 PHP Framework
PHP Framework
 Workerman
Workerman
 A brief analysis of how to use workerman in thinkphp6 [tutorial sharing]
A brief analysis of how to use workerman in thinkphp6 [tutorial sharing]
A brief analysis of how to use workerman in thinkphp6 [tutorial sharing]
thinkphp6中怎么使用workerman?下面本篇文章给大家介绍一下thinkphp6整合workerman的教程,希望对大家有所帮助。
![A brief analysis of how to use workerman in thinkphp6 [tutorial sharing]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/024/6391d85f50fad817.jpg)
thinkphp6整合workerman教程
thinkphp6安装workerman命令:
composer require topthink/think-worker
第一步,创建一个自定义命令类文件,运行指令。【相关推荐:《workerman教程》】
php think make:command Spider spider
会生成一个app\command\Spider命令行指令类,我们修改内容如下:
<?php
namespace app\command;
// tp指令特性使用的功能
use think\console\Command;
use think\console\Input;
use think\console\input\Argument;
use think\console\Output;
// 引用项目的基类,该类继承自worker
use app\server\controller\Start;
/**
* 指令类
* 在此定义指令
* 再次启动多个控制器
* @var mixed
*/
class Spider extends Command
{
/**
* 注册模块名称
* 使用命令会启动该模块控制器
* @var mixed
*/
public $model_name = 'server';
/**
* 注册控制器名称
* 使用命令启动相关控制器
* @var mixed
*/
public $controller_names = ['WebhookTimer'];
/**
* configure
* tp框架自定义指令特性
* 注册命令参数
* @return mixed
*/
protected function configure()
{
$this->setName('spider')
->addArgument('status', Argument::OPTIONAL, "status")
->addArgument('controller_name', Argument::OPTIONAL, "controller_name/controller_name")
->addArgument('mode', Argument::OPTIONAL, "d")
->setDescription('spider control');
/**
* 以上设置命令格式为:php think spider [status] [controller_name/controller_name] [d]
* think 为thinkphp框架入口文件
* spider 为在框架中注册的命令,上面setName设置的
* staus 为workerman框架接受的命令
* controller_name/controller_name 为控制器名称,以正斜线分割,执行制定控制器,为空或缺省则启动所有控制器,控制器列表在controller_name属性中注册
* d 最后一个参数为wokerman支持的-d-g参数,但是不用加-,直接使用d或者g
* php think spider start collect/SendMsg
*/
}
/**
* execute
* tp框架自定义指令特性
* 执行命令后的逻辑
* @param mixed $input
* @param mixed $output
* @return mixed
*/
protected function execute(Input $input, Output $output)
{
//获得status参数,即think自定义指令中的第一个参数,缺省报错
$status = $input->getArgument('status');
if(!$status){
$output->writeln('pelase input control command , like start');
exit;
}
//获得控制器名称
$controller_str = $input->getArgument('controller_name');
//获得模式,d为wokerman的后台模式(生产环境)
$mode = $input->getArgument('mode');
//分析控制器参数,如果缺省或为all,那么运行所有注册的控制器
$controller_list = $this->controller_names;
if($controller_str != '' && $controller_str != 'all' )
{
$controller_list = explode('/',$controller_str);
}
//重写mode参数,改为wokerman接受的参数
if($mode == 'd'){
$mode = '-d';
}
if($mode == 'g'){
$mode = '-g';
}
//将wokerman需要的参数传入到其parseCommand方法中,此方法在start类中重写
Start::$argvs = [
'think',
$status,
$mode
];
$output->writeln('start running spider');
$programs_ob_list = [];
//实例化需要运行的控制器
foreach ($controller_list as $c_key => $controller_name) {
$class_name = 'app\\'.$this->model_name.'\controller\\'.$controller_name;
$programs_ob_list[] = new $class_name();
}
//将控制器的相关回调参数传到workerman中
foreach (['onWorkerStart', 'onConnect', 'onMessage', 'onClose', 'onError', 'onBufferFull', 'onBufferDrain', 'onWorkerStop', 'onWorkerReload'] as $event) {
foreach ($programs_ob_list as $p_key => $program_ob) {
if (method_exists($program_ob, $event)) {
$programs_ob_list[$p_key]->$event = [$program_ob,$event];
}
}
}
Start::runAll();
}
}例如我们创建一个定时器的命令app\server\controller创建WebhookTimer.php
<?php
namespace app\server\controller;
use Workerman\Worker;
use \Workerman\Lib\Timer;
use think\facade\Cache;
use think\facade\Db;
use think\Request;
class WebhookTimer extends Start
{
public $host = '0.0.0.0';
public $port = '9527';
public $name = 'webhook';
public $count = 1;
public function onWorkerStart($worker)
{
Timer::add(2, array($this, 'webhooks'), array(), true);
}
public function onConnect()
{
}
public function onMessage($ws_connection, $message)
{
}
public function onClose()
{
}
public function webhooks()
{
echo 11;
}
}执行start命令行
php think spider start
