 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 The use of JavaScript computed properties and monitoring (listening) properties
The use of JavaScript computed properties and monitoring (listening) properties
The use of JavaScript computed properties and monitoring (listening) properties
This article brings you relevant knowledge about JavaScript, which mainly introduces the use of calculated properties and monitoring properties. Calculated properties refer to the final result after a series of operations. A value of , the monitor allows developers to monitor changes in data and perform specific operations based on changes in data; let’s take a look at it together, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: JavaScript video tutorial, web front-end]
Calculated properties ( computed)
Computed properties refer toAfter a series of operations, a value is finally obtained. This dynamically calculated attribute value can be used by the template structure or methods method. The case is as follows:
<div id="root">
R:<input type="text" v-model.number="r"><br>
G:<input type="text" v-model.number="g"><br>
B:<input type="text" v-model.number="b">
<div class="box" :style="{backgroundColor:rgb}">
{{rgb}}
</div>
<button @click="show">按钮</button>
</div>
<script src="/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
r:0 , g:0, b:0,
},
methods: {
show() {
console.log(this.rgb);
}
},
//所有计算属性都要定义到computed节点之下
computed: {
// 计算属性在定义的时候,要定义成“方法格式”,在这个方法中会生成好的rgb(x,x,x)的字符串
//实现了代码的复用,只要计算属性中依赖的数据变化了,则计算属性会自动重新赋值
rgb() {
return `rgb(${this.r},${this.g},${this.b})`
}
}
})
</script>
Use the name to dynamically change the calculated attribute case:
<div id="root">
<input type="text" v-model="firstname"><br>
<input type="text" v-model="lastname"><br>
全名:<span>{{fullname}}</span>
</div>
