
The 7-layer network structure refers to the OSI seven-layer model, which includes application layer, presentation layer, session layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer, and physical layer. The physical layer is used to transparently transmit bit streams; the data link layer mainly encapsulates and decapsulates the MAC address of the data received from the physical layer, and transmits it error-free on the line between two adjacent nodes, in units of frames. data; the session layer manages remote access; the presentation layer handles the presentation of information exchanged between multiple communication systems; and the application layer provides various services to network users or applications.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
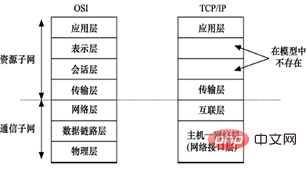
Layer 7 refers to the OSI seven-layer protocol model, which is mainly: application layer (Application), presentation layer (Presentation), session layer (Session), transport layer (Transport), network layer (Network), data Link layer (Data Link), physical layer (Physical).

1. Physical layer: The main task of the physical layer is to transmit transparently bitstream. The physical layer does not care about the actual meaning and structure of the bit stream, but is only responsible for receiving and transmitting the bit stream. The physical layer defines the characteristics of the network hardware, including what kind of transmission media is used and the connectors connected to the transmission media and other physical characteristics for easy understanding: (mainly defines physical equipment standards, such as network cable interface types, optical fiber interface types, various transmission media The transmission rate, etc.) The data transmission unit of the physical layer is bits.
2. Data link layer: It mainly encapsulates and decapsulates the MAC address (address of the network card) of the data received from the physical layer, and transmits it without errors on the line between two adjacent nodes. Data in Frame units, and frame boundaries must be generated and identified. The data link layer also provides error control and traffic control methods to ensure that the data transmitted on the physical line is error-free.
3. Network layer: (mainly encapsulates and decapsulates the IP address (for example 192.168.0.1) of the data received from the lower layer) for routing selection to ensure that the data packet (Packet) arrives from the sending end The receiving end performs congestion control when data packets are blocked. The network layer also needs to solve the interconnection problem of heterogeneous networks to realize the transmission of data packets in different types of networks. Representatives of network layer protocols include: IP, IPX, RIP, OSPF, etc.
4. Transport layer: (mainly segments and transmits the data received from the lower layer, and then reassembles it after reaching the destination address. This layer of data is often called segments) communicates for the upper layer A reliable end-to-end service is provided between the two processes, so that the layers above the transport layer no longer care about information transmission issues. The transport layer receives data from the session layer, forms a message (Message), divides it into several packets when necessary, and then hands it to the network layer for transmission. Representatives of transport layer protocols include: TCP, UDP, SPX, etc.
5. Session layer: Management of remote access (such as breakpoint resumption), including session management, transmission synchronization, and data exchange management, etc. . The session layer is responsible for maintaining the establishment, management, and termination of connections between two session hosts, as well as the exchange of data. A data transmission path is established through the transport layer (port number: transmission port and receiving port). (Mainly initiate sessions or accept session requests between your systems (devices need to know each other, which can be IP, MAC or host name))
6. Presentation layer: used to handle multiple The representation of information exchanged between communication systems, including data format conversion, data encryption and decryption, data compression and recovery, etc., mainly the interpretation, encryption and decryption, compression and decompression of received data (that is, Convert things that computers can recognize into things that humans can recognize (such as pictures, sounds, etc.).
7. Application layer: Provide various services for network users or applications, such as file transfer, electronic Mail, network management and remote login, etc. are mainly terminal applications, such as FTP (various file downloads), WEB (IE browsing), QQ and the like (it can be understood as what we can see on the computer screen The thing. It is the terminal application).
Network interface Layer - corresponds to the physical layer and data link layer of the OSI reference model;
Network layer - corresponds to the network layer of the OSI reference model;
Transport layer--corresponds to the transport layer of the OSI reference model;
Application layer--corresponds to layers 5, 6, and 7 of the OSI reference model.
