This article will take you to learn more about Vue scaffolding
This article will introduce you to vue scaffolding, talk about how to initialize Vue scaffolding, introduce ref and props, mixin (mixing), etc. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

1. Initialize Vue scaffolding
1. Description
Generally choose the latest version of scaffolding
2. Specific steps
- ##Global installation of vue/cli scaffolding
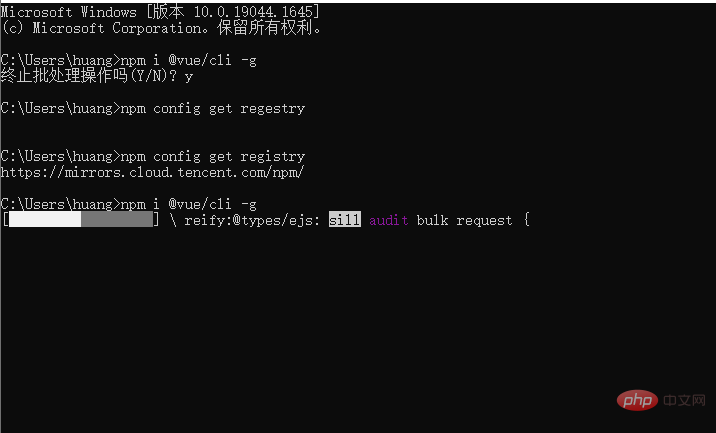
- Switch to the project directory, run
vue create and add the name of a non-mainstream library to create one vue project [Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial, web front-end development]
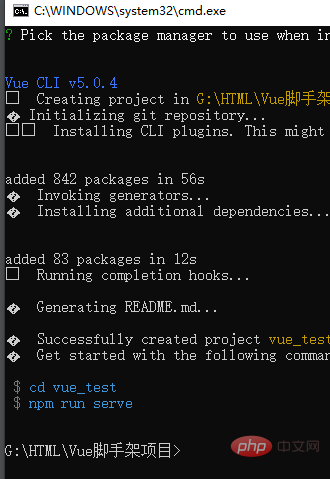
- Run
npm run serveRun the project on the server
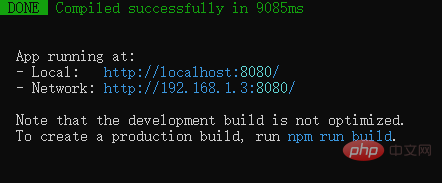
- You can see that vue has created a hello word component for us by default
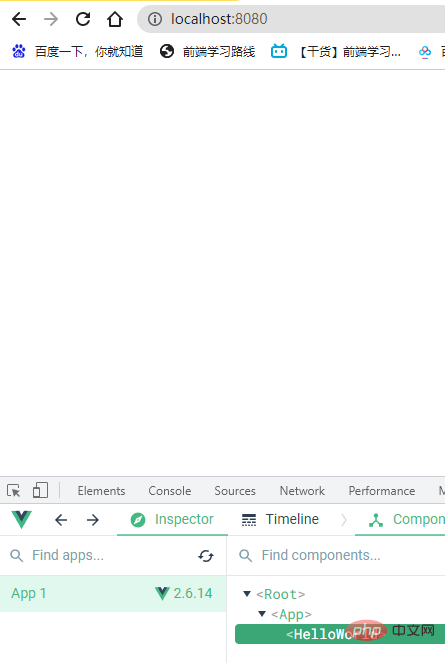
3. Analyze the project structure
#After you create a project with vue scaffolding, you will find that The following structure
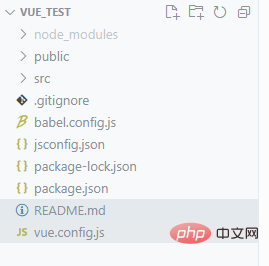
- First start with the files in the root directory. Needless to say, the first .gitignore is the ignored content uploaded by git
- babel.config, we know that babel downgrades js syntax in webpack to comply with compatibility, and the same is true for the function here
- Needless to say, the two json packages of package, lock is the package Some detailed information, including which packages have been downloaded, configuration entry files, and custom npm instructions are all here
- readme is an introduction to some basic operations of scaffolding
Enter our first folder src
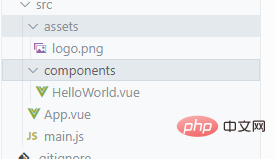
- First of all, we often see the assets file directory, which usually contains are static resources, some unchanging pictures (logos), audio and video and other files
- Then you can see our main.js entry file, new Vue is in it, We also introduced our prime minister’s app that is worth less than ten thousand people

- Then all our components will be written under the components folder , except the app component
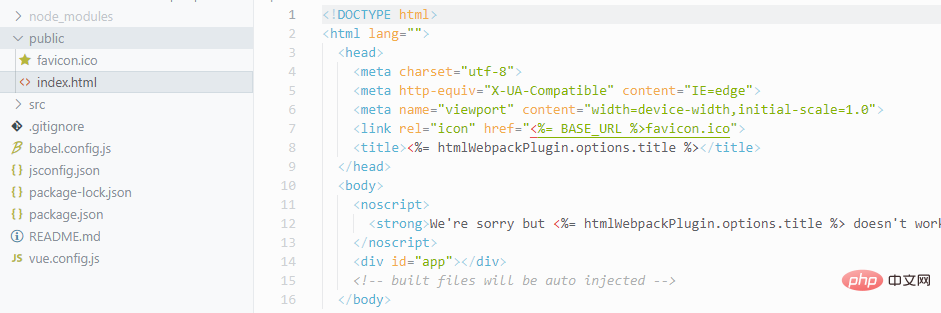