<script src="/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
firstname:'张',
lastname:'三'
},
computed:{
fullname:{
//当初次读取fullname或所依赖的数据发生变化时,get被调用
get(){
console.log('get被调用了');
return this.firstname+'-'+this.lastname
},
//当主动修改fullname时,set被调用
set(value){
console.log('set', value);
const arr = value.split('-');
this.firstname = arr[0]
this.lastname = arr[1]
}
}
}
})
</script>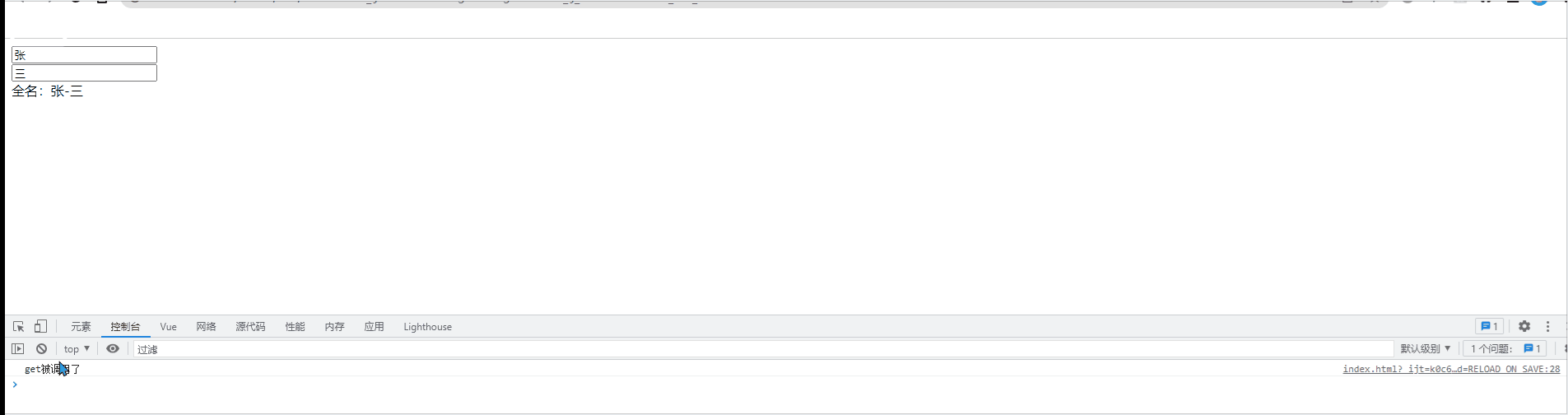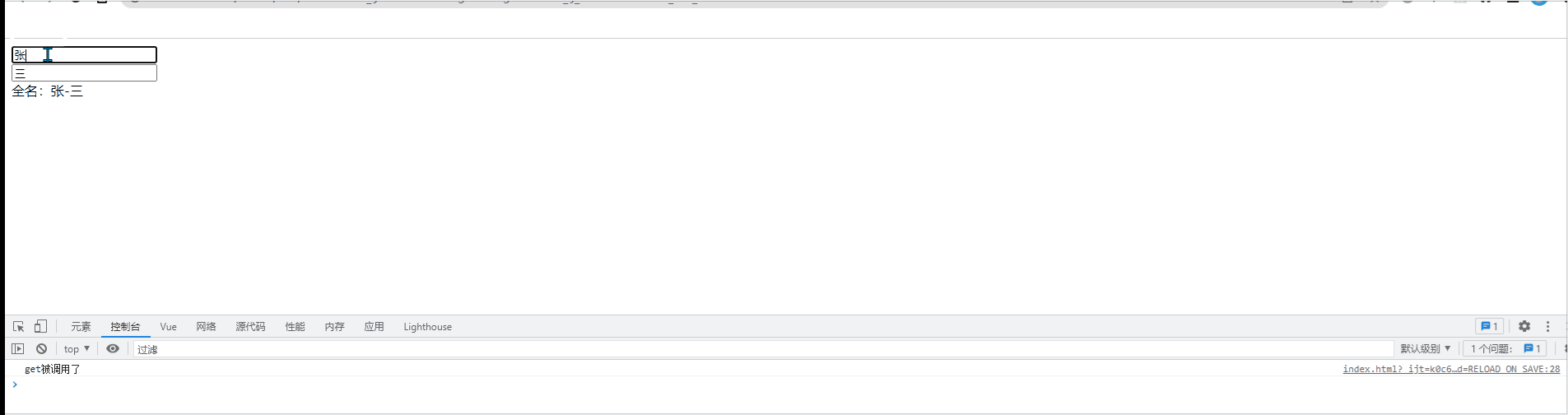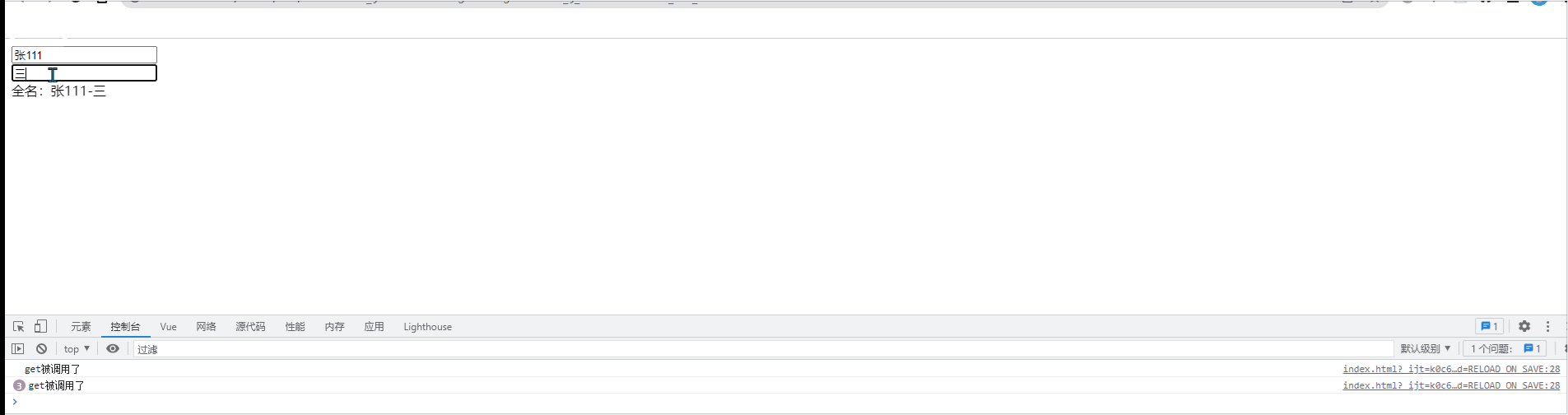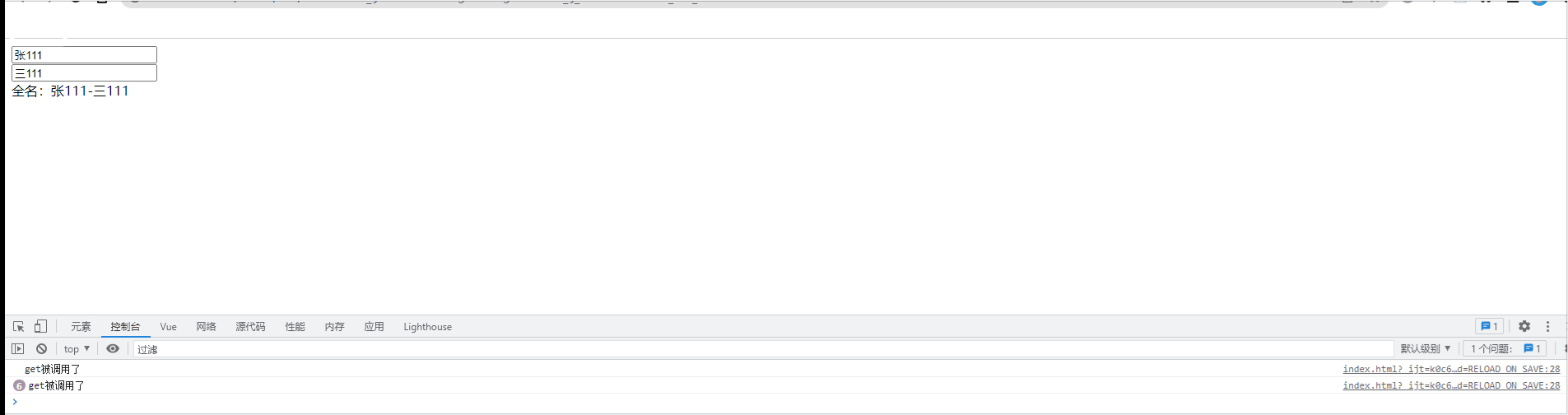
Calculated attribute:
1. Definition: The attribute to be used does not exist, and the existing attribute must be passed Properties are obtained
2. Principle: The bottom layer uses the getters and setters provided by the Object.defineproperty method
3. Advantages: Compared with methods implementation, there is an internal caching mechanism (reuse), More efficient and convenient for debugging