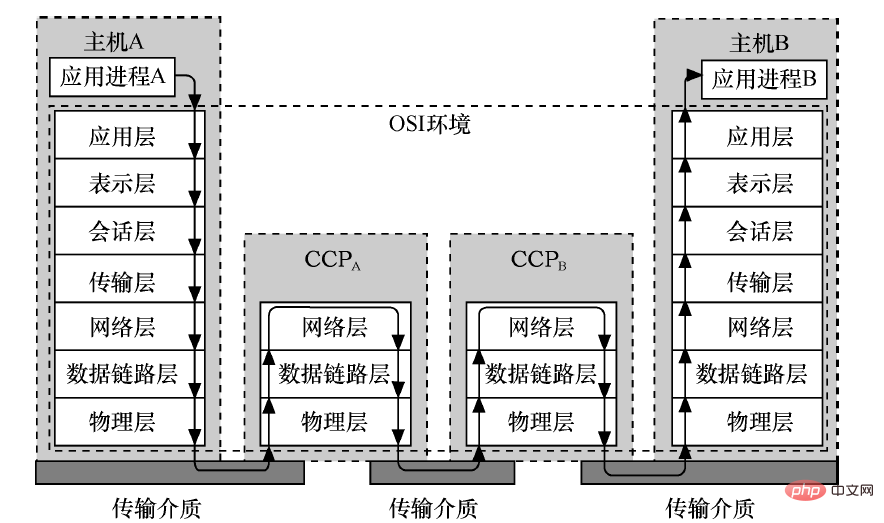
1. All data communications must be encapsulated and transmitted through physical physical lines
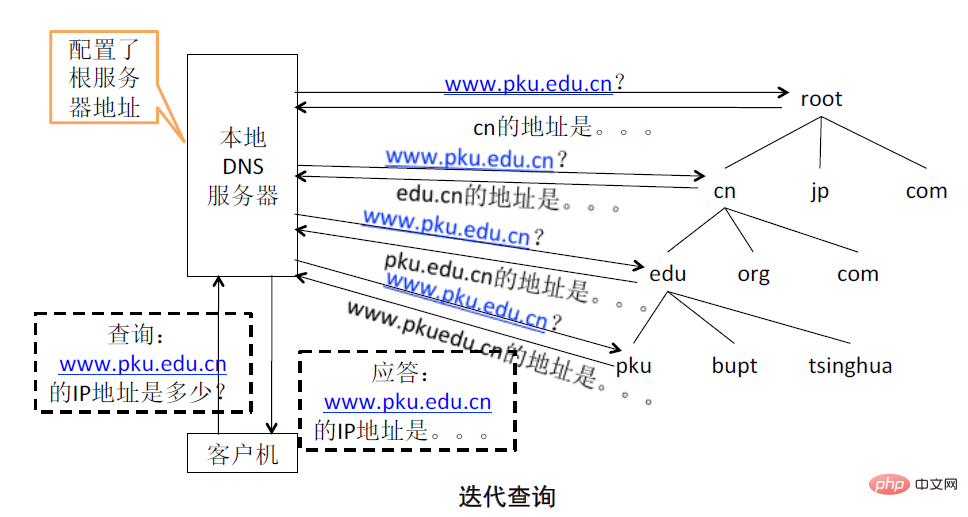
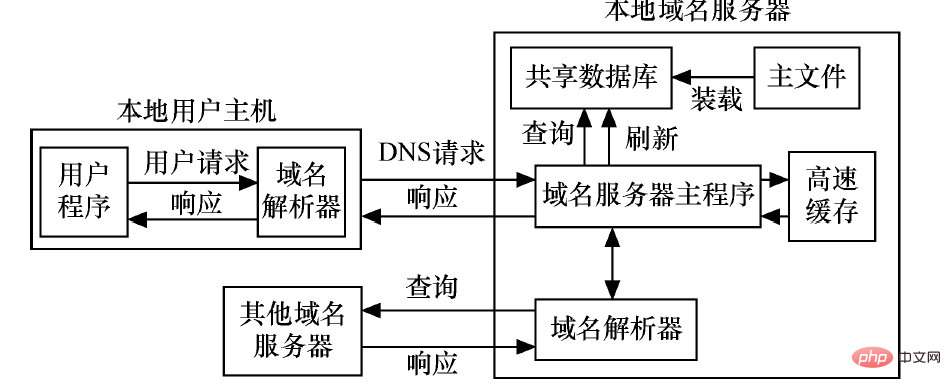
2. All host names are required Resolved to IP address
3. The application layer uses the HTTP protocol and utilizes the connection-oriented TCP protocol at the transport layer
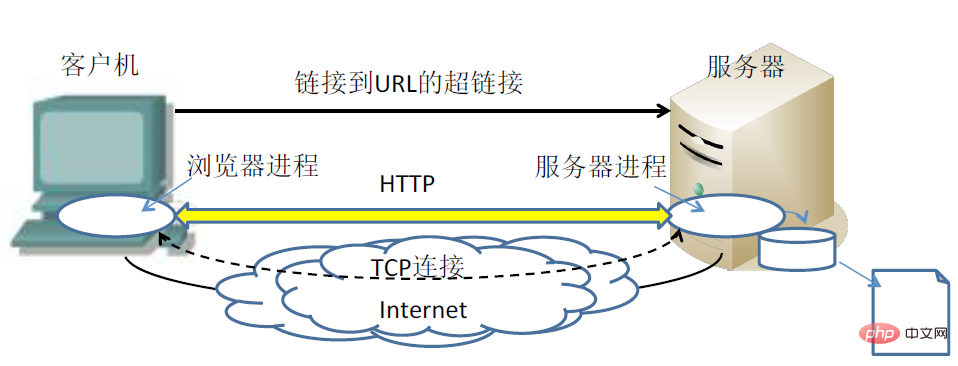
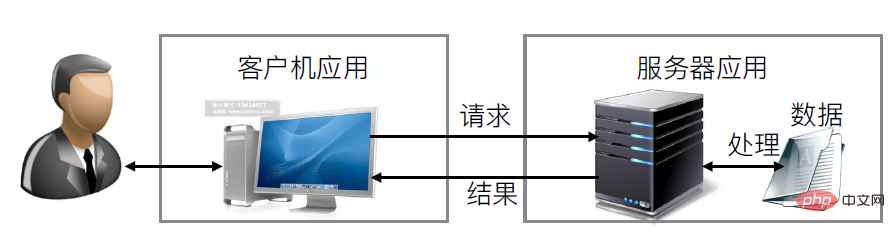
4. WEB application adopts client/server working mode
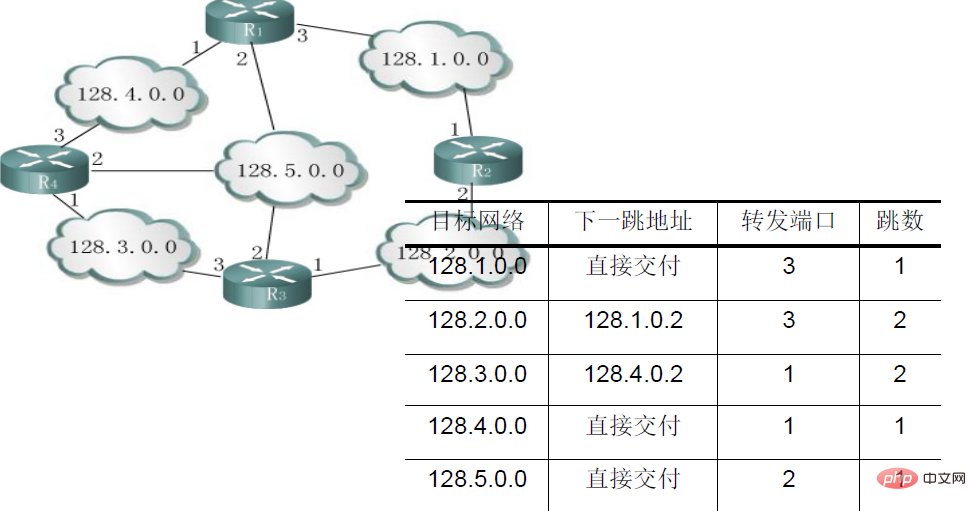
5. Data packets pass through the router , forwarding according to the routing table
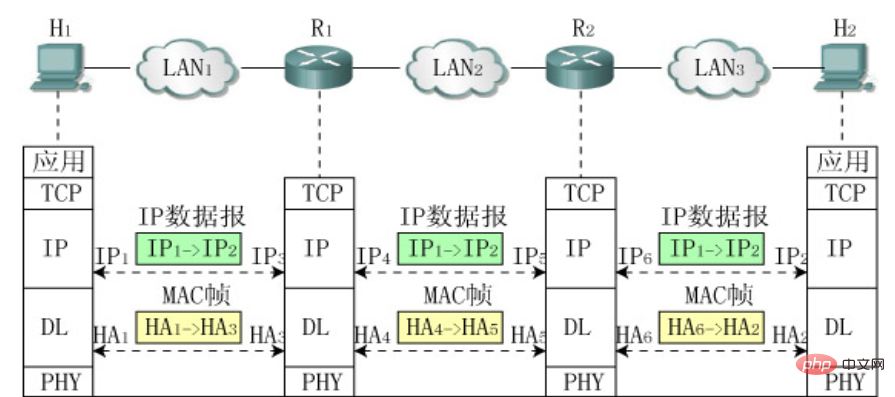
6. Within each network, the IP address must be converted into a MAC address
7. The WEB service process on the server is listening on TCP port 80
8. The server generates an HTML document and sends it to the client according to the request
9. The client browser interprets the HTML document and generates the page
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What model does the 7-layer network structure refer to?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What is star network topology?
What is star network topology?
 What are the dos commands?
What are the dos commands?
 How to buy and sell Bitcoin legally
How to buy and sell Bitcoin legally
 What are the python artificial intelligence libraries?
What are the python artificial intelligence libraries?
 What are the parameters of marquee?
What are the parameters of marquee?
 Five reasons why your computer won't turn on
Five reasons why your computer won't turn on
 How is the performance of php8?
How is the performance of php8?
 How to dress up Douyin Xiaohuoren
How to dress up Douyin Xiaohuoren
 How to uninstall phpnow
How to uninstall phpnow