- Officially placed in this directory, please note that the title tag uses the webpack plug-in that conveniently generates HTML, and then it has some syntax, which means that we go to package.json to get the name as our title
Note: The html file does not need to introduce vue, and you can start running the project directly without introducing main.js
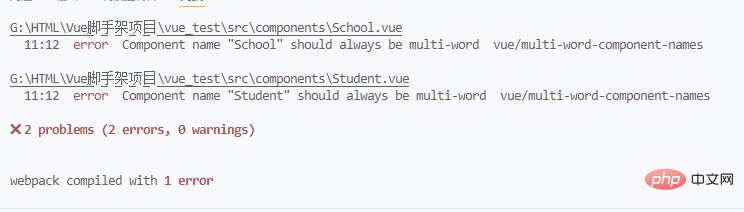
Knowledge vue official The recommended style is hump naming or - splicing. Logically speaking, there is no problem with a single word. After checking Baidu, I found out that this should be just a reminder. However, during the grammar check, the non-standard code reminder was regarded as an error. , after changing the name, it was successfully executed

4.render function
problem Throw: main.js cannot be parsed according to the standard writing method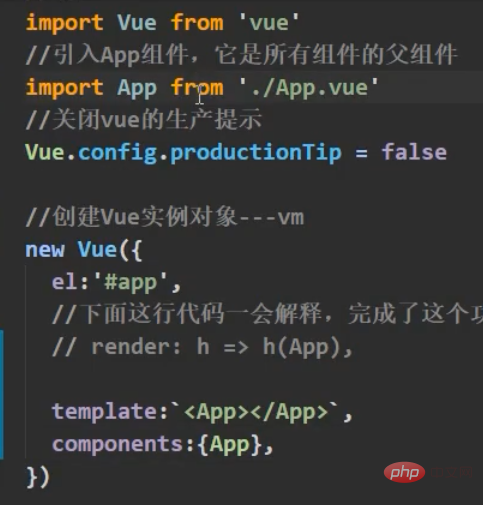
The problem actually occurs in the vue package we introduced. When you open the vue package, you can find that if our vue package.json is defined, it uses es6 modularization. Import, Then the js file module is automatically introduced (the incomplete version of Vue, the incomplete one is the template parser)
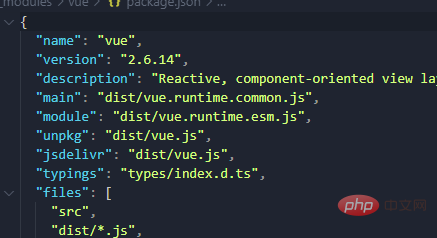
Two solutions, One is to introduce the complete version of vue, which will not be considered here. The second method is to use this incomplete version of vue. There is no template parser. I also have something that can help us write web pages, render function, he It will accept a parameter, which is also a function. There are two formal parameters in this function, one is the label, and the other is the content. If this function is used as the return value of render, then it will help us write a web page
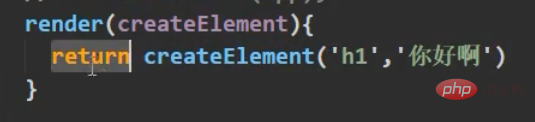
In the end, it can be abbreviated as arrow function, which is the one we see in main.js. Why is the parameter here only an app? Because if the parameter passed is a component, there is no need to pass our parameter. The content part, because the content is all in the

vue file is actually divided into two parts, one is the vue core (events, life cycle hooks , monitoring, etc.), one is our template parser