4. Note: The calculated attributes will eventually appear on the vm and can be directly read and used; if the calculated attributes are to be modified, the set function must be written to respond to the change, and set In order to cause the data relied upon for calculation to change.
Monitoring properties (watch)
watch monitoring (listener)Allows developers to monitor changes in data, thereby targeting data Changes do specific operations.
Two methods of monitoring
Pass in the watch configuration when passing new Vue:
<div id="root">
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:''
},
//所有的侦听器,都应该被定义到watch节点下
watch:{
// 侦听器本质上是一个函数,要监视哪个数据的变化,就把数据名作为方法名即可
//newVal是“变化后的新值”,oldVal是“变化之前旧值”
name(newVal,oldVal){ //监听name值的变化
console.log("监听到了新值"+newVal, "监听到了旧值"+oldVal);
}
}
})
</script>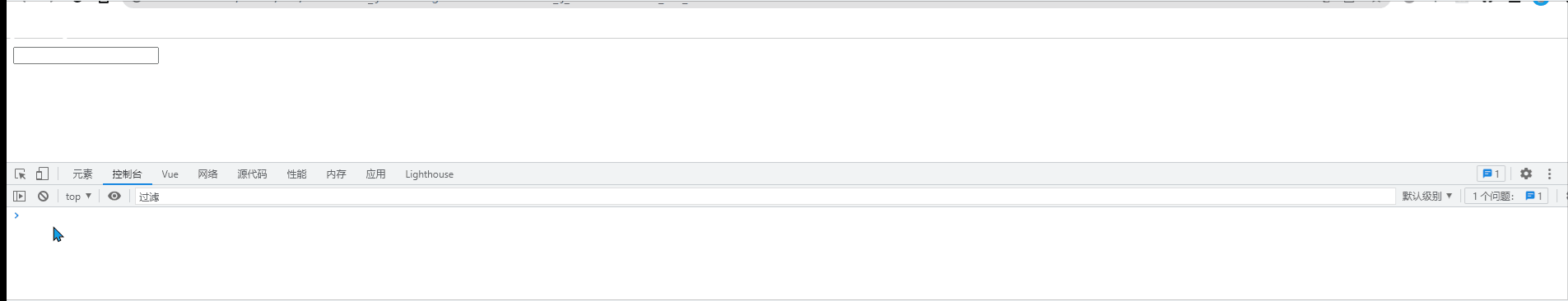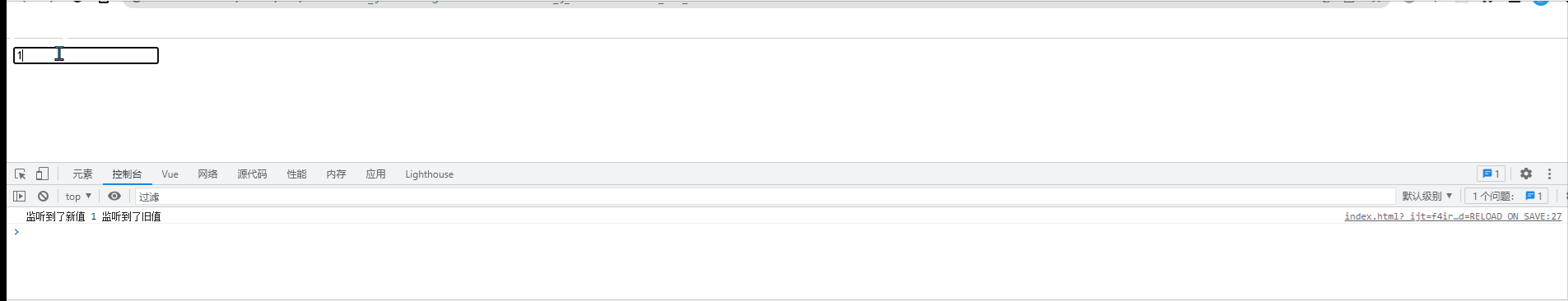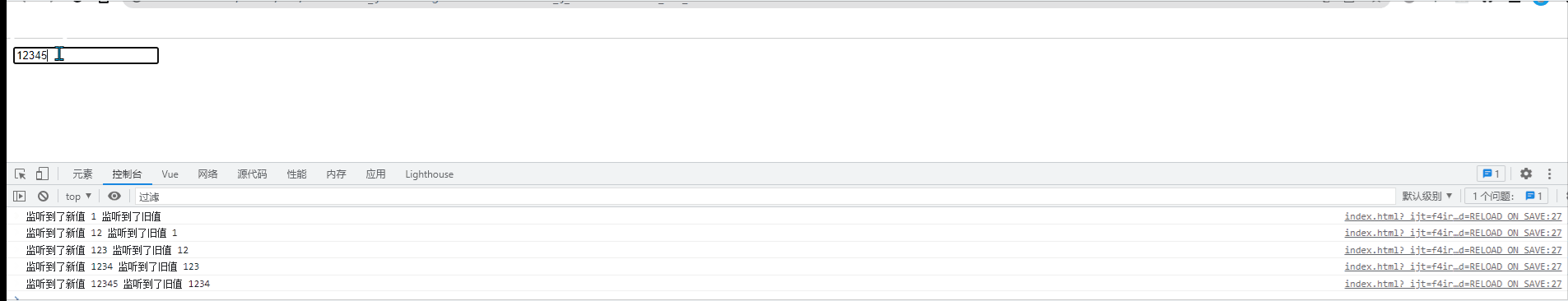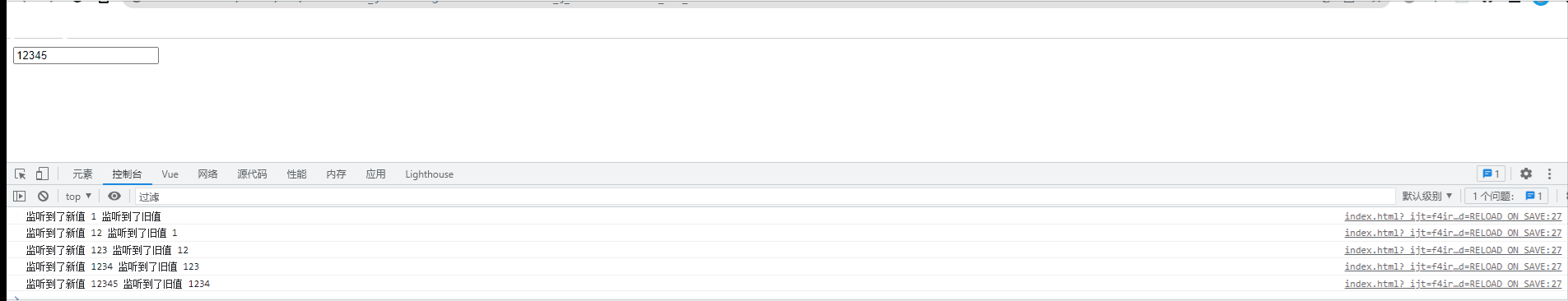
