What is the meaning of goto statement in c language
In C language, the goto statement is called an unconditional transfer statement, which allows the control to be unconditionally transferred to a labeled statement within the same function; the syntax is "goto label;...label: statement;", where label can be any plain text except C keywords, and it can be set before or after the goto statement in the C program.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, c99 version, Dell G3 computer.
C language goto statement
The goto statement is also called an unconditional transfer statement in C. It is said to be unconditional, but in fact it is still conditional, and the jump range is still Restricted, allows unconditional transfer of control to marked statements within the same function.
Grammar
The syntax of goto statement in C language:
goto label; .. . label: statement;
Here, label can be any plain text except C keyword, It can be set before or after the goto statement in the C program.
Flowchart

Usage
First, we need to determine Well, where we want to transfer, that is, the transfer end point, we need to set an identifier, that is, label (I am not showing English, when the goto statement makes an error, this word is likely to appear in the error content), and at the same time , we need to add a colon (:) after the label. In this way, we have set the identifier, and then we set the starting point - the goto identifier;. First we have to tell the computer that we are going to jump, which is the role of goto. Then we have to tell it where we want to jump, which is the identifier we just set. Finally, like other statements, we add points to it. (;) means the end of the statement. Here's what the editor page looks like.

and the running results

It can be seen that our printf in line 5 is not executed, and it goes directly to line 7 printf.
It can jump to the next statement or jump to the front.

This way it becomes a simple loop with no end condition

You can try running this For a piece of code, of course we can use a counter and add if judgment, give it an end condition, and let it have the ability of for and while.
Unfortunately, we cannot use goto across functions. There are other statements that can be implemented, so we will not go into details here.
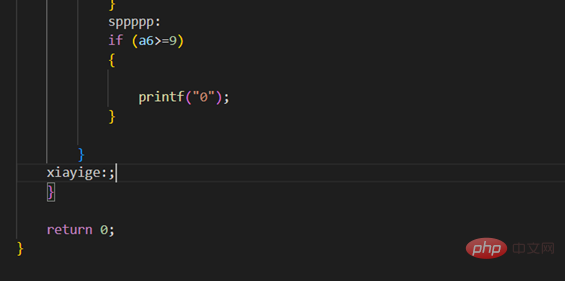
Here, if the if condition is true, after we output it, looking at the long string of uneven brackets below, I know what I want to do They set conditions there, and then break over and over again. It's annoying to think about it. How can I wait without goto at this time? Very soon! We directly goto and jump to