Look at the picture below
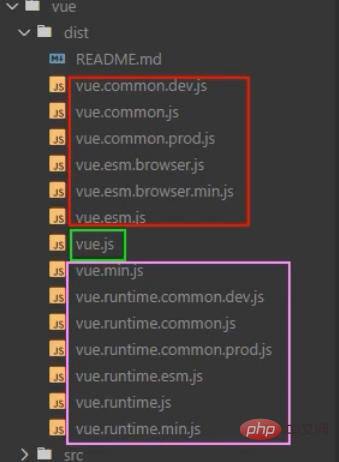
This version of our esm is es6 modular The reduced version of vue, the one with runtime is the running version of vue, which only contains core functions. The above two are the reduced version of vue imported by commonjs. With so many vue versions, only the middle one is the complete vue version
So why are we divided into so many versions? Because we need to take one thing into consideration, template parsing is used to parse the templates in our vue suffix file. This parser occupies one-third of the entire vue file, which is quite large. The most important thing is that in the end, our project When we go online and package it through webpack, it will automatically separate the files in Vue for us. What is the css part, what is the js part, and where is the html part? It will be divided into what our browser knows and what the client knows. There is no need for a .vue suffix. file, so the template parser has no effect at this time. If it is not used in the online project at all, why should I package it? It consumes resources
Why is it in other components such as app Can I write a template template?
Because the scaffolding has installed a parser for us that specifically parses the templates in .vue, main.js cannot be used

5. Modify the default configuration
Because our vue scaffolding is written based on webpack, so the configuration must be written in webpack.config.js, but vue gives her It is hidden, you need to enter vue inspect > output.jsThis output.js is just You can view all the configuration content in webpack.config.js
Pay attention to the red color Parts cannot be changed, only the pink part can be changed (for details, please refer to the vue cli official website configuration items)
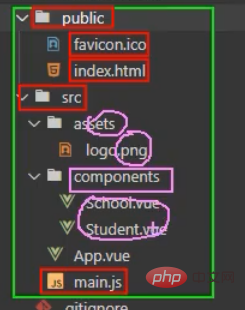
How to modify it?
are all modified based on the file vue.config.js. Refer to the cli official website. For example, if you want to modify the entry file, find pages
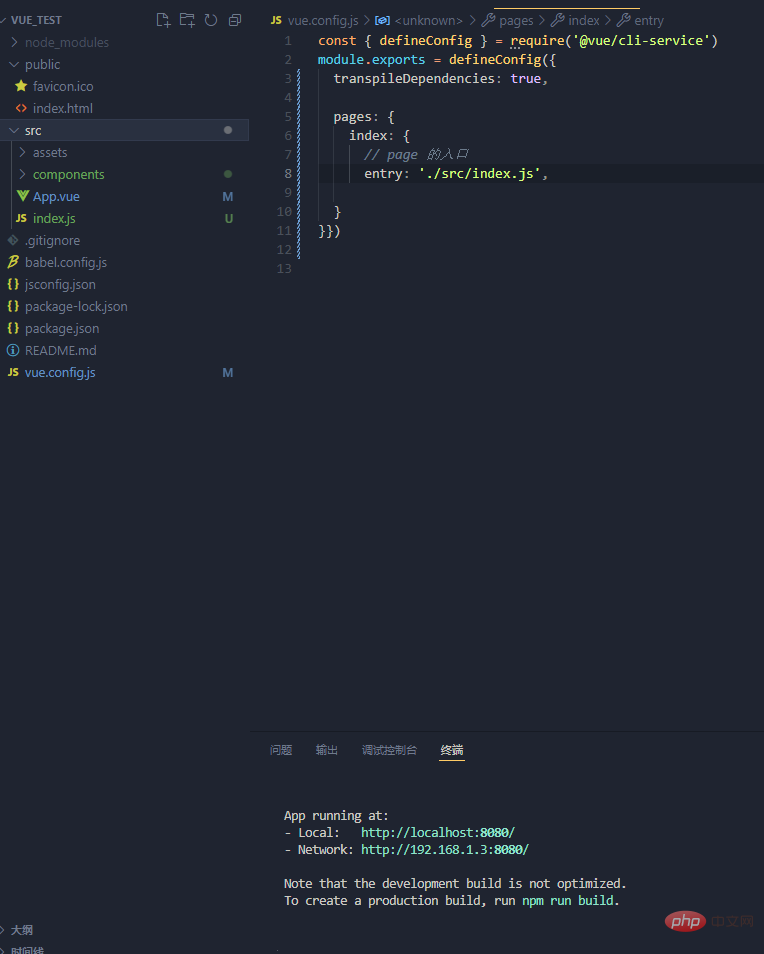
Similarly, changing lintOnSave to false can turn off the grammar check, which means that the single-word errors encountered previously will be eliminated.