Monitoring via vm.$watch:
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
isHot:true
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods:{
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
})
vm.$watch('info',{
handler(newVal,oldVal){
console.log('天气被修改了', newVal, oldVal);
}
})
</script>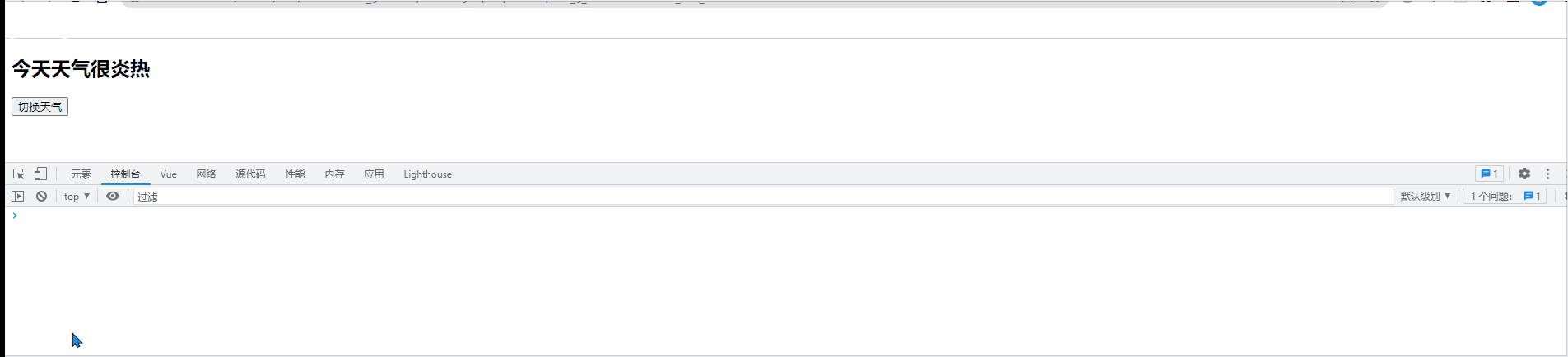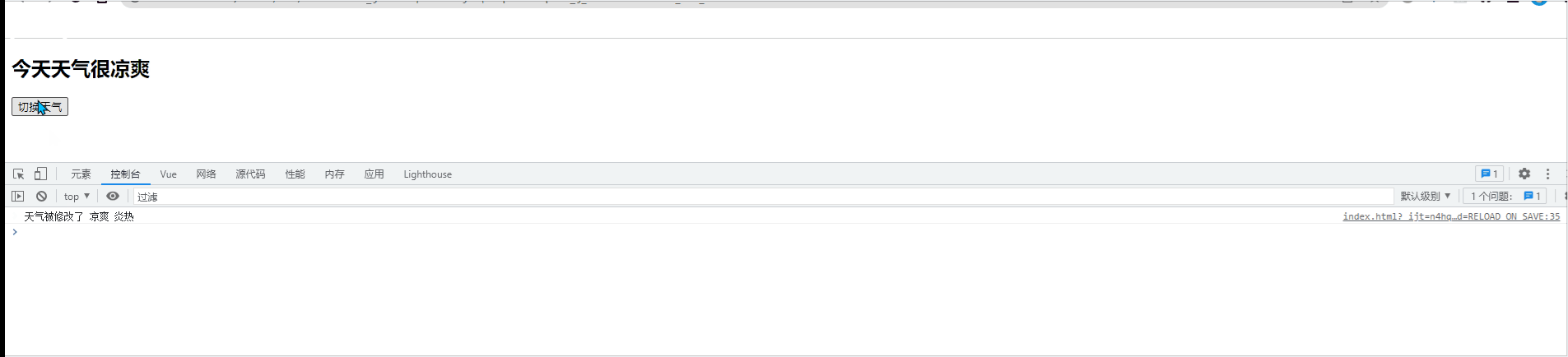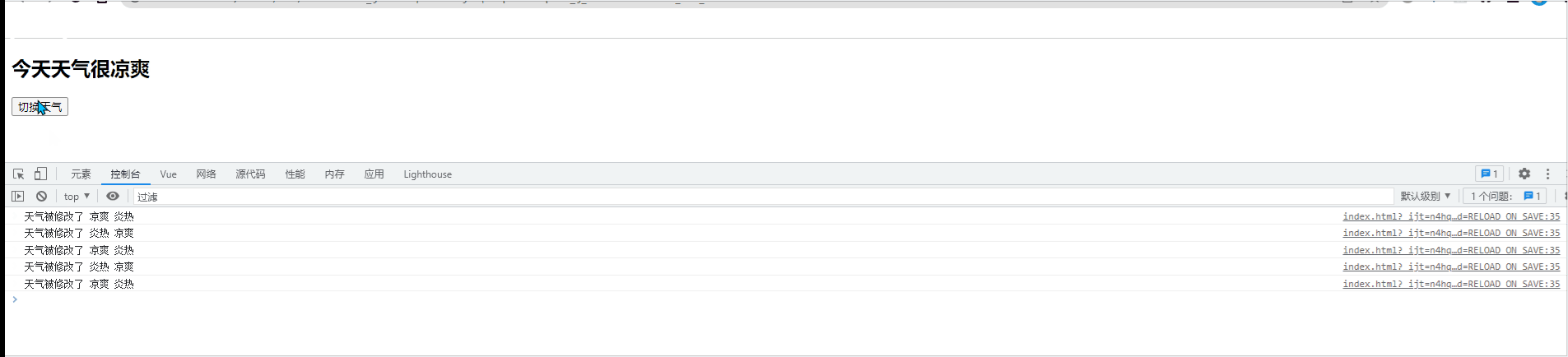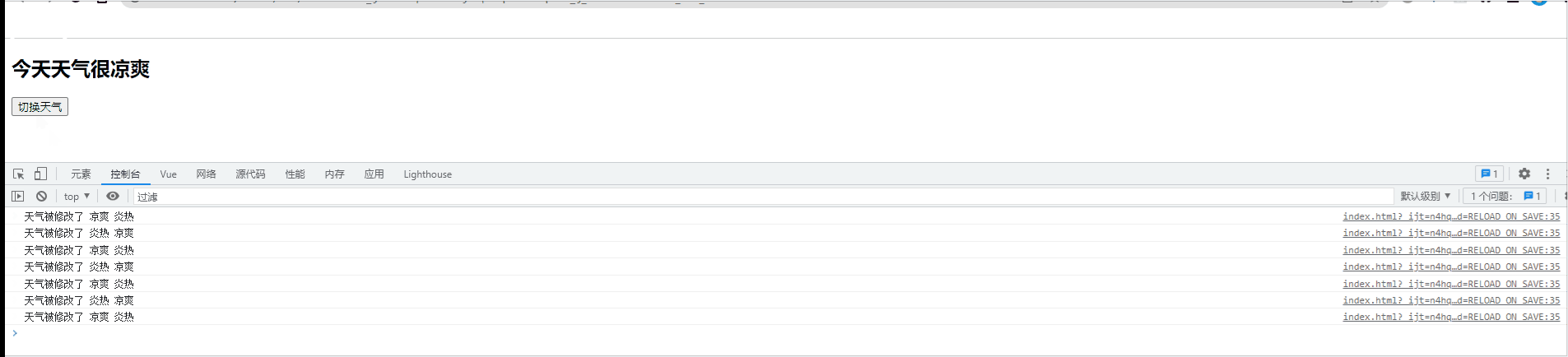
##immediate option
by default , the component will not call the watch listener after the initial loading. If you want the watch listener to be called immediately, you need to use the immediate option. The function of immediate is to control whether the listeneris automatically triggered once. , the default value of the option is: false
<div id="root">
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'admin'
