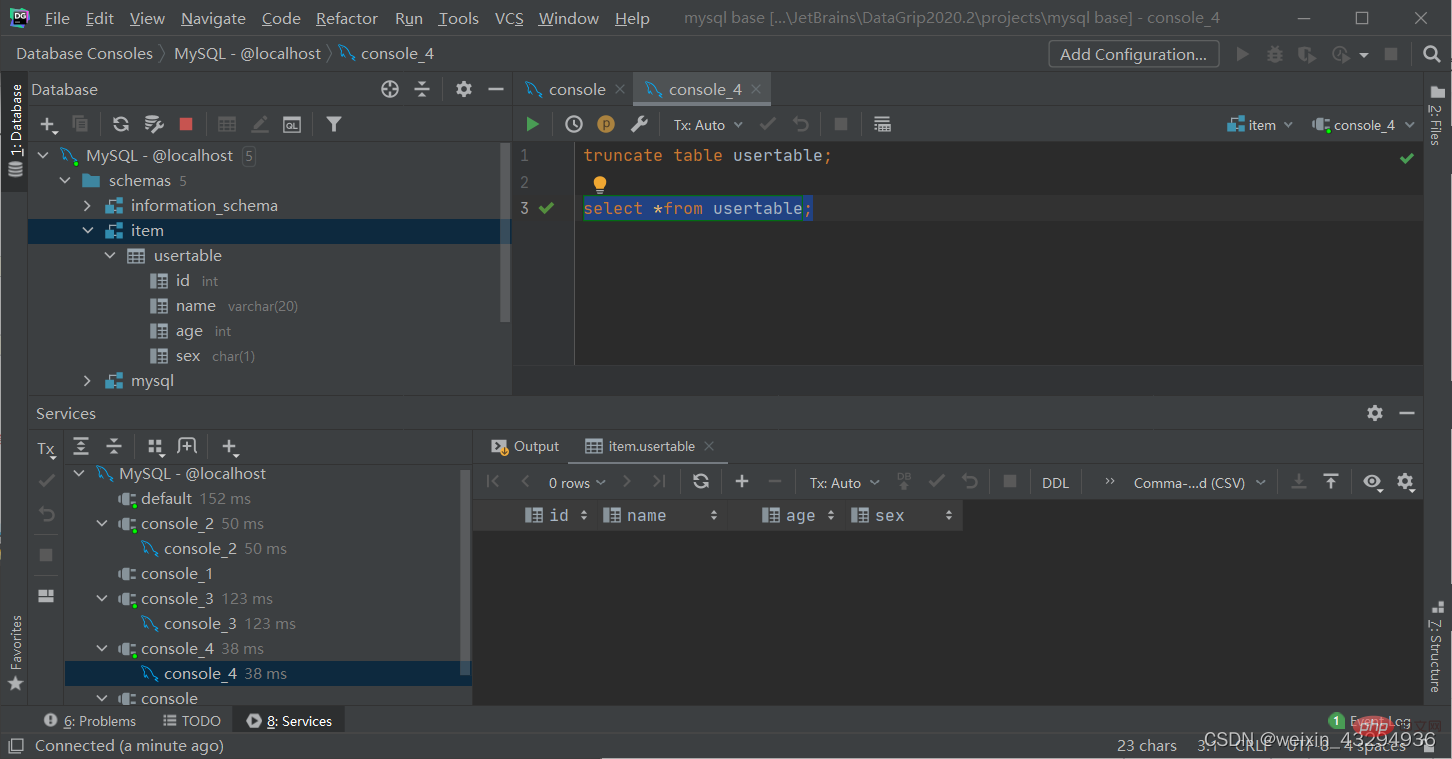
Delete the specified table and re-create the table (commonly known as formatting)
truncate table 表名;
2. DML (Data Manipulation Language)
Data operation language, used to add, delete and modify data in database tables
auxiliary table creation format
create table worktable( id int comment '编号', worknum int comment '工号', name varchar(20) comment '姓名', sex char(1) comment '性别', age int comment '年龄', idcard int comment '身份证号', entrydate date comment '入职日期' )comment '员工信息表';
Add data
Add data to the specified field
insert into 表名(字段名1,字段名2,.....) values(值1,值2,......);
Add data to all fields
insert into 表名 values (值1,值2,.....);
Add data in batches
insert into 表名(字段名1,字段名2,.....) values(值1,值2,......),(值1,值2,......),(值1,值2,......); insert into 表名 values (值1,值2,.....),(值1,值2,......),(值1,值2,......);
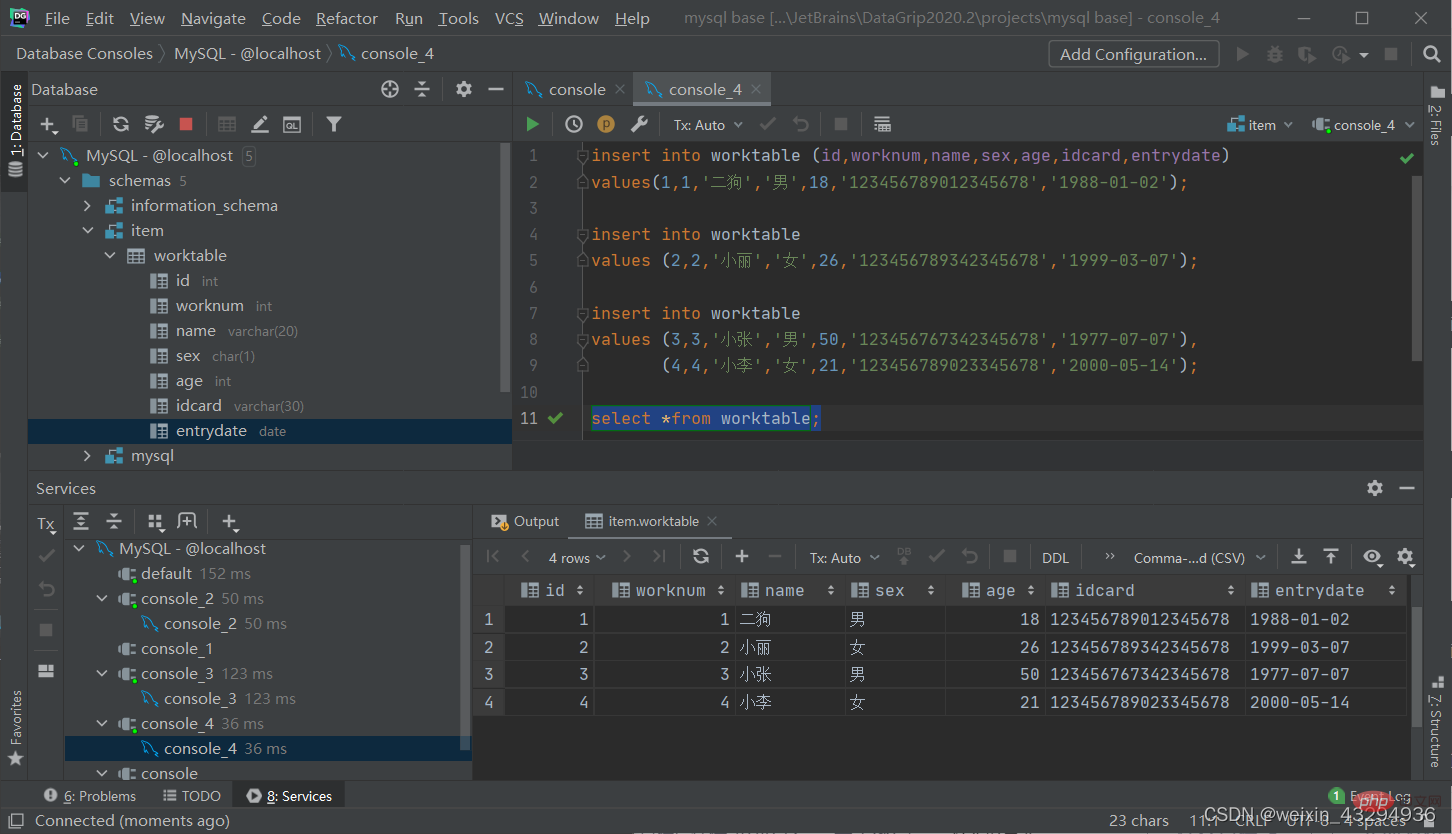
[Note]:
· When inserting data, the specified field order needs to be in one-to-one correspondence with the value order
·String and date data should be enclosed in quotes
·The size of the inserted data, should Modify data within the specified range of the field
Modify data
update 表名 set 字段名1=值1,字段名2=值2,....[where 条件];
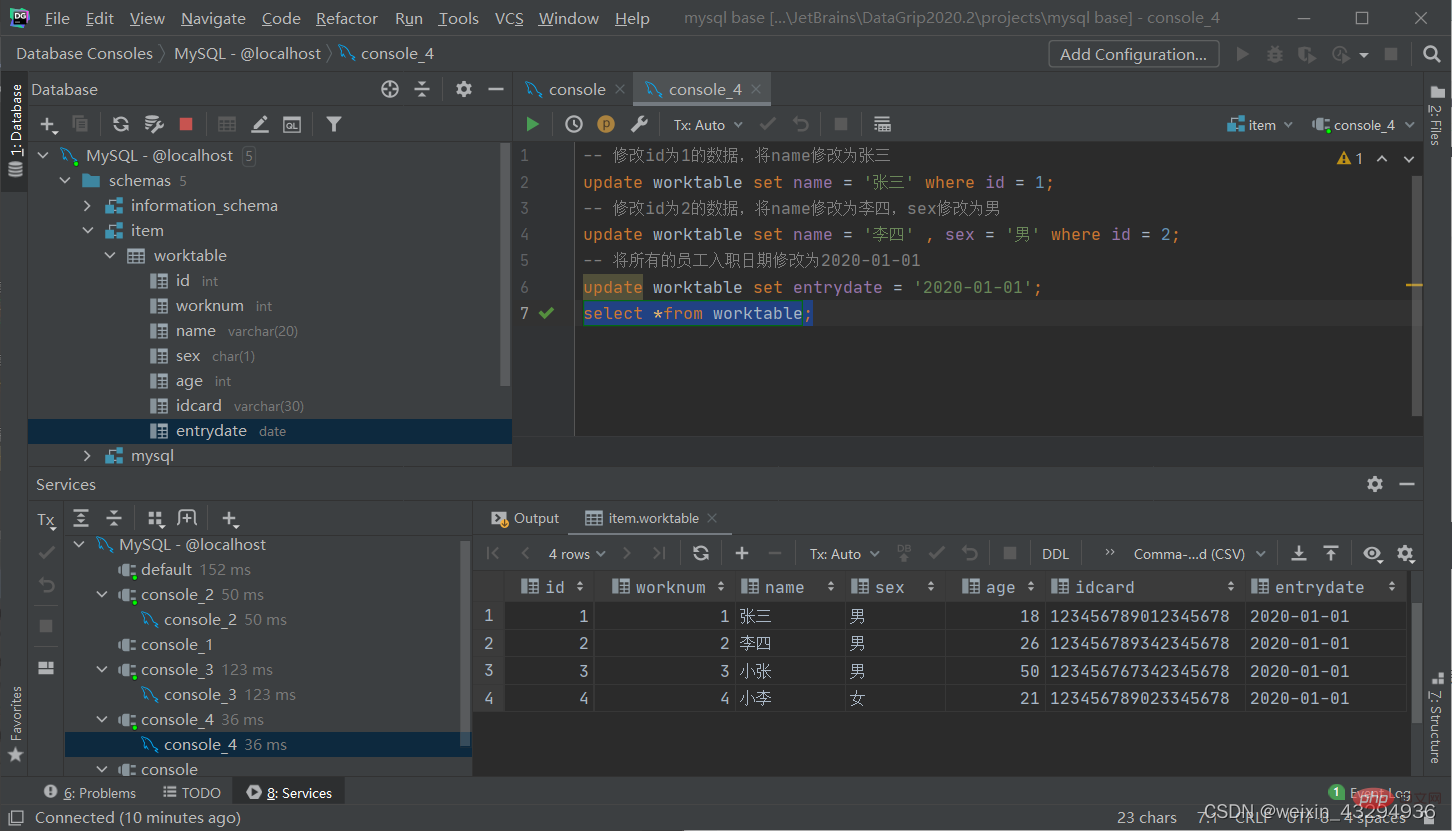