2. ref and props
1.ref (mark)
I have a requirement to click a button to display the above DOM element
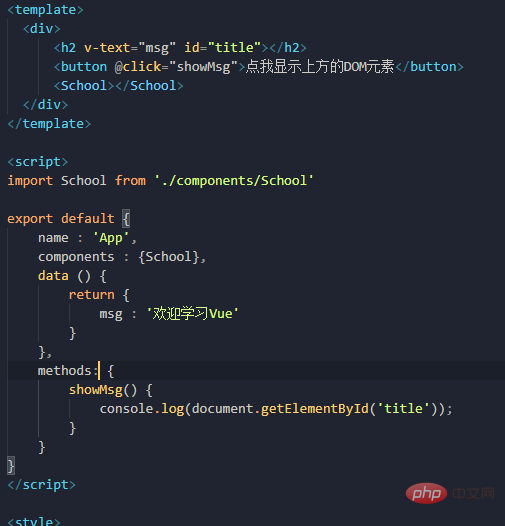
The DOM operation does not conform to vue's specifications, so vue has an apiref
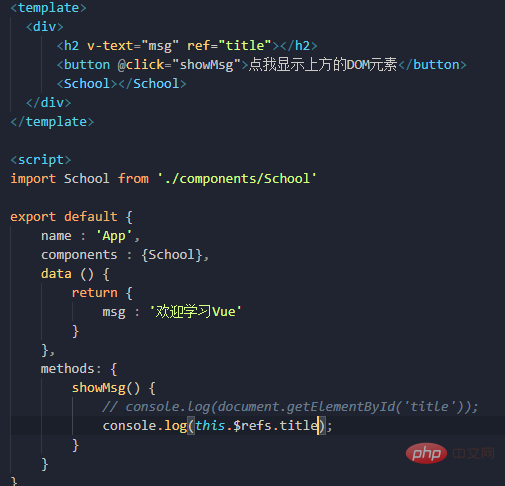
Equivalent to a substitute for id. All those configured with ref can obtain DOM elements through the $refs object, which are stored in this object, but note that If the ref is on the component label, then obtain It will be vc and it will be the vc
of this component. The difference between the id and the id is that the id obtained on the component label is the dom element
# of this component label. ##2.props
Let the component receive data from the outside
I used to write a component and want to reuse it, just copy and paste it in The following is enough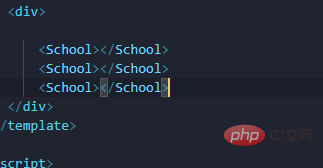
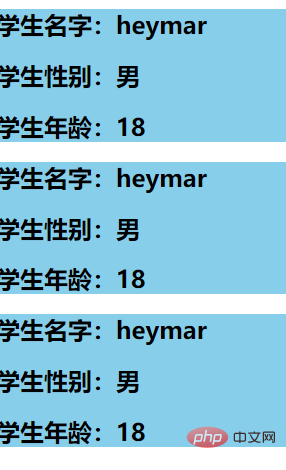
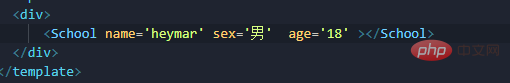
props, and it needs to be written in the subcomponent and must be in the form of an array
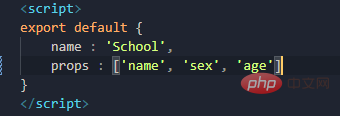
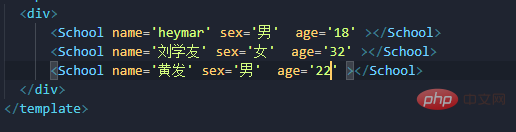
Develop simple statements using multiple )
-
Receive data while limiting the type
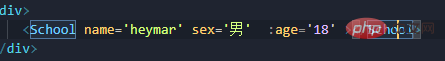
Simple statement needs to be written If the type is incorrect, the console will report an error. If it is defined,
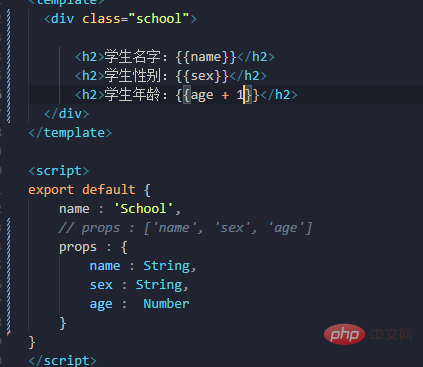
- ##receives data while limiting the type. ➕Necessity➕Default value
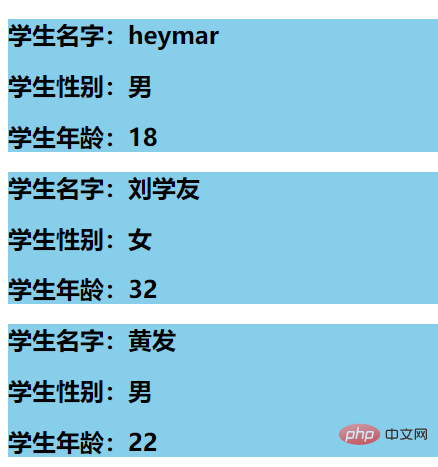
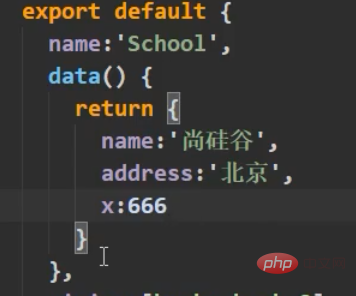