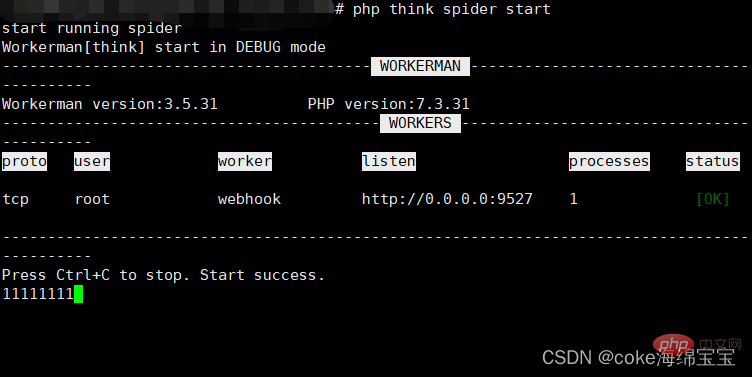
执行stop命令
php think spider stop
执行全部进程命令
php think spider start all d
在app\command\Spider.php文件
public $controller_names = ['WebhookTimer','其他方法','其他方法'];
其他方法 就是app\server\controller下创建的其他类文件方法
完结
Start.php文件
<?php
namespace app\server\controller;
use Workerman\Worker;
class Start extends Worker
{
public static $argvs = [];
public static $workerHost;
public $socket = '';
public $protocol = 'http';
public $host = '0.0.0.0';
public $port = '2346';
public $context = [];
public function __construct()
{
self::$workerHost = parent::__construct($this->socket ?: $this->protocol . '://' . $this->host . ':' . $this->port, $this->context);
}
/**
* parseCommand
* 重写wokerman的解析命令方法
* @return mixed
*/
public static function parseCommand()
{
if (static::$_OS !== OS_TYPE_LINUX) {
return;
}
// static::$argvs;
// Check static::$argvs;
$start_file = static::$argvs[0];
$available_commands = array(
'start',
'stop',
'restart',
'reload',
'status',
'connections',
);
$usage = "Usage: php yourfile <command> [mode]\nCommands: \nstart\t\tStart worker in DEBUG mode.\n\t\tUse mode -d to start in DAEMON mode.\nstop\t\tStop worker.\n\t\tUse mode -g to stop gracefully.\nrestart\t\tRestart workers.\n\t\tUse mode -d to start in DAEMON mode.\n\t\tUse mode -g to stop gracefully.\nreload\t\tReload codes.\n\t\tUse mode -g to reload gracefully.\nstatus\t\tGet worker status.\n\t\tUse mode -d to show live status.\nconnections\tGet worker connections.\n";
if (!isset(static::$argvs[1]) || !in_array(static::$argvs[1], $available_commands)) {
if (isset(static::$argvs[1])) {
static::safeEcho('Unknown command: ' . static::$argvs[1] . "\n");
}
exit($usage);
}
// Get command.
$command = trim(static::$argvs[1]);
$command2 = isset(static::$argvs[2]) ? static::$argvs[2] : '';
// Start command.
$mode = '';
if ($command === 'start') {
if ($command2 === '-d' || static::$daemonize) {
$mode = 'in DAEMON mode';
} else {
$mode = 'in DEBUG mode';
}
}
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] $command $mode");
// Get master process PID.
$master_pid = is_file(static::$pidFile) ? file_get_contents(static::$pidFile) : 0;
$master_is_alive = $master_pid && posix_kill($master_pid, 0) && posix_getpid() != $master_pid;
// Master is still alive?
if ($master_is_alive) {
if ($command === 'start') {
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] already running");
exit;
}
} elseif ($command !== 'start' && $command !== 'restart') {
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] not run");
exit;
}
// execute command.
switch ($command) {
case 'start':
if ($command2 === '-d') {
static::$daemonize = true;
}
break;
case 'status':
while (1) {
if (is_file(static::$_statisticsFile)) {
@unlink(static::$_statisticsFile);
}
// Master process will send SIGUSR2 signal to all child processes.
posix_kill($master_pid, SIGUSR2);
// Sleep 1 second.
sleep(1);
// Clear terminal.
if ($command2 === '-d') {
static::safeEcho("\33[H\33[2J\33(B\33[m", true);
}
// Echo status data.
static::safeEcho(static::formatStatusData());
if ($command2 !== '-d') {
exit(0);
}
static::safeEcho("\nPress Ctrl+C to quit.\n\n");
}
exit(0);
case 'connections':
if (is_file(static::$_statisticsFile) && is_writable(static::$_statisticsFile)) {
unlink(static::$_statisticsFile);
}
// Master process will send SIGIO signal to all child processes.
posix_kill($master_pid, SIGIO);
// Waiting amoment.
usleep(500000);
// Display statisitcs data from a disk file.
if(is_readable(static::$_statisticsFile)) {
readfile(static::$_statisticsFile);
}
exit(0);
case 'restart':
case 'stop':
if ($command2 === '-g') {
static::$_gracefulStop = true;
$sig = SIGTERM;
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] is gracefully stopping ...");
} else {
static::$_gracefulStop = false;
$sig = SIGINT;
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] is stopping ...");
}
// Send stop signal to master process.