},
watch:{
//定义对象格式的侦听器
name:{
handler(newVal,oldVal){
console.log(newVal, oldVal);
},
immediate:true
}
}
})
</script>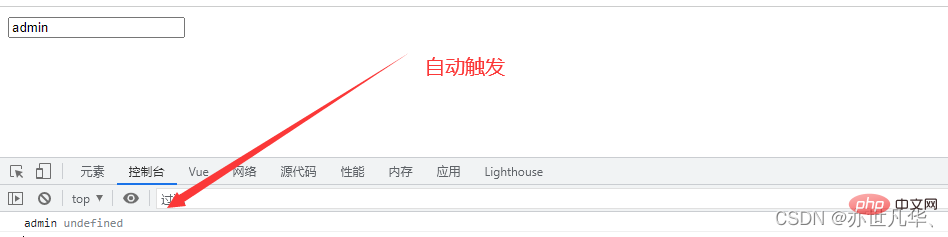
Deep monitoring
If the watch is listening An object cannot be monitored if the property value in the object changes. At this time, you need to use the deep option to enable deep monitoring. As long as any attribute in the object changes, the "object listener" will be triggered.<div id="root">
<input type="text" v-model="info.name">
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
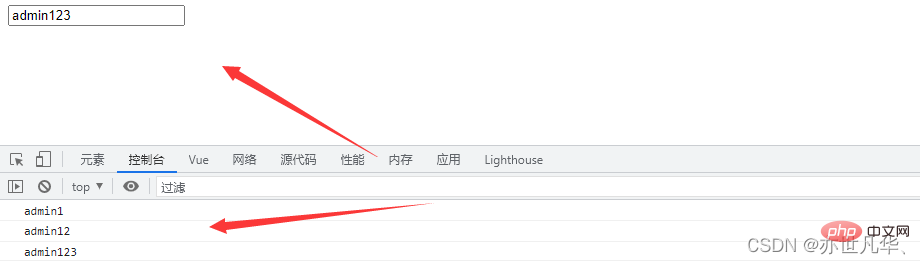
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
info:{
name:'admin'
}
},
watch:{
info: {
handler(newVal){
console.log(newVal);
},
//开启深度监听
deep:true
}
}
})
</script>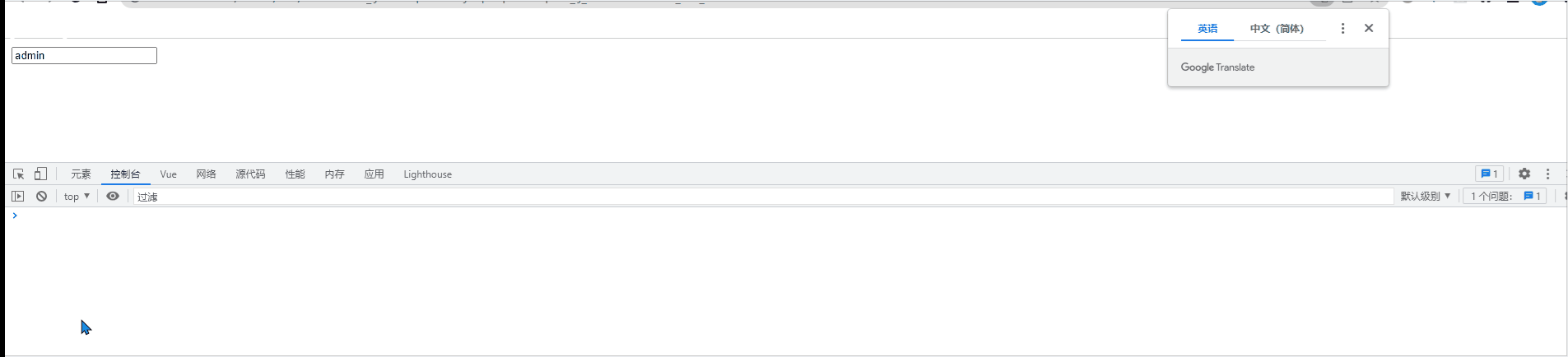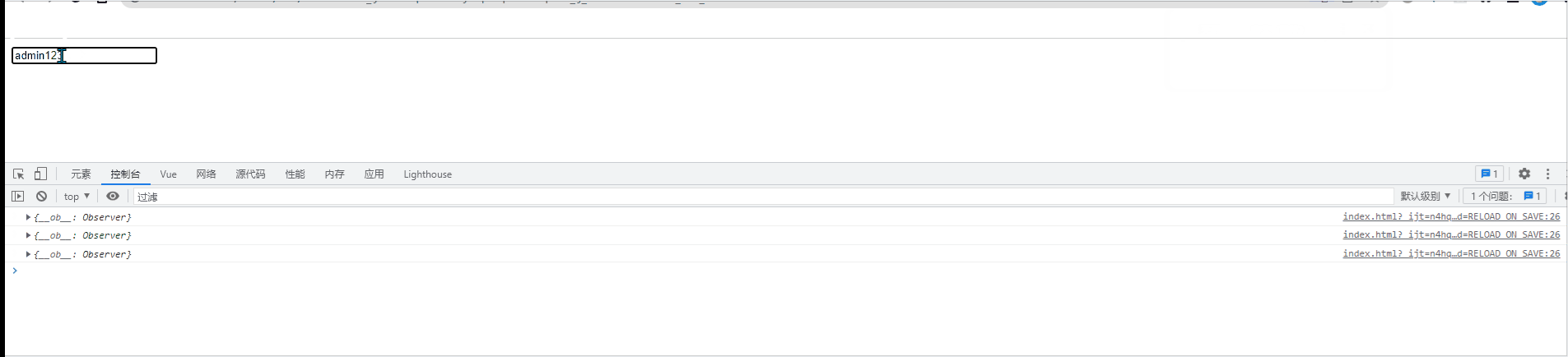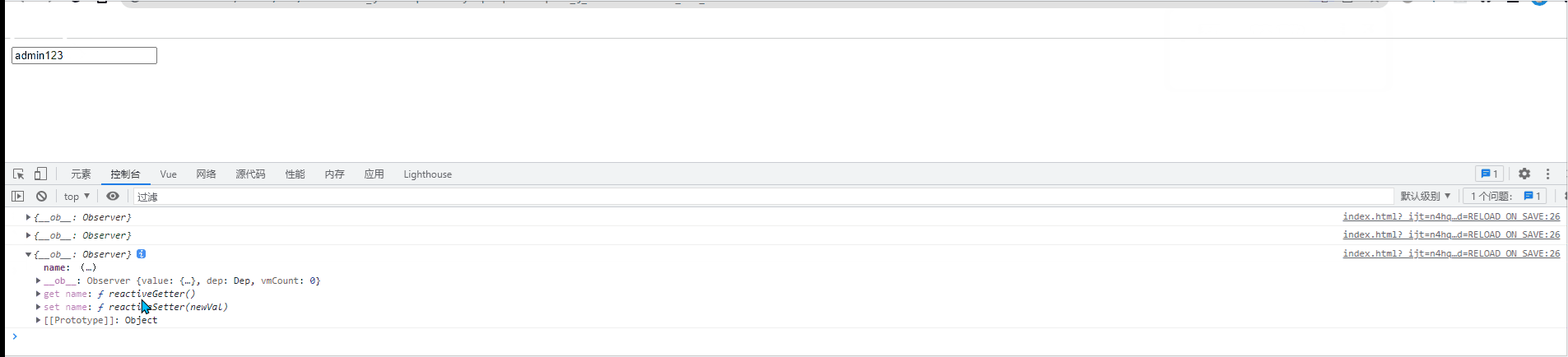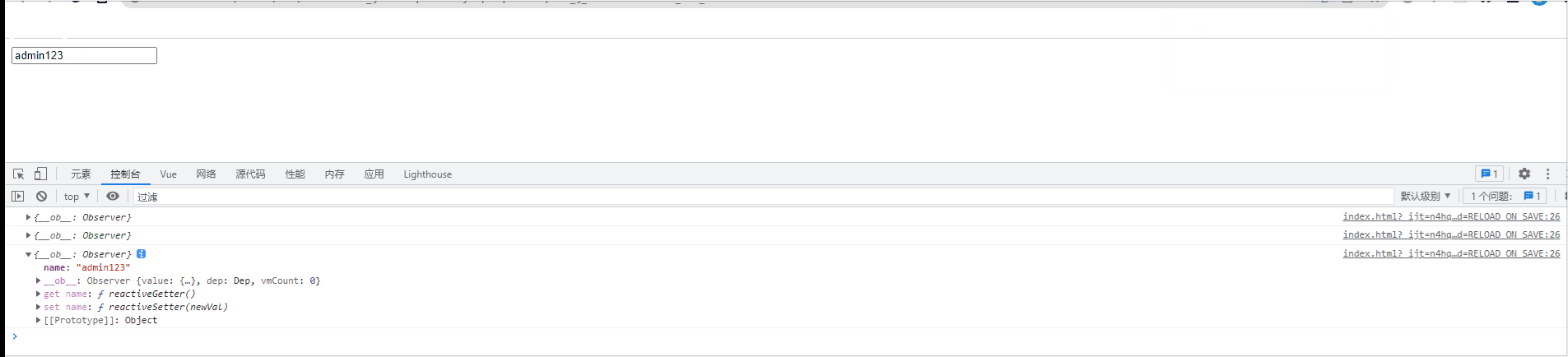