to proceed to the next stage of our program.
But I wonder if you noticed that in the previous picture, we used two gotos, but they pointed to the same label. Yes, we can make the program jump at different starting points. to the same end point, but it should be noted that we cannot jump to two labels under the same goto. This is easy to understand. If it were you, receiving an order asking you to go to two or even more different places, You will also be confused, where should I go?
Another difference from before is that I added a semicolon (;) after the identifier xiayige:. Why is this? The identifier must be followed by a statement, which can be an assignment or a statement. But if there is really no way to add a statement after it, we can add a semicolon and treat it as an empty statement to make the identifier run.
Ps: In fact, you can declare a garbage variable here, or other meaningless statements, but it will make the code difficult to understand, and it is not recommended to do so.
This is what everyone does most with goto. As for other uses, it depends on your imagination. As the old saying goes, how bold a person is, how productive the land is.
The following is when I use goto.
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
printf("请输入要计算的算式,四则运算优先级一样高,从左到右依次计算\n");
int jieguo=0,sz,gongju=0,gongju2=1;
char ysf;
scanf("%d",&jieguo);
if (jieguo==0)
//直接输入等号的话%d似乎是0,有待商榷!!!!!!!!
//二次修改,if语句中判断量时只有0为假,除此之外的数字都表真
{
printf("**,你算**呢\n");
goto chaojijieshu;
gongju=1;
gongju2=0;
}
else if (gongju2)
{
printf("请输入运算符\n");
scanf(" %c",&ysf);
//enter包含两个命令,算是两个字符\r和\n,后面的一个会占据scanf的输入位,所以要清空,或者用空格占位
if(ysf=='=')
printf("**,你算**呢\n");
}
loop:
while(ysf!='=')
{
if (ysf=='-')
{
printf("请输入数字\n");
scanf("%d",&sz);
jieguo-=sz;
printf("请输入运算符\n");
fflush(stdin);//清空标准输入流(stdin) fflush是stdio.h中的函数
scanf("%c",&ysf);
if(ysf=='=')
{
goto jieshu;
}
else
{
goto loop;
}
}
else if (ysf=='+')
{
printf("请输入数字\n");
scanf("%d",&sz);
jieguo+=sz;
printf("请输入运算符\n");
fflush(stdin);//清空标准输入流(stdin) fflush是stdio.h中的函数
scanf("%c",&ysf);
if(ysf=='=')
{
goto jieshu;
}
else
{
goto loop;
}
}
else if(ysf=='*')
{
printf("请输入数字\n");
scanf("%d",&sz);
jieguo*=sz;
printf("请输入运算符\n");
fflush(stdin);//清空标准输入流(stdin) fflush是stdio.h中的函数
scanf("%c",&ysf);
if(ysf=='=')
{
goto jieshu;
}
else
{
goto loop;
} }
else if(ysf=='/')
{
printf("请输入数字\n");
scanf("%d",&sz);
while(sz==0)
{
printf("0能做分母吗?你算**呢\n");
}
jieguo/=sz;
printf("请输入运算符\n");
fflush(stdin);//清空标准输入流(stdin) fflush是stdio.h中的函数
scanf("%c",&ysf);
if(ysf=='=')
{
goto jieshu;
}
else
{
goto loop;
}
}
}
jieshu:
printf("结果是%d\n",jieguo);
chaojijieshu:
if (gongju)
printf("真无语,重开吧\n");
return 0;
}
//注意注意!!!!!!!!!!!!
//enter算是两个命令,所以有两个字符,在进行上一次输入之后
//在来一个enter,会占据scanf的字符位
//所以要清空标准输入流
//可以利用下述语句
//fflush(stdin);
//清空标准输入流(stdin) fflush是stdio.h中的函数
//以上是最好的解决办法
//初次之外,还有被称作偏方的办法
//二次修改 除此之外,而不是初次之外,打错字了
//如
//scanf(“ %c”,&ysf”)
//在scanf中加一个空格,可以顶掉enter多出来的一个字符
//还有
//加一句
//getchar()
//用getchar来捕捉多出来的\n说明
在任何编程语言中,都不建议使用 goto 语句。因为它使得程序的控制流难以跟踪,使程序难以理解和难以修改。任何使用 goto 语句的程序可以改写成不需要使用 goto 语句的写法。
不推荐使用goto语句的原因:
①由于goto语句是无条件跳转指令,使用goto语句后回使得程序结构变得更加复杂,不利于以后代码维护,特别是需要交交接给被人维护的时候。
②由于目前编程采用的都是结构化编程,方便移植,而当采用goto语句后就会导致在结构化编程的项目中代码不便移植,因为如果使用goto从一个结构中跳转到另一个结构,而使得结构之间有了联系,不便移植。
③由于目前C语言等高级语言具有break、continue等语法,可以很好地代替goto,所以能不使用goto就不使用goto。
推荐使用goto的场景:
①从多重循环中直接跳出。
②出错时清除资源。
③可增加程序清晰度的情况。
使用goto函数的原则:
①使用goto语句只能goto到同一函数内,而不能从一个函数里goto到另外一个函数里。
②使用goto语句在同一函数内进行goto时,goto的起点应是函数内一段小功能的结束处,goto的目的label处应是函数内另外一段小功能的开始处,不能破坏功能的实现。
③不能从一段复杂的执行状态中的位置goto到另外一个位置,比如,从多重嵌套的循环判断中跳出去就是不允许的。
④应该避免向两个方向跳转。这样最容易导致"面条代码",即逻辑混乱。
相关推荐:《C视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What is the meaning of goto statement in c language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 C language data structure: data representation and operation of trees and graphs
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:18 AM
C language data structure: data representation and operation of trees and graphs
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:18 AM
C language data structure: The data representation of the tree and graph is a hierarchical data structure consisting of nodes. Each node contains a data element and a pointer to its child nodes. The binary tree is a special type of tree. Each node has at most two child nodes. The data represents structTreeNode{intdata;structTreeNode*left;structTreeNode*right;}; Operation creates a tree traversal tree (predecision, in-order, and later order) search tree insertion node deletes node graph is a collection of data structures, where elements are vertices, and they can be connected together through edges with right or unrighted data representing neighbors.
 The truth behind the C language file operation problem
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The truth behind the C language file operation problem
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The truth about file operation problems: file opening failed: insufficient permissions, wrong paths, and file occupied. Data writing failed: the buffer is full, the file is not writable, and the disk space is insufficient. Other FAQs: slow file traversal, incorrect text file encoding, and binary file reading errors.
 C language multithreaded programming: a beginner's guide and troubleshooting
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:15 AM
C language multithreaded programming: a beginner's guide and troubleshooting
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:15 AM
C language multithreading programming guide: Creating threads: Use the pthread_create() function to specify thread ID, properties, and thread functions. Thread synchronization: Prevent data competition through mutexes, semaphores, and conditional variables. Practical case: Use multi-threading to calculate the Fibonacci number, assign tasks to multiple threads and synchronize the results. Troubleshooting: Solve problems such as program crashes, thread stop responses, and performance bottlenecks.
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 C language data structure: the key role of data structures in artificial intelligence
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:45 AM
C language data structure: the key role of data structures in artificial intelligence
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:45 AM
C Language Data Structure: Overview of the Key Role of Data Structure in Artificial Intelligence In the field of artificial intelligence, data structures are crucial to processing large amounts of data. Data structures provide an effective way to organize and manage data, optimize algorithms and improve program efficiency. Common data structures Commonly used data structures in C language include: arrays: a set of consecutively stored data items with the same type. Structure: A data type that organizes different types of data together and gives them a name. Linked List: A linear data structure in which data items are connected together by pointers. Stack: Data structure that follows the last-in first-out (LIFO) principle. Queue: Data structure that follows the first-in first-out (FIFO) principle. Practical case: Adjacent table in graph theory is artificial intelligence
 Troubleshooting tips for processing files in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Troubleshooting tips for processing files in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Troubleshooting Tips for C language processing files When processing files in C language, you may encounter various problems. The following are common problems and corresponding solutions: Problem 1: Cannot open the file code: FILE*fp=fopen("myfile.txt","r");if(fp==NULL){//File opening failed} Reason: File path error File does not exist without file read permission Solution: Check the file path to ensure that the file has check file permission problem 2: File reading failed code: charbuffer[100];size_tread_bytes=fread(buffer,1,siz
 The concept of c language functions and their definition format
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
The concept of c language functions and their definition format
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
C language functions are reusable code blocks, receive parameters for processing, and return results. It is similar to the Swiss Army Knife, powerful and requires careful use. Functions include elements such as defining formats, parameters, return values, and function bodies. Advanced usage includes function pointers, recursive functions, and callback functions. Common errors are type mismatch and forgetting to declare prototypes. Debugging skills include printing variables and using a debugger. Performance optimization uses inline functions. Function design should follow the principle of single responsibility. Proficiency in C language functions can significantly improve programming efficiency and code quality.