[Note]: The conditions for modifying the statement may or may not be , if there is no condition, all data in the entire table will be modified
Delete data
delete from 表名 [where 条件];
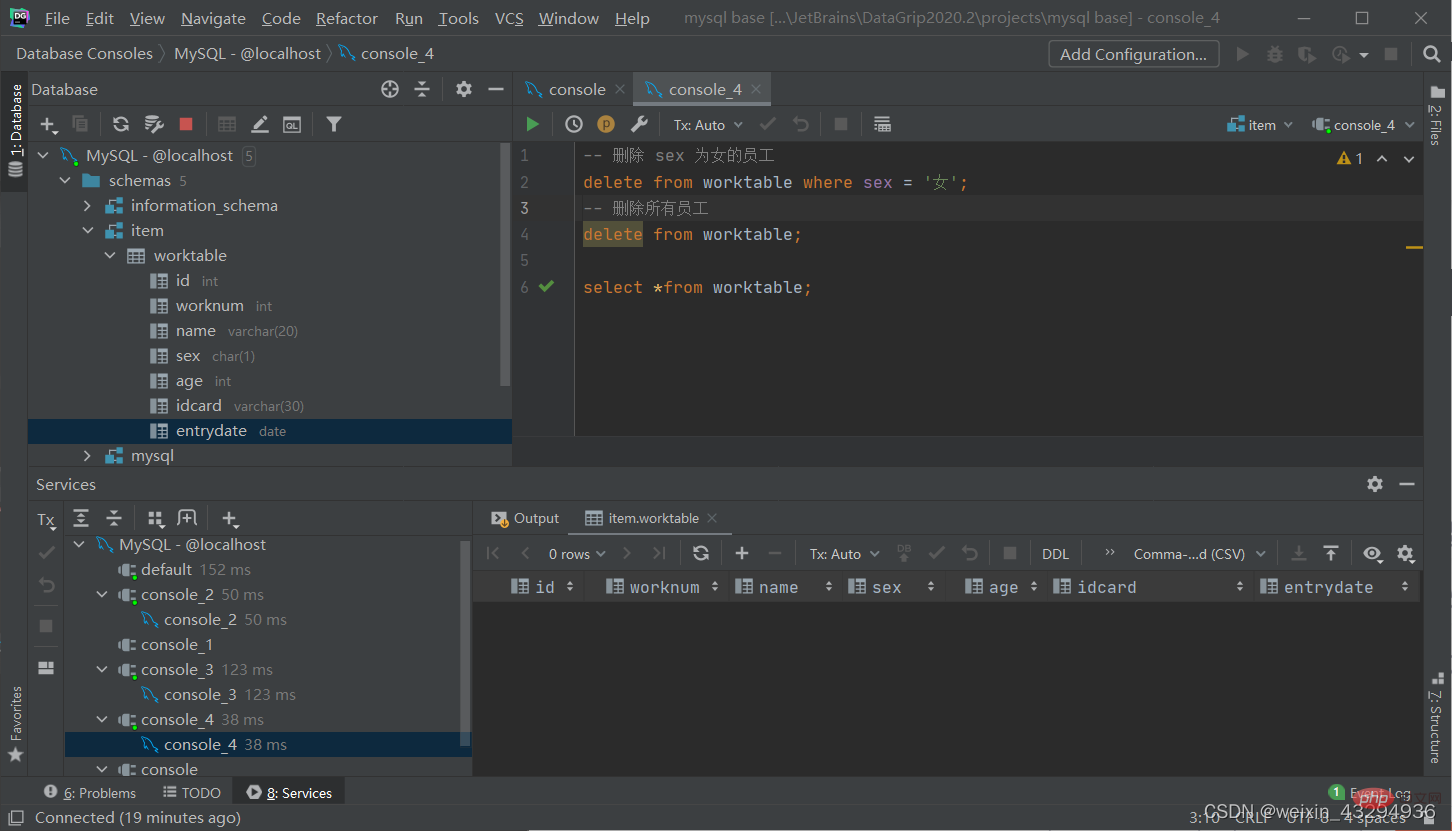
[Note]:
·The condition of the delete statement may or may not be present. If there is no condition, all data in the entire table will be deleted
·The delete statement cannot delete the value of a certain field (you can use update)
3. DQL (Data Query Language)
Data query language, used to query records in tables in the database
Overall syntax overview
| select | 字段列表 |
| from | 表名列表 |
| where | 条件列表 |
| group by | 分组字段列表 |
| having | 分组后条件列表 |
| order by | 排序字段列表 |
| limit | 分页参数 |
- 基本查询
- 条件查询(where)
- 聚合函数(count,max,min,avg,sum)
- 分组查询(group by)
- 排序查询(order by)
- 分页查询(limit)
辅助建表内容
create table emp( id int comment '编号', worknum varchar(10) comment '工号', name varchar(10) comment '姓名', gender char(1) comment '性别', age tinyint unsigned comment '年龄', idcard char(18) comment '身份证号', workaddress varchar(50) comment '工作地址', entrydate date comment '入职时间' )comment '员工表'; insert into emp (id,worknum,name,gender,age,idcard,workaddress,entrydate) values (1,'1','柳岩','女',20,'123456789012345678','北京','2000-01-01'), (2,'2','张无忌','男',18,'123456789012345670','北京','2005-09-01'), (3,'3','韦一笑','男',38,'123456789712345670','上海','2005-08-01'), (4,'4','赵敏','女',18,'123456757123845670','北京','2009-12-01'), (5,'5','小昭','女',16,'123456769012345678','上海','2007-07-01'), (6,'6','杨逍','男',28,'12345678931234567X','北京','2006-01-01'), (7,'7','范瑶','男',40,'123456789212345670','北京','2005-05-01'), (8,'8','黛绮丝','女',38,'123456157123645670','天津','2015-05-01'), (9,'9','范凉凉','女',45,'123156789012345678','北京','2010-04-01'), (10,'10','陈友谅','男',53,'123456789012345670','上海','2011-01-01'), (11,'11','张士诚','男',55,'123567897123465670','江苏','2015-05-01'), (12,'12','常遇春','男',32,'123446757152345670','北京','2004-02-01'), (13,'13','张三丰','男',88,'123656789012345678','江苏','2020-11-01'), (14,'14','灭绝','女',65,'123456719012345670','西安','2019-05-01'), (15,'15','胡青牛','男',70,'12345674971234567X','西安','2018-04-01'), (16,'16','周芷若','女',18,null,'北京','2012-06-01');
基本查询
查询多个字段
select 字段1,字段2,字段3.....from 表名; select *from 表名;
设置别名
select 字段1 [as 别名1],字段2 [as 别名2] .... from 表名; #as可省略
去除重复记录
select distinct 字段列表 from 表名;
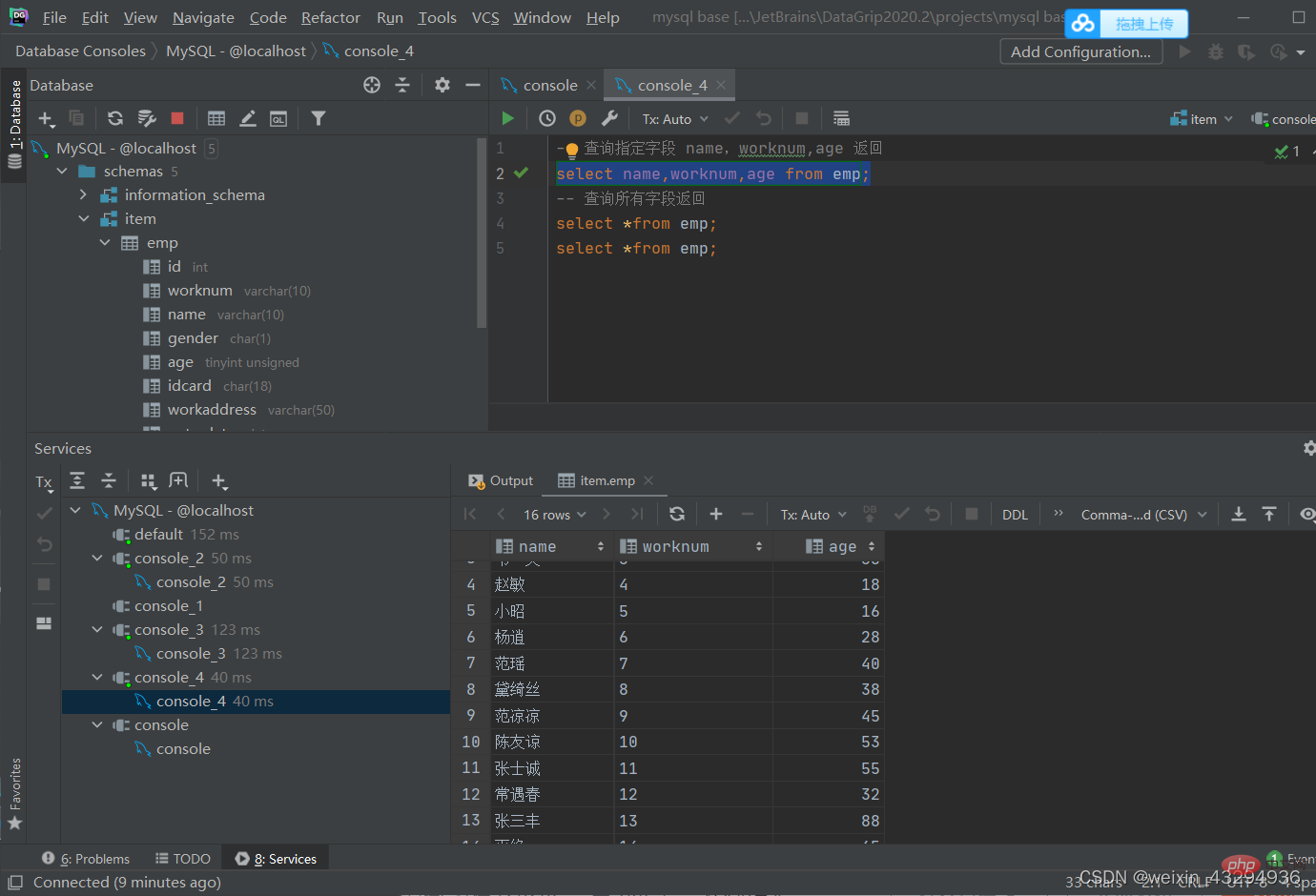
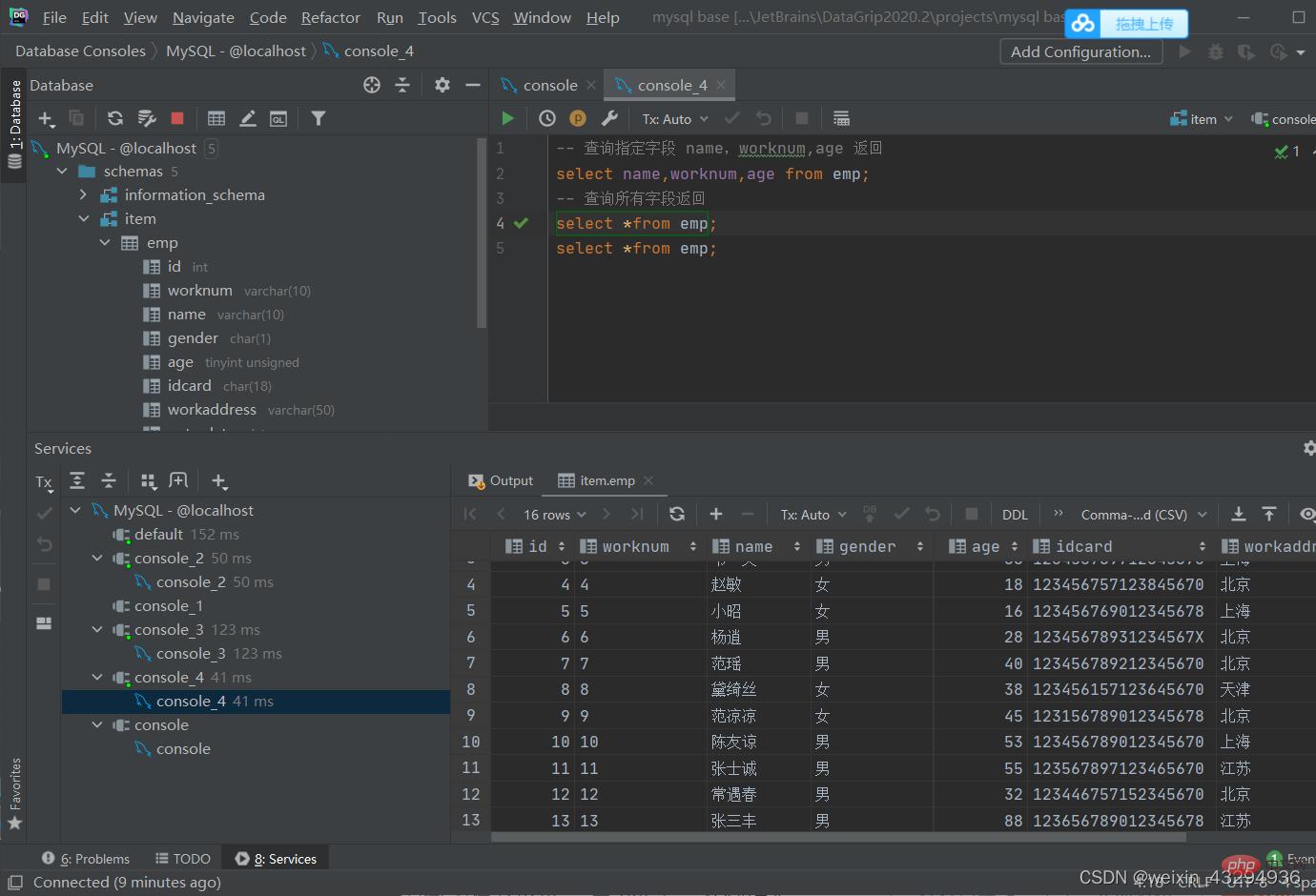
条件查询
语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 where 条件列表;
条件
| 比较运算符 | 功能 | 逻辑运算符 | 功能 |
| > | 大于 | and 或 && | 并且(多个条件同时成立) |
| >= | 大于等于 | or 或 || | 或者(多个条件任意一个成立) |