$master_pid && posix_kill($master_pid, $sig);
// Timeout.
$timeout = 5;
$start_time = time();
// Check master process is still alive?
while (1) {
$master_is_alive = $master_pid && posix_kill($master_pid, 0);
if ($master_is_alive) {
// Timeout?
if (!static::$_gracefulStop && time() - $start_time >= $timeout) {
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] stop fail");
exit;
}
// Waiting amoment.
usleep(10000);
continue;
}
// Stop success.
static::log("Workerman[$start_file] stop success");
if ($command === 'stop') {
exit(0);
}
if ($command2 === '-d') {
static::$daemonize = true;
}
break;
}
break;
case 'reload':
if($command2 === '-g'){
$sig = SIGQUIT;
}else{
$sig = SIGUSR1;
}
posix_kill($master_pid, $sig);
exit;
default :
if (isset($command)) {
static::safeEcho('Unknown command: ' . $command . "\n");
}
exit($usage);
}
}
}更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程教学!!
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of how to use workerman in thinkphp6 [tutorial sharing]. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to run thinkphp project
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
How to run thinkphp project
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
To run the ThinkPHP project, you need to: install Composer; use Composer to create the project; enter the project directory and execute php bin/console serve; visit http://localhost:8000 to view the welcome page.
 Implement file upload and download in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Implement file upload and download in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
To implement file upload and download in Workerman documents, specific code examples are required. Introduction: Workerman is a high-performance PHP asynchronous network communication framework that is simple, efficient, and easy to use. In actual development, file uploading and downloading are common functional requirements. This article will introduce how to use the Workerman framework to implement file uploading and downloading, and give specific code examples. 1. File upload: File upload refers to the operation of transferring files on the local computer to the server. The following is used
 There are several versions of thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
There are several versions of thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
ThinkPHP has multiple versions designed for different PHP versions. Major versions include 3.2, 5.0, 5.1, and 6.0, while minor versions are used to fix bugs and provide new features. The latest stable version is ThinkPHP 6.0.16. When choosing a version, consider the PHP version, feature requirements, and community support. It is recommended to use the latest stable version for best performance and support.
 How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Steps to run ThinkPHP Framework locally: Download and unzip ThinkPHP Framework to a local directory. Create a virtual host (optional) pointing to the ThinkPHP root directory. Configure database connection parameters. Start the web server. Initialize the ThinkPHP application. Access the ThinkPHP application URL and run it.
 Which one is better, laravel or thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Which one is better, laravel or thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Performance comparison of Laravel and ThinkPHP frameworks: ThinkPHP generally performs better than Laravel, focusing on optimization and caching. Laravel performs well, but for complex applications, ThinkPHP may be a better fit.
 Development suggestions: How to use the ThinkPHP framework to implement asynchronous tasks
Nov 22, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
Development suggestions: How to use the ThinkPHP framework to implement asynchronous tasks
Nov 22, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
"Development Suggestions: How to Use the ThinkPHP Framework to Implement Asynchronous Tasks" With the rapid development of Internet technology, Web applications have increasingly higher requirements for handling a large number of concurrent requests and complex business logic. In order to improve system performance and user experience, developers often consider using asynchronous tasks to perform some time-consuming operations, such as sending emails, processing file uploads, generating reports, etc. In the field of PHP, the ThinkPHP framework, as a popular development framework, provides some convenient ways to implement asynchronous tasks.
 How to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:46 AM
How to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:46 AM
Introduction to how to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents: Workerman is a high-performance PHP development framework that can help developers easily build high-concurrency network applications. This article will introduce the basic usage of Workerman, including installation and configuration, creating services and listening ports, handling client requests, etc. And give corresponding code examples. 1. Install and configure Workerman. Enter the following command on the command line to install Workerman: c
 Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Swoole and Workerman are both high-performance PHP server frameworks. Known for its asynchronous processing, excellent performance, and scalability, Swoole is suitable for projects that need to handle a large number of concurrent requests and high throughput. Workerman offers the flexibility of both asynchronous and synchronous modes, with an intuitive API that is better suited for ease of use and projects that handle lower concurrency volumes.