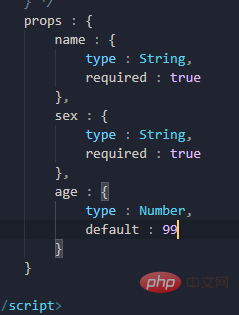 For name and gender, first limit the type, and then set it as a required input item, which cannot be empty, age In addition to restricting the type, a default value is also set, that is, it can be filled in or left out, and the default value of 99 is used.
For name and gender, first limit the type, and then set it as a required input item, which cannot be empty, age In addition to restricting the type, a default value is also set, that is, it can be filled in or left out, and the default value of 99 is used.
Generally required and default do not appear at the same time. Why do you choose it yourself? There is also the fact that the data received by props cannot be changed If you have to change it forcibly, notice a point
The priority of props is higher than that of data, use this One point, you can define a data in data, use this data to receive the passed age value, let our page display the age value in the data, and then the click event changes the value in the data
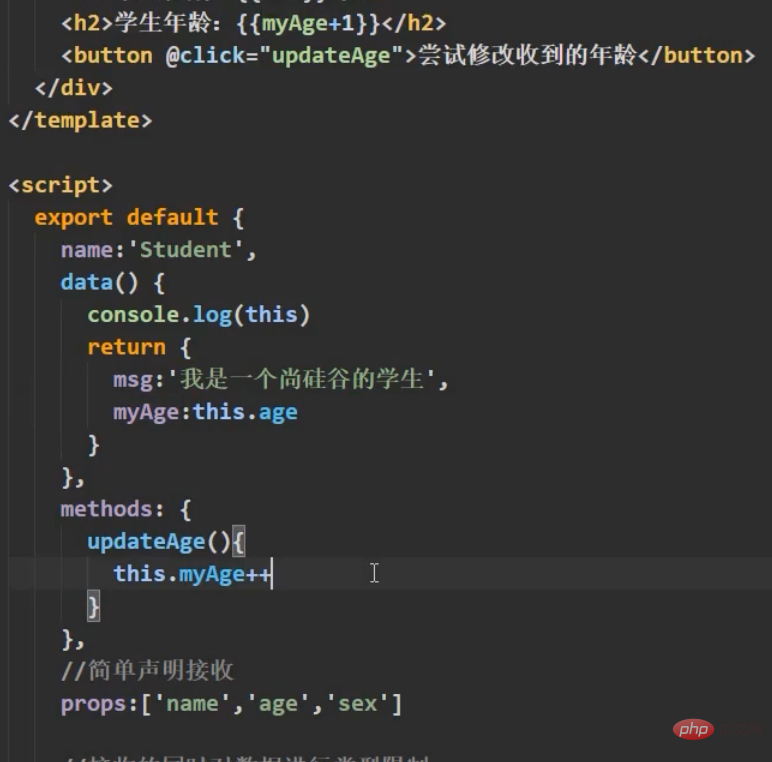
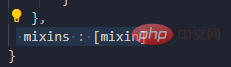
Extract the configuration shared by multiple components into a mixed object
It is defined that both components can complete a similar function
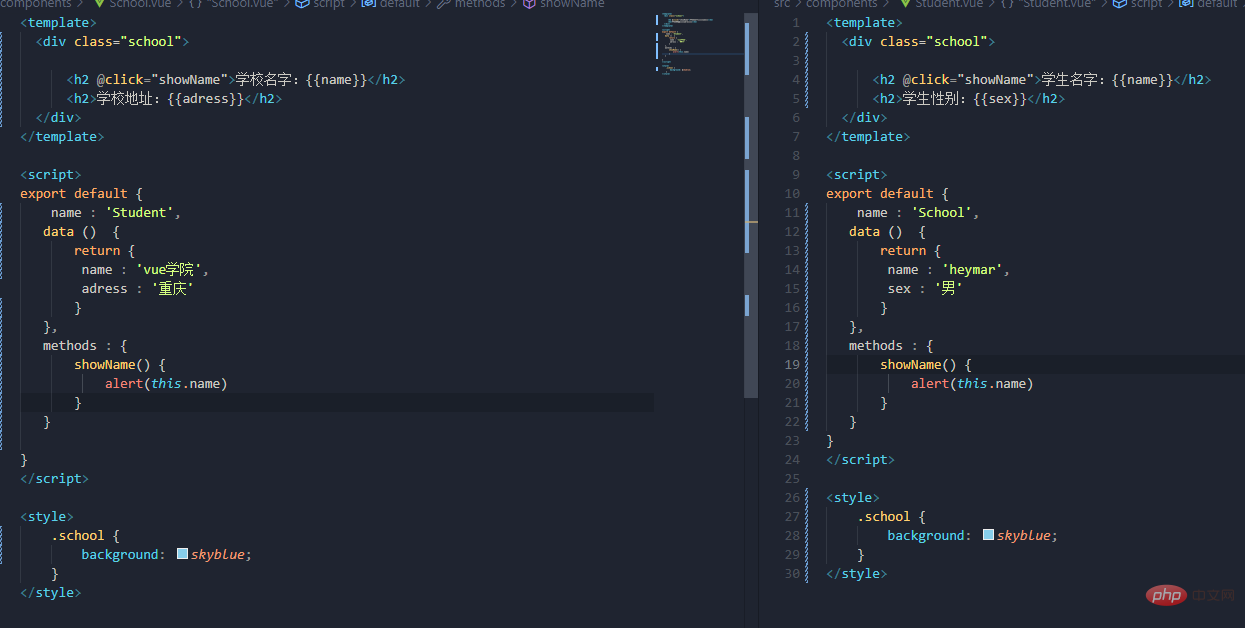 Is there any way to integrate the two methods and use them as one, which will be used at this time Our
Is there any way to integrate the two methods and use them as one, which will be used at this time Our
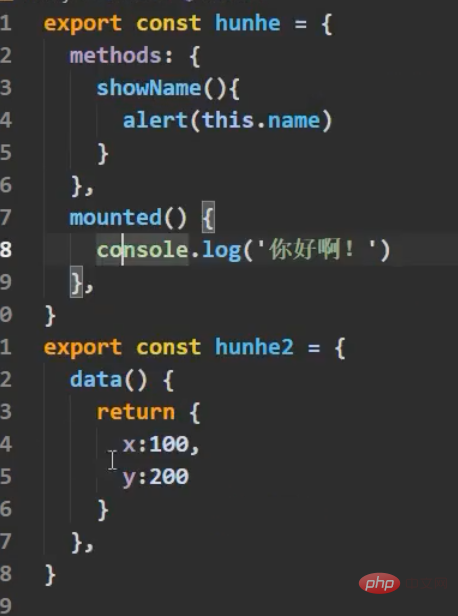
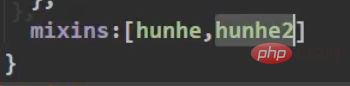
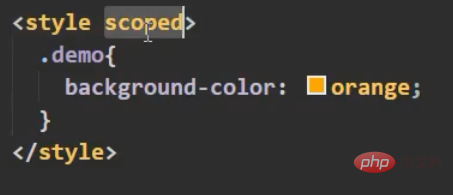
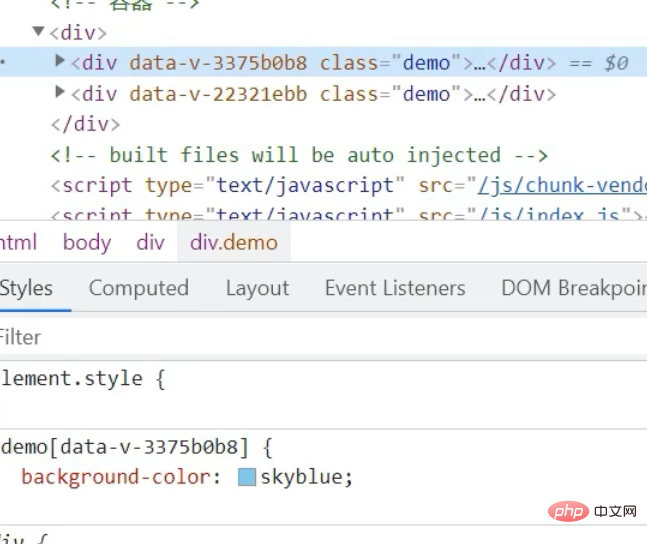