| < | 小于 | not 或 ! | 非,不是 |
| <= | 小于等于 | ||
| = | 等于 | ||
| <> 或 != | 不等于 | ||
| between...and... | 在某个范围内(含最小,最大值) | ||
| in(.....) | 在in之后的列表中的值,多选一 | ||
| like 占位符 | 模糊匹配(_匹配单个字符,%匹配任意个字符) | ||
| is null | 是null |
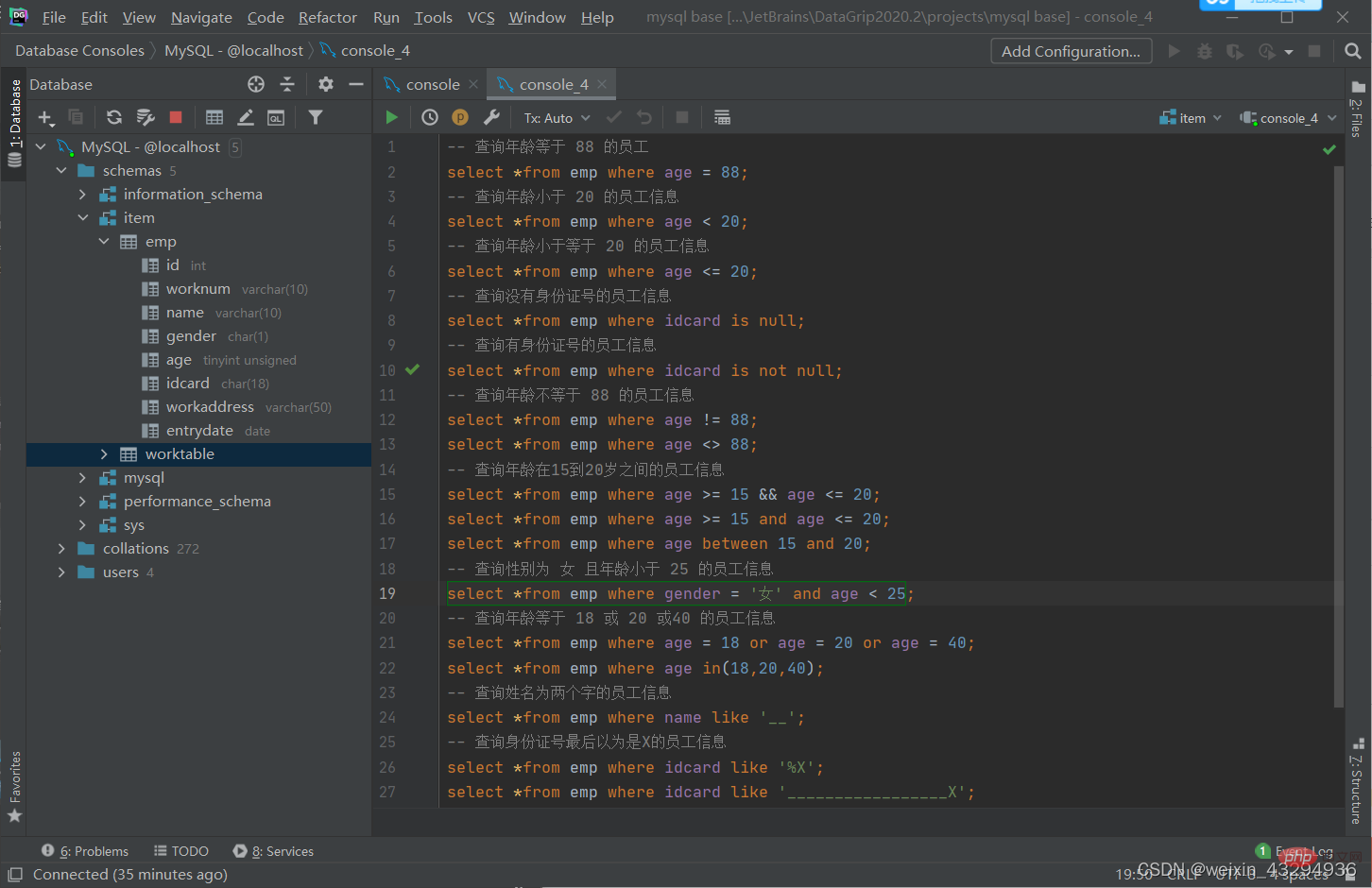
聚散函数
常见聚合函数
| 函数 | 功能 |
| count | 统计数量 |
| max | 最大值 |
| min | 最小值 |
| avg | 平均值 |
| sum | 求和 |
语法
select 聚合函数(字段列表) from 表名;
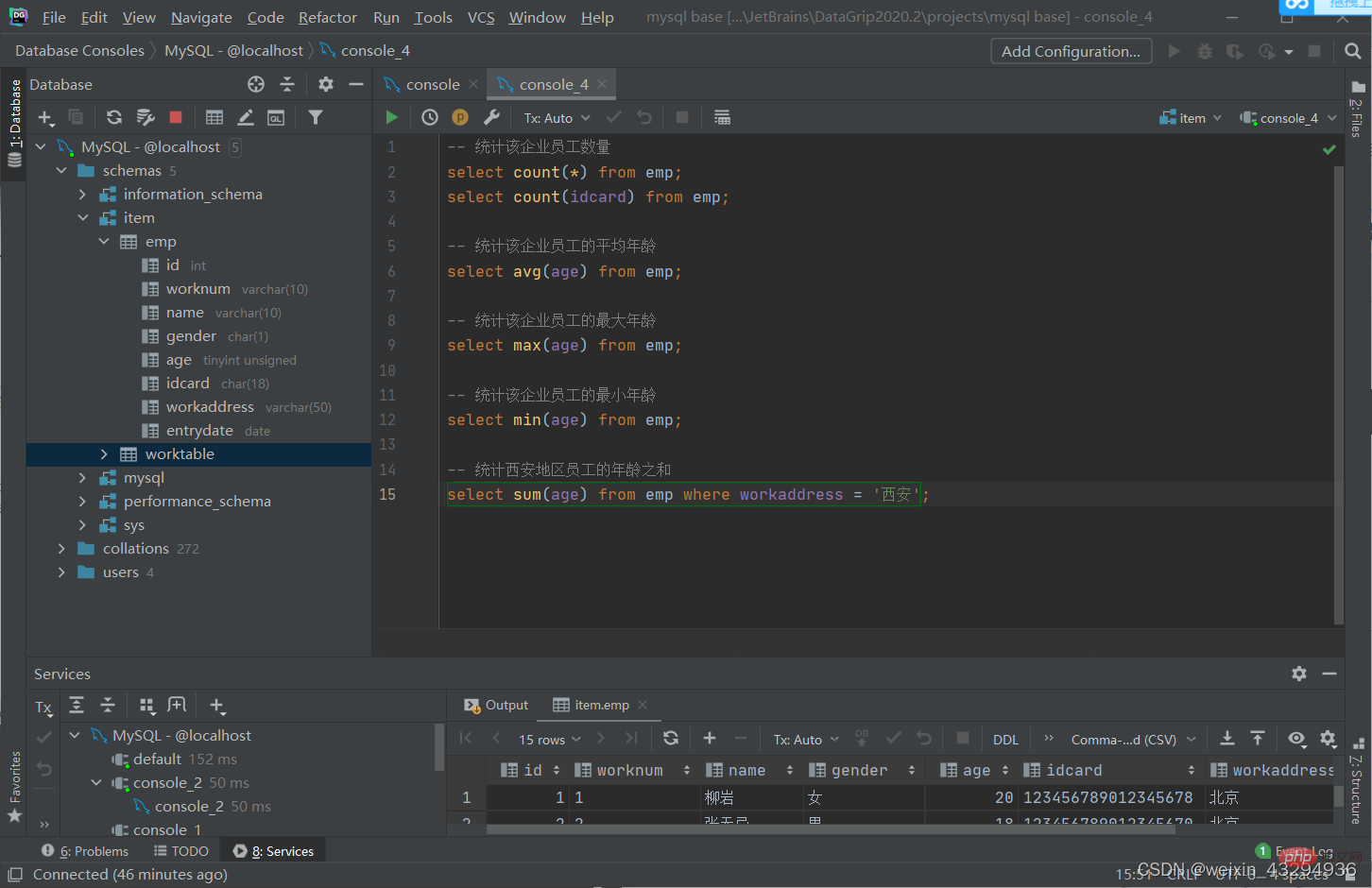
[注]:null值不参与所有聚合函数运算
分组查询
语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 [where 条件] group by 分组字段名 [having 分组过滤条件];
where 与 having 区别
1.执行时机不同:where是分组之前进行过滤,不满足where条件,不参与分组;
having是分组之后对结果进行过滤。
2.判断条件不同:where不能对聚合函数进行判断,而having可以。
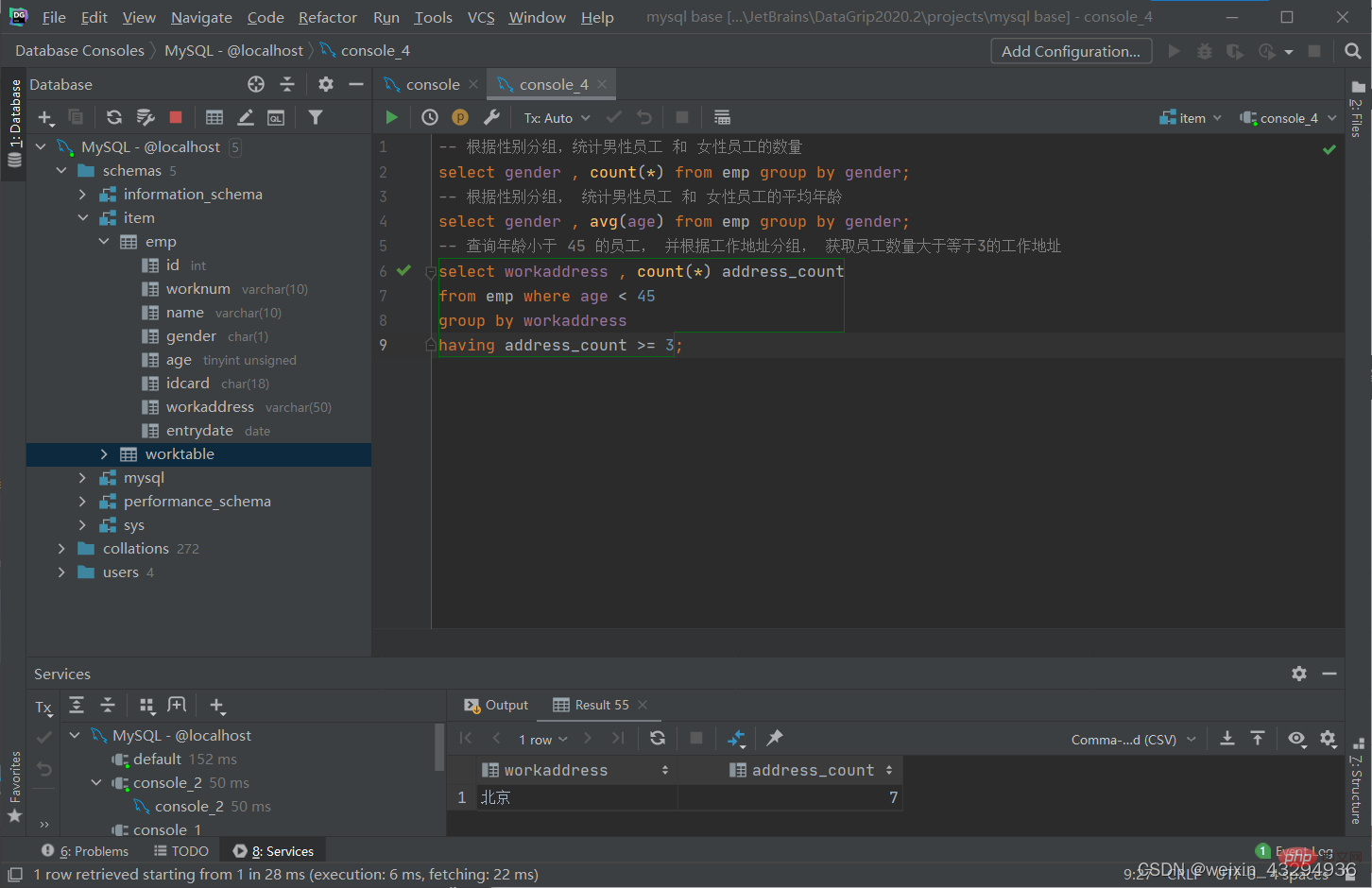
排序查询
语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 order by 字段1 排序方式1 , 字段2 排序方式2; #排序方式 #asc:升序(默认值) #desc:降序
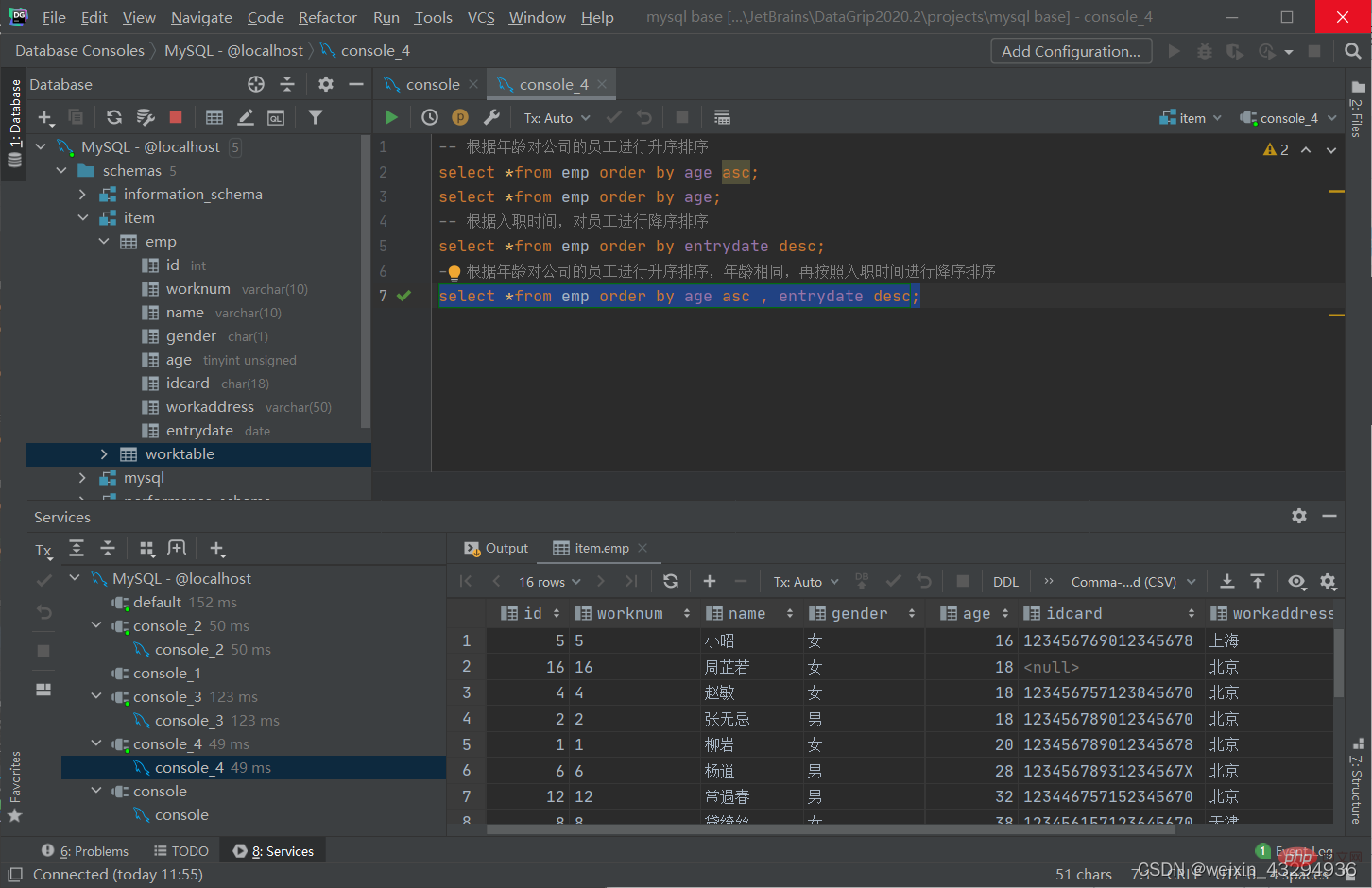
[注]:如果是多字段排序,当第一个字段值相同时,才会根据第二个字段进行排序。
分页查询
语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 limit 起始索引,查询记录数;
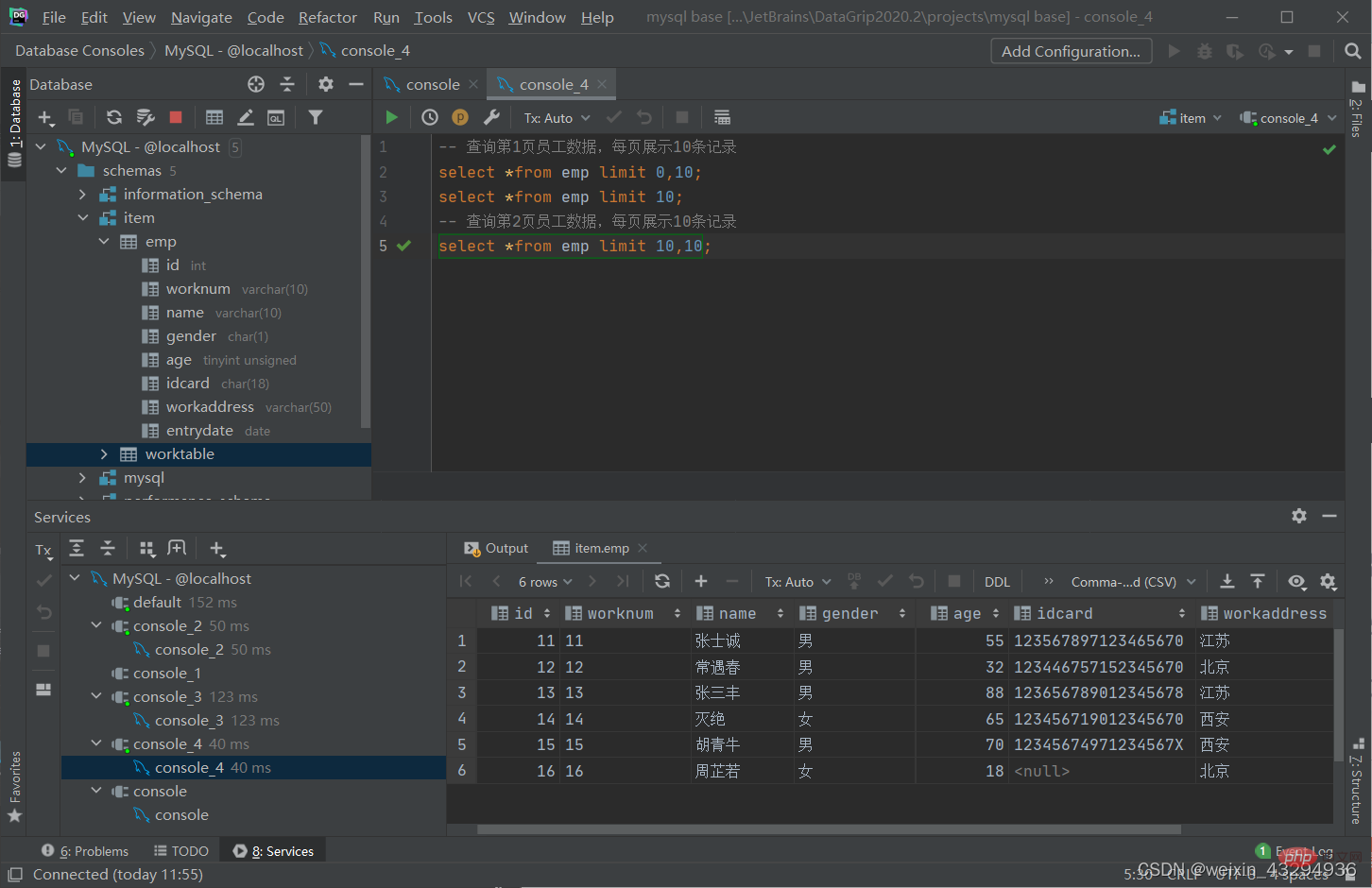
[注]:
- 起始索引从0开始,起始索引 = (查询页码 - 1) * 每页显示记录数
- 分页查询是数据库的方言,不同的数据库有不同的实现,MySQL中是limit
- 如果查询的是第一页数据,起始索引可以省略,直接简写为limit 10
案例练习
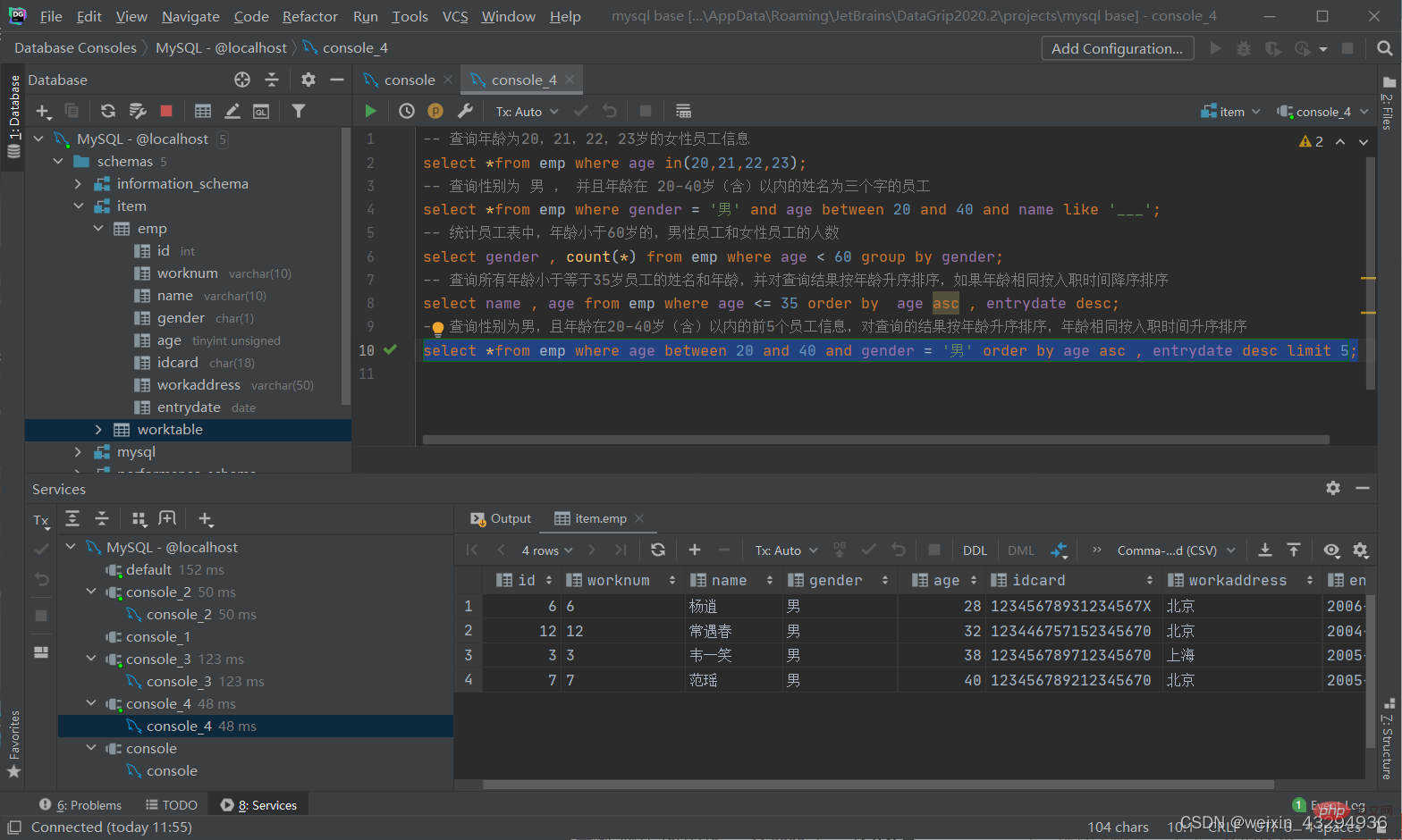
整体语法顺序

四、DCL(Data Control Language)
数据控制语言,用来创建数据库用户,控制数据库的访问权限