watch:{
"info.name"(newVal){
console.log(newVal);
}
}
Summary:
1) The watch in Vue does not monitor changes in the internal value of the object by default (one layer )2) Configure deep:true to monitor changes in the internal value of the object (multi-layer)3) Vue itself can monitor changes in the internal value of the object, but the watch provided by Vue cannot by default4) When using watch, decide whether to use in-depth monitoring based on the specific structure of the data
watch can start asynchronous tasks, the case is as follows:
<div id="root">
<input type="text" v-model="firstname"><br>
<input type="text" v-model="lastname"><br>
全名:<span>{{fullname}}</span>
</div>
<script src="/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
firstname:'张',
lastname:'三',
fullname:'张-三'
},
//watch能开启异步任务
watch:{
firstname(val){
setTimeout(()=>{
this.fullname = val + '-' + this.lastname
},1000)
},
lastname(val){
this.fullname = this.firstname+'-'+val
}
}
})
</script>
The difference between computed and watch:
1.Watch can complete all the functions that computed can complete. 2. The functions that watch can complete may not be completed by computed. For example: watch can perform asynchronous operations.Implicit principles:
1. Functions managed by Vue are best written as ordinary functions, so that this points to the vm or component instance object2. Functions that are not managed by Vue (timer callback function, ajax callback function, Promise callback function) are best written as arrow functions, so that this points to the vm or component instance object.
[Related recommendations: JavaScript video tutorial, web front-end development]
The above is the detailed content of The use of JavaScript computed properties and monitoring (listening) properties. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).