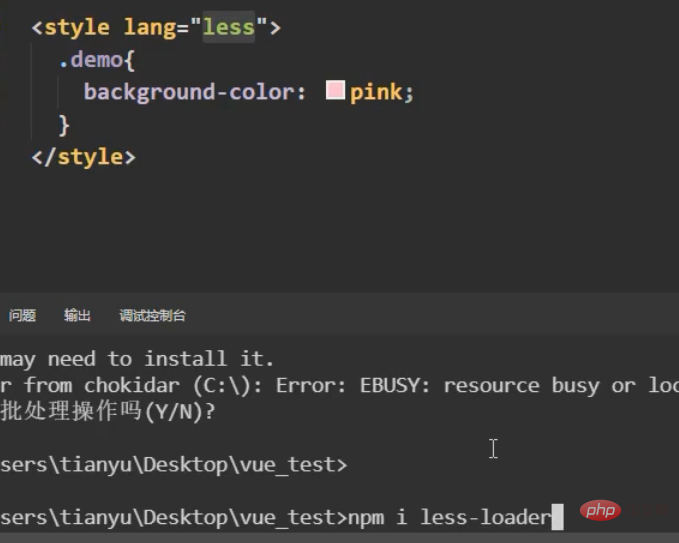
, and a js file is defined to be exported directly on demand. A variable is an object, and our methods are placed in it. Then import our component on demand, and a brand new configuration item comes mixinsNote that there is s, and it is in the form of an array After both components are matched, you can use a common method What can be written in the mix? , you can write everything in the Vue.extend configuration item we established, including life cycle hooks, data data, etc., which is equivalent to adding this configuration item to your vc instance object, as long as you configure mixin mixing Notes Mixes can be combined. Multiple mixes are exposed in the same js file. The component import corresponds to the mixin array configuration item. The name can be ##A principle: If If you don't have the configuration items, Mixing can give it to you, but if you have data, use your own data as the main one, like here, the final x is 666 : Life cycle hooks are not restricted. If the hybrid is declared and you declare it yourself, then both will be executed, but the hybrid is executed first : The methods just mentioned are all local mixing, and there is also global mixing, which is written in the entry file and imported into the entry file, Vue.mixinTo configure, after such configuration, not only all the components in the mix, but also the app and vm instances will be included is a js file, which will expose an object. The most important thing is It contains an ##You can see globally defined filters, custom instructions, mixins, including