管理用户
查询用户
use mysql; select *from user;
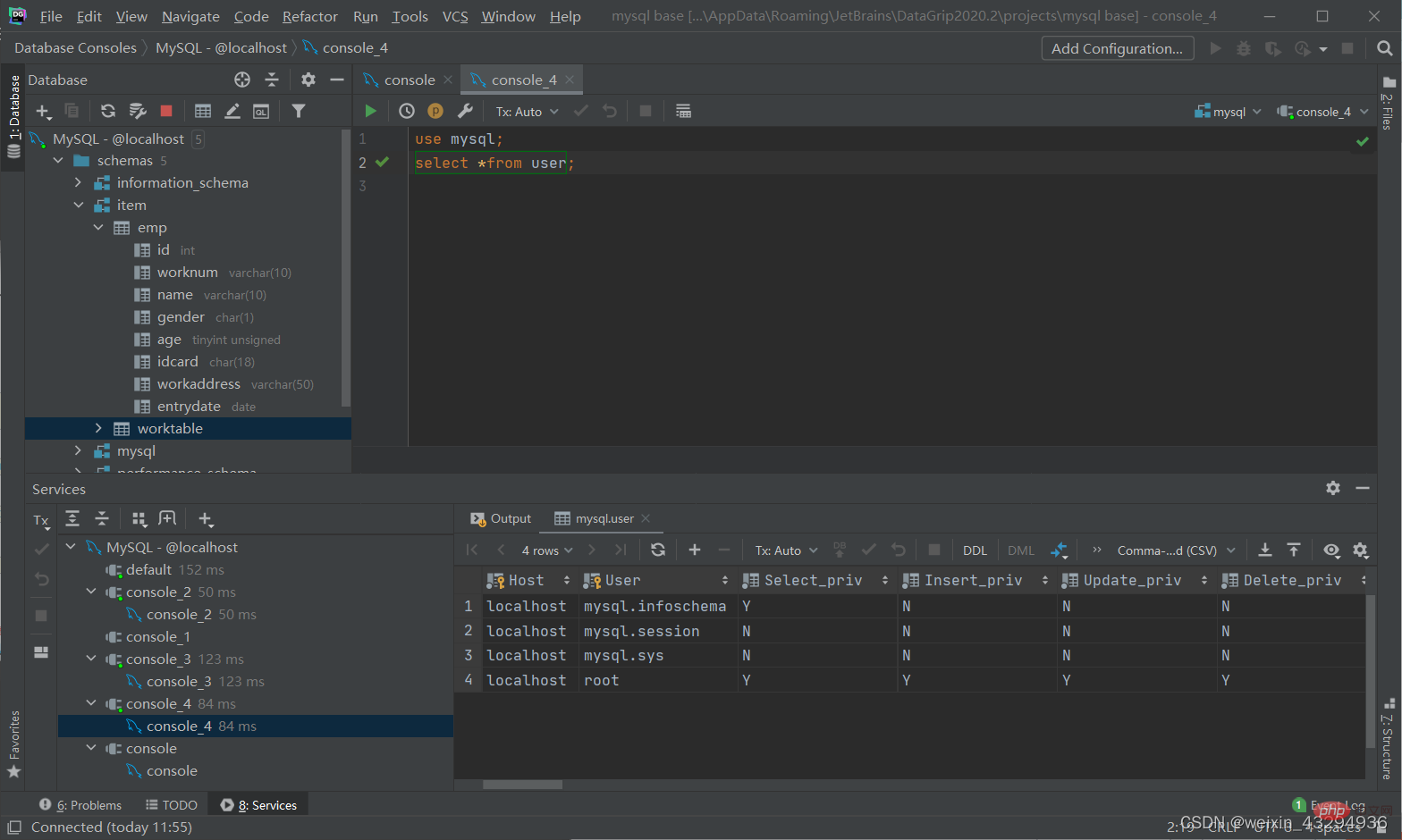
创建用户
create user '用户名'@'主机名' identified '密码';
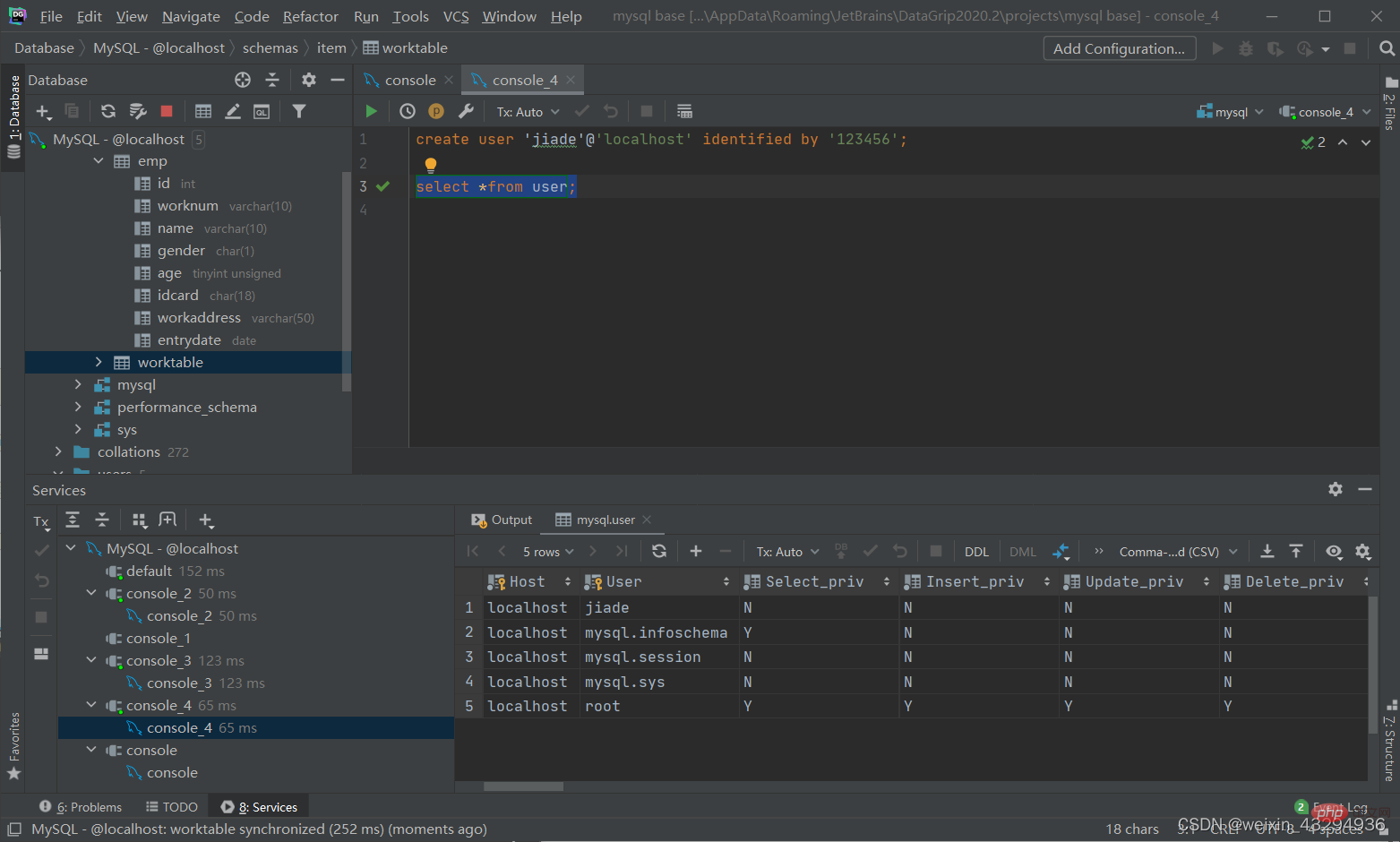
修改用户密码
alter user '用户名'@'主机名' identified with mysql_native_password by '新密码';
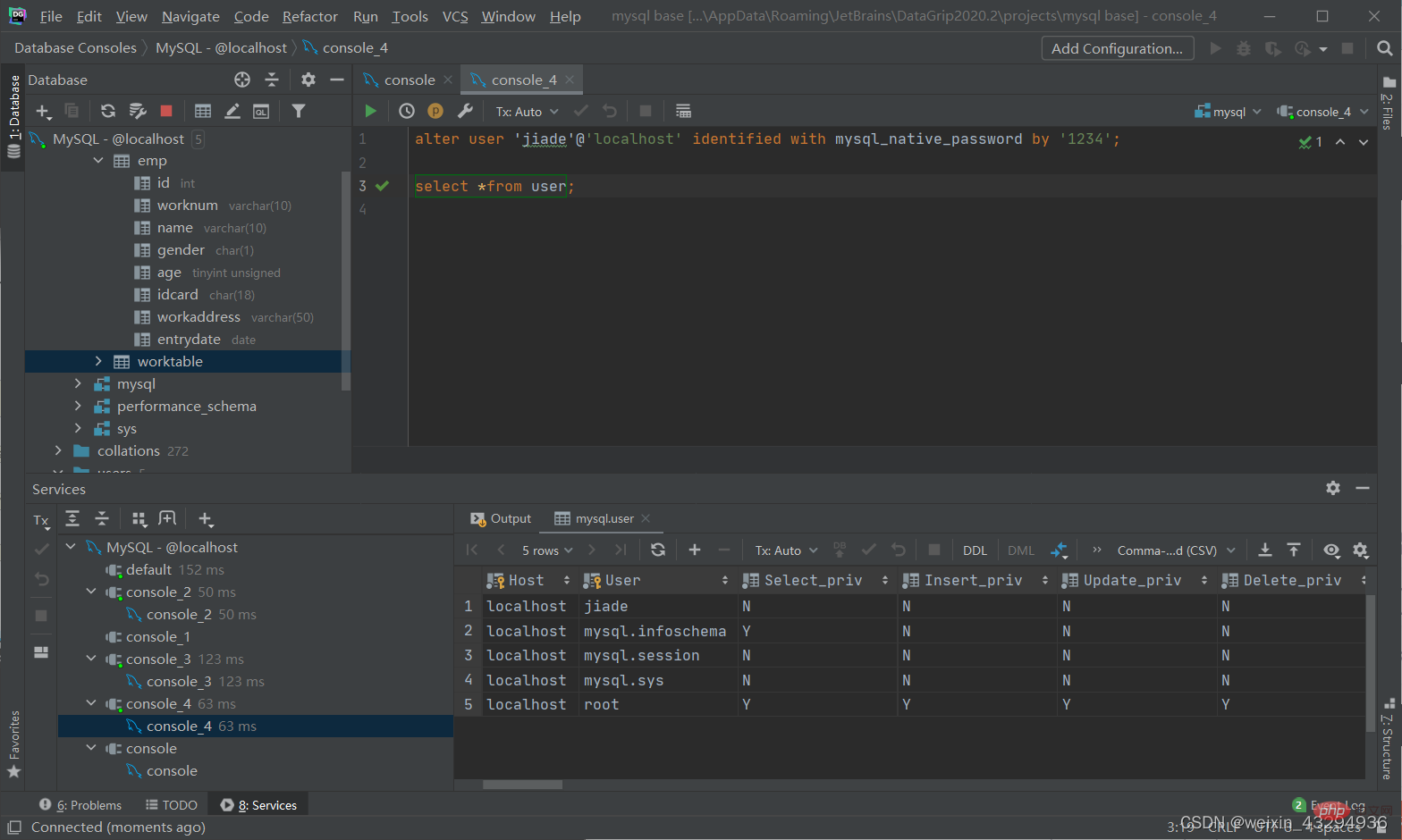
删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'主机名';
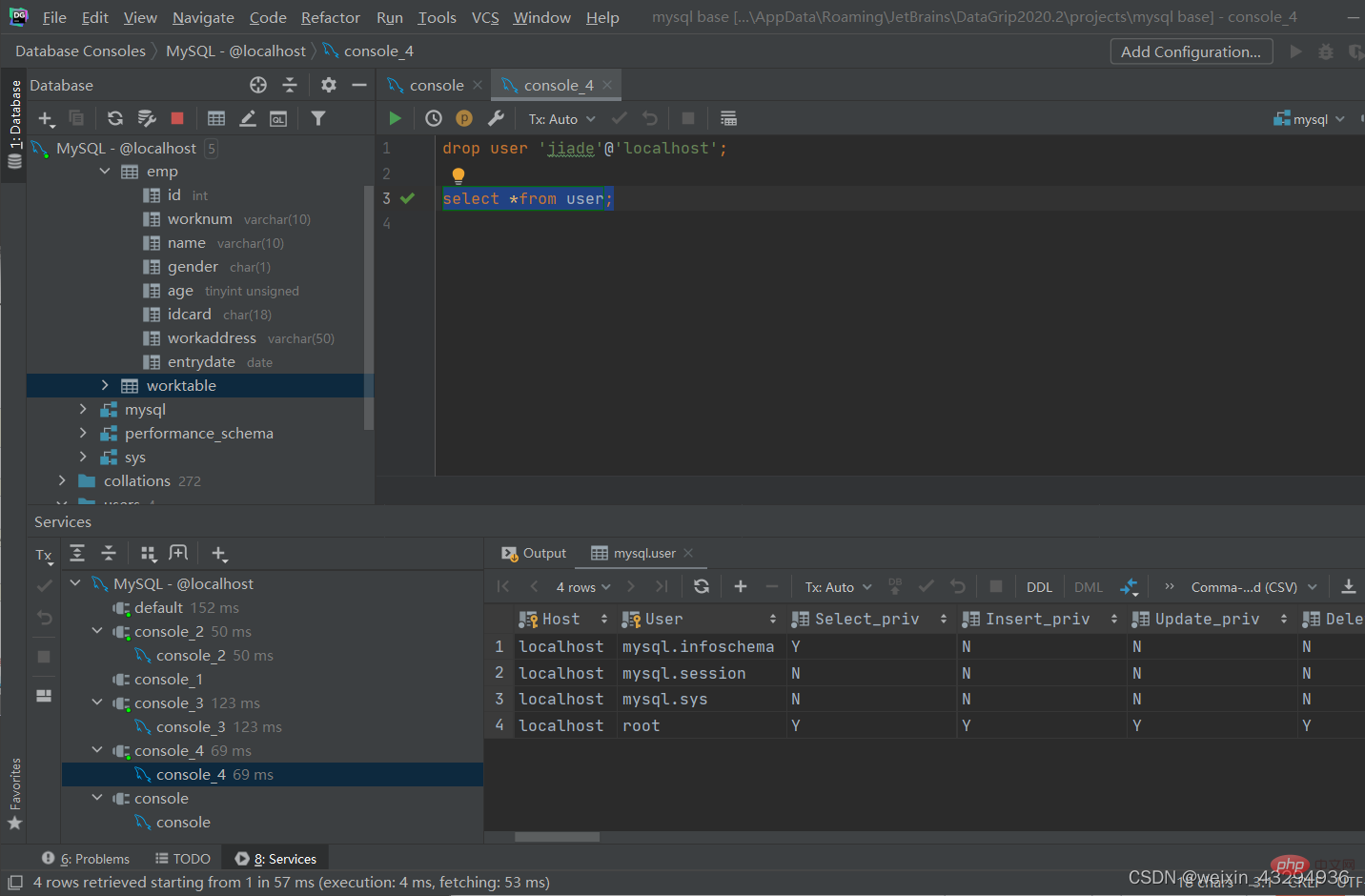
[注]:
- 主机名可以使用%通配
- 这类SQL开发人员操作的比较少,主要是DBA(Database Administrator)使用
权限控制
常用的权限
| 权限 | 说明 |
| all,all privileges | 所有权限 |
| select | 查询数据 |
| insert | 插入数据 |
| update | 修改数据 |
| delete | 删除数据 |
| alter | 修改表 |
| drop | 删除数据库/表/视图 |
| create | 创建数据库/表 |
查询权限
show grants for '用户名'@'主机名';
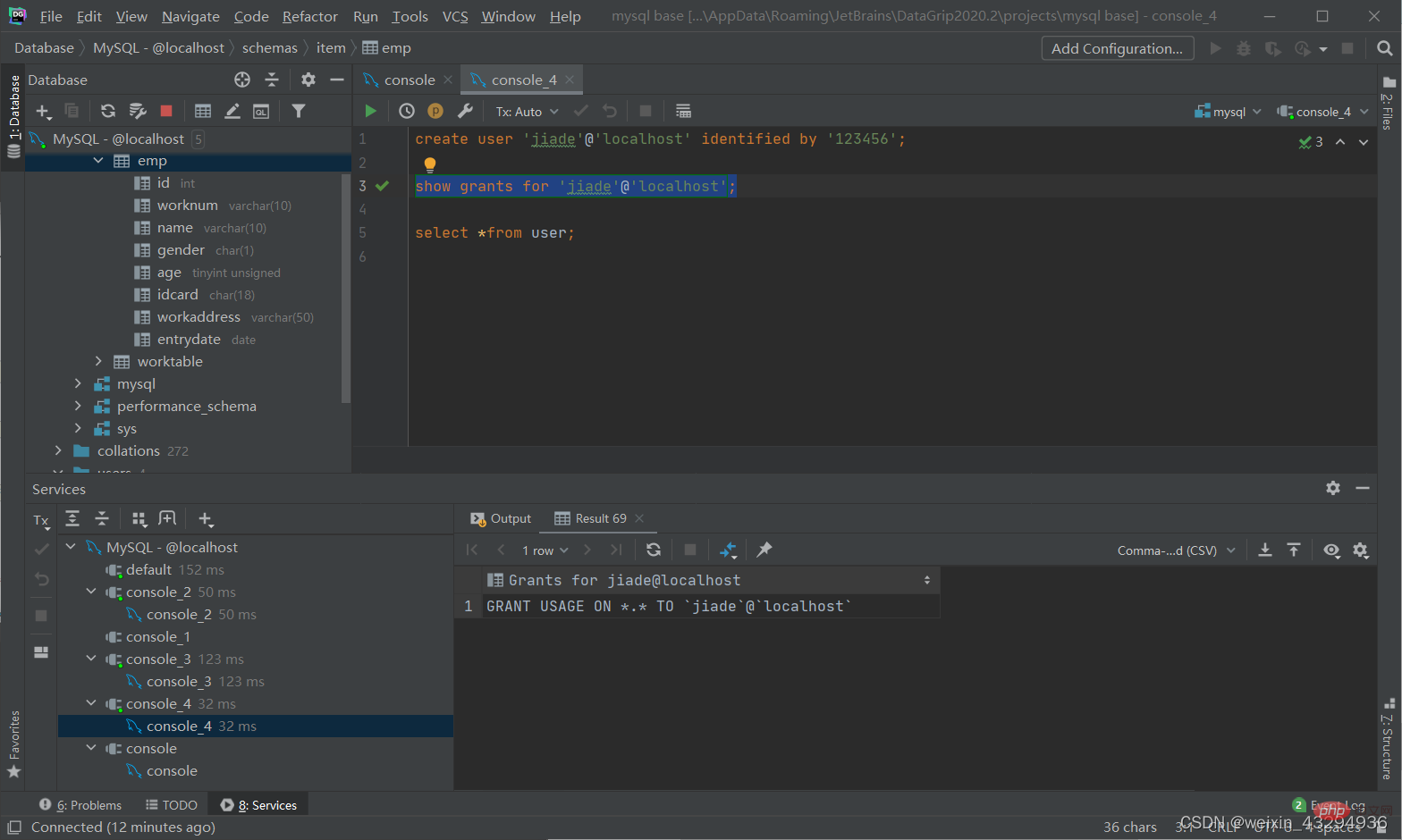
授予权限
grant 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 to '用户名'@'主机名';
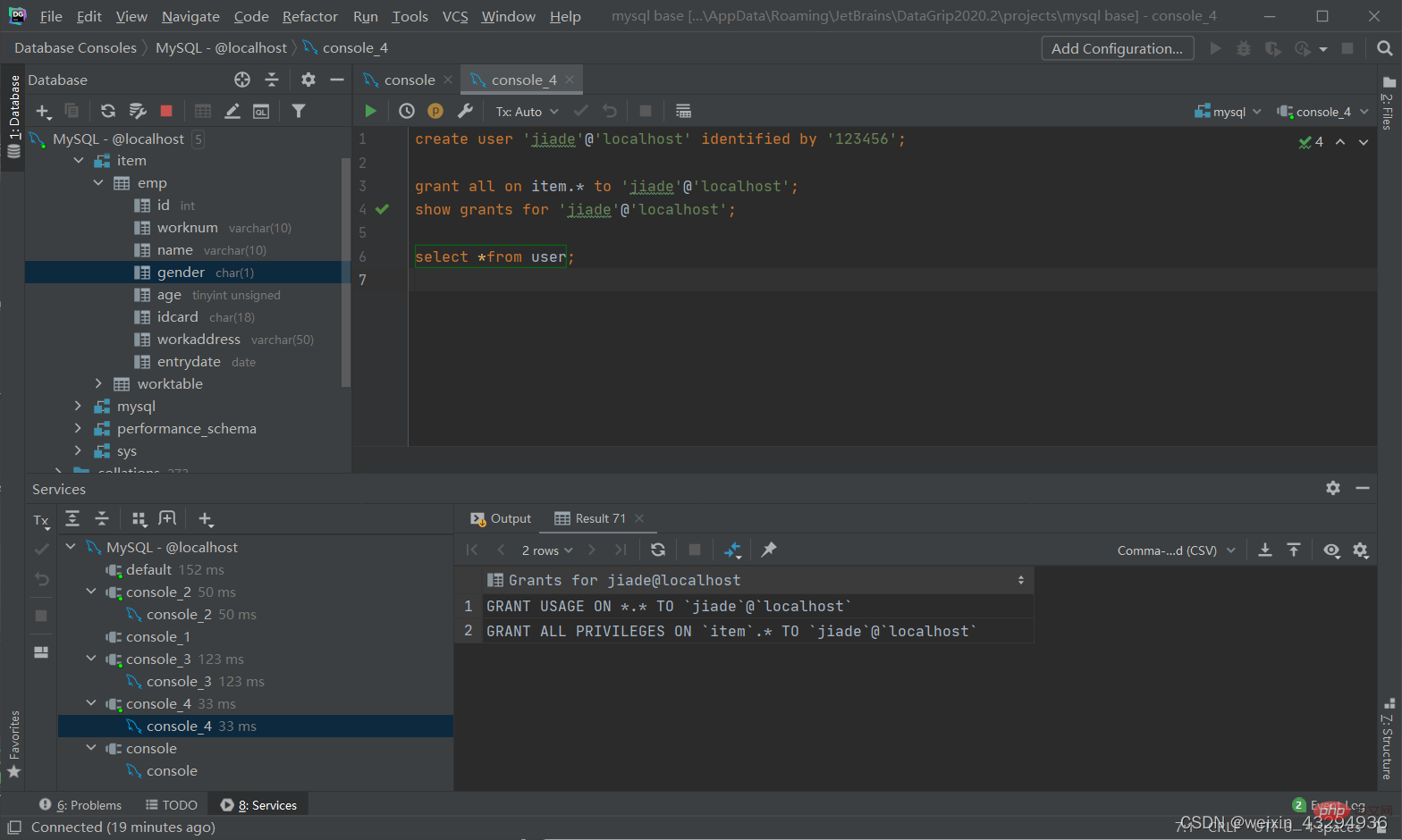
撤销权限
revoke 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 from '用户名'@'主机名';
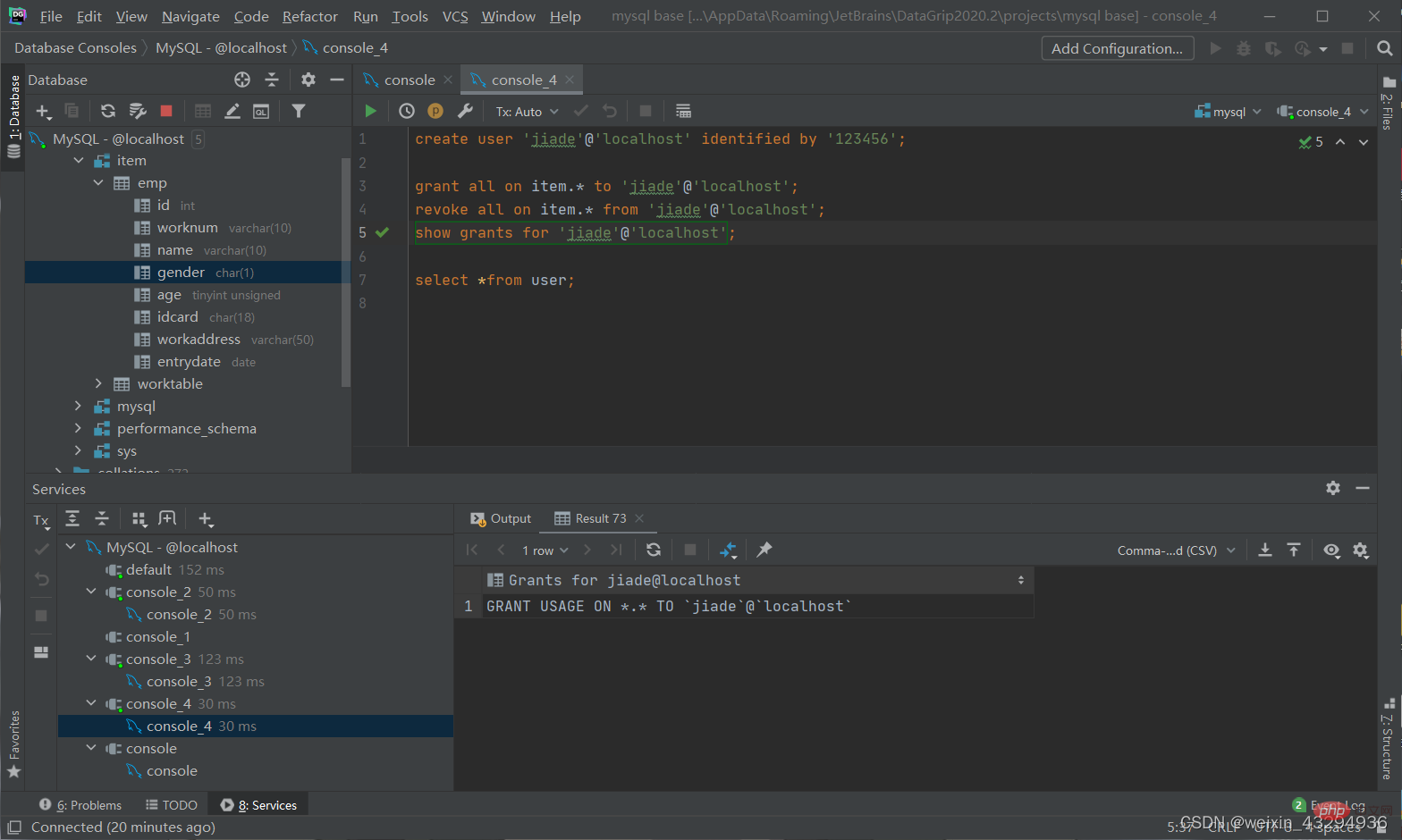
[注]:
- 多个权限之间,使用逗号分割
- 授权时,数据库名和表名可以使用 * 进行通配,代表所有
推荐学习:《SQL教程》
The above is the detailed content of Organize and summarize basic SQL statements based on examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
