There are several ways to register vue custom components.
There are three ways to register vue custom components: 1. Partial registration, register the custom component in the components of the App. 2. Global registration, register (mount) custom components in "main.js". 3. Create a folder with the same name as the component in the "src/plugin" directory, then place the custom component file in this directory, and then create another "index.js" file in this directory. Write the registration code in the file to register the custom component as a plug-in.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue3 version, DELL G3 computer.
Create project
Execute the following example command through cmd to initialize our Vue project
vue create helloworld cd helloworld code . npm run serve
After the command is executed, the project structure is as shown below :
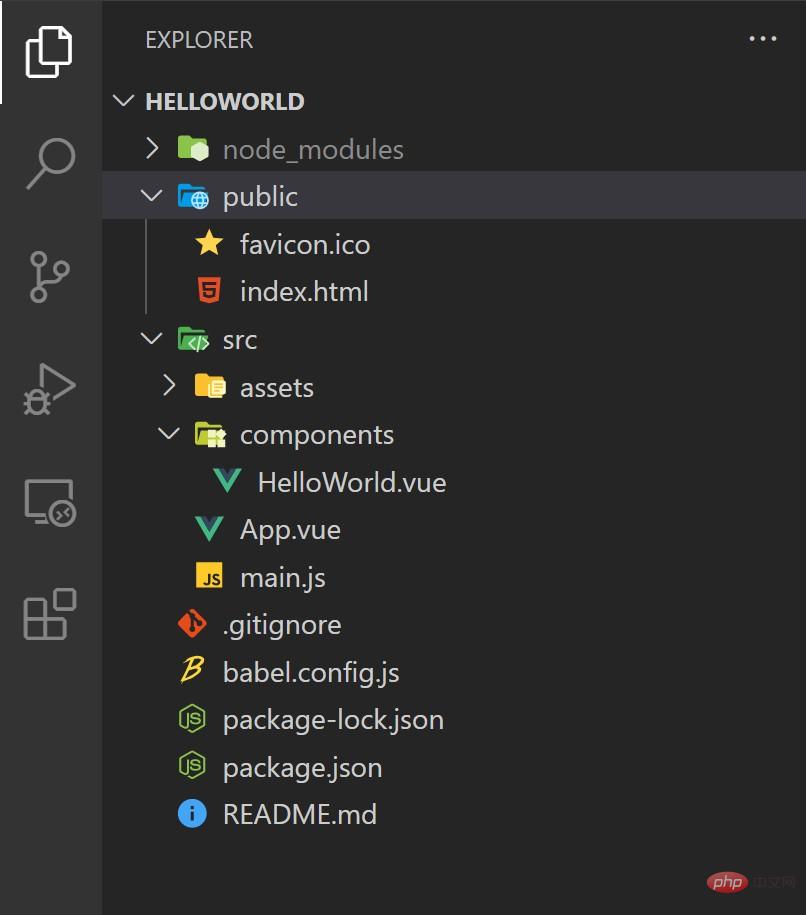
Next, we create a custom component splash.vue in the src/components directory. The sample code is as follows Shown:
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ title }}</p>
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "splash",
props:['title'],
data: function () {
return {
message: "组件启动中...",
};
},
};
</script>Registered as a local component
We know that vue will automatically create a project for us through Vue-CLI The root component of App.vue is used to host the entire application. If we register our custom component in App's components, then it is also considered a local component and can only be applied Within a component like App. The registration method is as follows:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="./assets/logo.png" class="lazy" alt="Vue logo" />
<!-- 3.应用自定义组件 -->
<splash title="hello world"></splash>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1.导入组件
import Splash from "./components/Splash.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
// 2.注册局部组件
Splash,
},
};
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>Execute npm run serve, and the following effect will appear:
Register as a global component
If we want to register our component as a global component so that all other components can use it, we need to register our component as a global component. Similarly, we need to register our global component in 'main.js', the sample code is as follows:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1. 导入自定义组件
import Splash from './components/Splash.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 2. 将自定义组件注册成全局组件
Vue.component(Splash.name, Splash)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')ModifyHelloWorld.vue, use the global component registered above, The sample code is as follows:
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1 id="nbsp-msg-nbsp">{{ msg }}</h1>
<!-- 应用自定义组件 -->
<splash></splash>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "HelloWorld",
props: {
msg: String,
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.hello {
border: 1px dashed #00f;
}
</style>Modify App.vue and use the global component registered above. The sample code is as follows:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="./assets/logo.png" class="lazy" alt="Vue logo" />
<splash></splash>
<hello-world msg="我是子组件"></hello-world>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from "./components/HelloWorld.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
HelloWorld,
},
};
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>Execute npm run serve, the following effect will appear:

Register as plug-in
Because plug-ins are more flexible , so we can register custom components as global components. According to Vue's convention, we need to adjust our project structure.
Create a folder with the same name as the component in the src/plugin directory, then put the splash.vue file we defined above into this directory, and then create it under this directory A index.js file, by writing the registration code in this file, register our custom component as a plug-in. The sample code is as follows:
import Splash from './Splash'
export default {
install: function (Vue, options) {
// 1.获取构造函数
const contructor = Vue.extend(Splash)
// 2. 实例化组件对象
const instance = new contructor()
// 3. 创建页面元素
const oDiv = document.createElement('div')
document.body.appendChild(oDiv)
// 4. 将组件挂载到页面元素上
instance.$mount(oDiv)
if (options !== null && options.title !== undefined) {
instance.title = options.title
}
// 添加全局方法
Vue.ToggleSplash = function () {
instance.isShow = !instance.isShow;
}
// 添加实例方法
Vue.prototype.$ToggleSplash = function () {
instance.isShow = !instance.isShow;
}
}
}Modify main.js, the sample code is as follows:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1. 导入自定义组件
import Splash from './plugin/splash/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 2. 将自定义组件注册成组件
Vue.use(Splash, { title: 'hello world' })
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')Next, we can call Vue in any component The global method or instance method of the object is used to control our custom components. For example, we can use it in hello-world like this:
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1 id="nbsp-msg-nbsp">{{ msg }}</h1>
<button @click="toggle1">使用全局方法控制显示或隐藏插件</button>
<button @click="toggle2">使用实例方法控制显示或隐藏插件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from "vue";
export default {
name: "HelloWorld",
props: {
msg: String,
},
methods: {
toggle1: function () {
// 通过全局方法来访问自定义组件
Vue.ToggleSplash();
},
toggle2: function () {
// 通过实例方法来访问自定义组件
this.$ToggleSplash();
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.hello {
border: 1px dashed #00f;
}
</style>Execute npm run serve, The following effect will appear:

[Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial, web front-end development]
The above is the detailed content of There are several ways to register vue custom components.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.