a method defined by yourself on the prototype object, all of which can be used 5.scoped style The styles we write actually mix the styles of all components into one css file when packaging, so it is easy to encounter a problem at this time, the problem of duplicate names Only required Adding an attribute scoped to our style tag is a quick solution. Its principle is to dynamically generate a randomly generated attribute for your component tag, and then match your css class name with the attribute selector to achieve a style that only belongs to you ##Special : At this time, only the component tag of the App itself can use this, and the sub-components cannot be used. You can specify a precompiled language, such as less, but it cannot be used directly. You need to install the corresponding parser Note: If the webpack of the scaffolding is the latest version 5 and above can install the latest version of less, otherwise install less than 8 (around 6.7), npm view webpack versionsYou can check which versions of this package currently exist less-loader, you can use less to write css 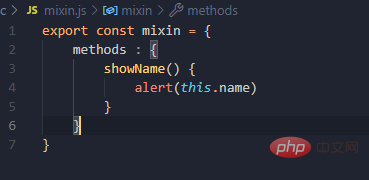
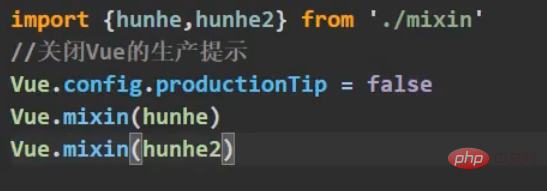
is used to enhance Vue
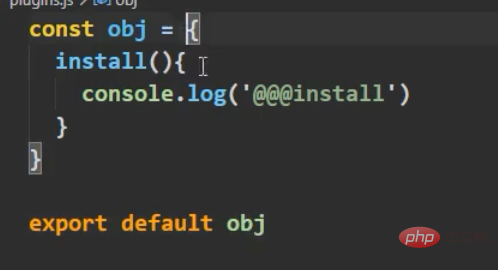 Abbreviated version:
Abbreviated version: 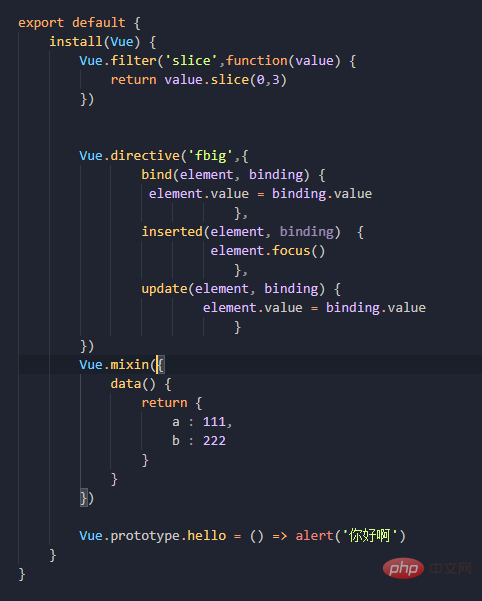 # Regarding what can be written in it, now that the Vue constructor is obtained, there are too many things that can be written. Now, the filters, custom instructions, and the mixing just mentioned can be put here for global configuration. The most important thing is that you can write your own methods and write them to the prototype prototype object.
# Regarding what can be written in it, now that the Vue constructor is obtained, there are too many things that can be written. Now, the filters, custom instructions, and the mixing just mentioned can be put here for global configuration. The most important thing is that you can write your own methods and write them to the prototype prototype object. Vue.use
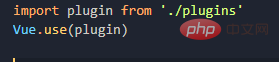 looks like this It is very similar to Node, and the magic is that with such registration, both vm and vc can use the global filters and instructions defined in the plug-in install
looks like this It is very similar to Node, and the magic is that with such registration, both vm and vc can use the global filters and instructions defined in the plug-in install 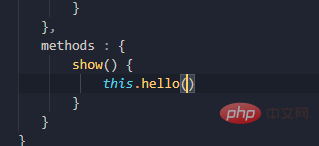
Let the style take effect locally to prevent conflicts
(Learning video sharing:
The above is the detailed content of This article will take you to learn more about Vue scaffolding. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump a tag to vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM
How to jump a tag to vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM
The methods to implement the jump of a tag in Vue include: using the a tag in the HTML template to specify the href attribute. Use the router-link component of Vue routing. Use this.$router.push() method in JavaScript. Parameters can be passed through the query parameter and routes are configured in the router options for dynamic jumps.