HQL and SQL are compared in the Hibernate framework: HQL (1. Object-oriented syntax, 2. Database-independent queries, 3. Type safety), while SQL directly operates the database (1. Database-independent standards, 2. Complex executable queries and data manipulation).
 Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
"Usage of Division Operation in OracleSQL" In OracleSQL, division operation is one of the common mathematical operations. During data query and processing, division operations can help us calculate the ratio between fields or derive the logical relationship between specific values. This article will introduce the usage of division operation in OracleSQL and provide specific code examples. 1. Two ways of division operations in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operations can be performed in two different ways.
 Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Oracle and DB2 are two commonly used relational database management systems, each of which has its own unique SQL syntax and characteristics. This article will compare and differ between the SQL syntax of Oracle and DB2, and provide specific code examples. Database connection In Oracle, use the following statement to connect to the database: CONNECTusername/password@database. In DB2, the statement to connect to the database is as follows: CONNECTTOdataba
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What is Identity in SQL? Specific code examples are needed. In SQL, Identity is a special data type used to generate auto-incrementing numbers. It is often used to uniquely identify each row of data in a table. The Identity column is often used in conjunction with the primary key column to ensure that each record has a unique identifier. This article will detail how to use Identity and some practical code examples. The basic way to use Identity is to use Identit when creating a table.
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
When Springboot+Mybatis-plus does not use SQL statements to perform multi-table adding operations, the problems I encountered are decomposed by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object with parameters to simulate passing parameters to the background. We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use tools such as Mybatis-plus-join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper.xml file and configure The smelly and long ResultMap, and then write the corresponding sql statement. Although this method seems cumbersome, it is highly flexible and allows us to
 How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL?
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL?
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL? Data aggregation and statistics are very important steps when performing data analysis and statistics. As a powerful relational database management system, MySQL provides a wealth of aggregation and statistical functions, which can easily perform data aggregation and statistical operations. This article will introduce the method of using SQL statements to perform data aggregation and statistics in MySQL, and provide specific code examples. 1. Use the COUNT function for counting. The COUNT function is the most commonly used
 How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Solution: 1. Check whether the logged-in user has sufficient permissions to access or operate the database, and ensure that the user has the correct permissions; 2. Check whether the account of the SQL Server service has permission to access the specified file or folder, and ensure that the account Have sufficient permissions to read and write the file or folder; 3. Check whether the specified database file has been opened or locked by other processes, try to close or release the file, and rerun the query; 4. Try as administrator Run Management Studio as etc.




