
In CSS, " " is an adjacent sibling element selector, used to select elements immediately after another element, and they have the same parent element; in other words, both E and F The elements have the same parent element, and the F element is behind and adjacent to the E element, so you can use the adjacent sibling element selector to select the F element, with the syntax "E F".

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, CSS3&&HTML5 version, Dell G3 computer.
Adjacent sibling element selector (E F)
Adjacent sibling selector can select elements immediately following another Elements after one element, and they have the same parent element. In other words, the two EF elements have the same parent element, and the F element is behind the E element and adjacent, so we can use adjacent sibling elements Selector to select F elements.
There are 2 key pieces of information here: (1) Immediately after another element; (2) Both have the same parent element
Example ①:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--[if lt IE 7]> <html class="no-js lt-ie9 lt-ie8 lt-ie7"> <![endif]-->
<!--[if IE 7]> <html class="no-js lt-ie9 lt-ie8"> <![endif]-->
<!--[if IE 8]> <html class="no-js lt-ie9"> <![endif]-->
<!--[if gt IE 8]><!--> <html class="no-js"> <!--<![endif]-->
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<title></title>
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
div+p{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--[if lt IE 7]>
<p class="browsehappy">You are using an <strong>outdated</strong> browser. Please <a href="#">upgrade your browser</a> to improve your experience.</p>
<![endif]-->
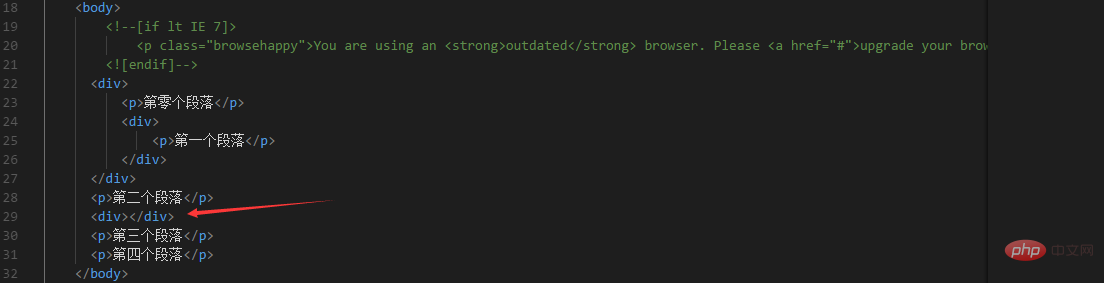
<div>
<p>第零个段落</p>
<div>
<p>第一个段落</p>
</div>
</div>
<p>第二个段落</p>
<p>第三个段落</p>
<p>第四个段落</p>
</body>
</html>
##div p indicates that all locations located in element after the element tag is after the element has the same parent element tag immediately after the tag If you want the "third paragraph" to also be selected, you need to make its tag also in the < Immediately after the div> tag, as follows tag is not immediately adjacent to div p{} immediately after an element represents the element immediately after selecting tag is not immediately adjacent to the element cannot be selected. Example ②: First analyze the selector style: li li{}, which literally means to select (1) Obviously the first (2) The second (3) The third Because the style of the css selector is li li{}, this "formula" can always be applied to the li tag in the code. The above is the detailed content of What is '+' css selector?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!The above-mentioned "zeroth paragraph" and "first paragraph" are not selected because they are nested in the



<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--[if lt IE 7]> <html class="no-js lt-ie9 lt-ie8 lt-ie7"> <![endif]-->
<!--[if IE 7]> <html class="no-js lt-ie9 lt-ie8"> <![endif]-->
<!--[if IE 8]> <html class="no-js lt-ie9"> <![endif]-->
<!--[if gt IE 8]><!--> <html class="no-js"> <!--<![endif]-->
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<title></title>
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
li+li{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--[if lt IE 7]>
<p class="browsehappy">You are using an <strong>outdated</strong> browser. Please <a href="#">upgrade your browser</a> to improve your experience.</p>
<![endif]-->
<ul>
<li>List item 1</li>
<li>List item 2</li>
<li>List item 3</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>List item 1</li>
<li>List item 2</li>
<LI>List item 3</LI>
</ol>
</body>
</html>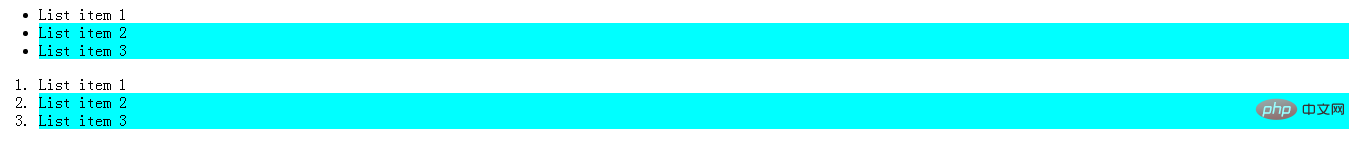 At first I was really wondering why “List Item 2" and "List item 3" are both selected~~~
At first I was really wondering why “List Item 2" and "List item 3" are both selected~~~
css video tutorial