
The Linux view history command is "history". You can view the recently executed commands by executing the "history" command; you can add options after the "history" command, such as the "-c" option, which means to clear the history commands, " The -w" option means writing the historical commands in the cache to the historical command saving file "~/.bash_history".

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.5 system, Dell G3 computer.
Linux view history command
View history command
You can execute the history command to view history command:
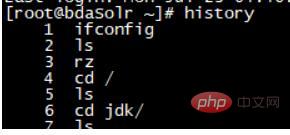
Go to the end to see:
These are the recently executed commands:
history command Options can be added later:
-c: Clear historical commands (including cache and files)
-w: Write historical commands in the cache to the historical command saving file ~/.bash_history (obviously Each user has his own file)
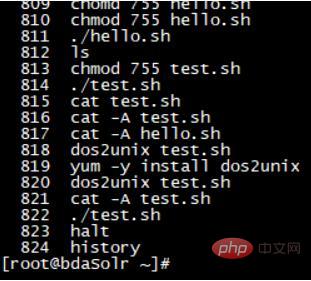
In fact, what we use history to view is the command in the cache:
For example, if I execute a command now:

Use history to view:
You can see the recently executed commands:
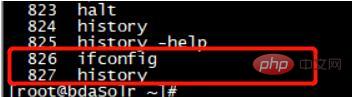
View files:
The last command that appears does not contain the previously executed command, because the historical command has not yet been written to the file at this time:
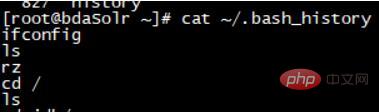
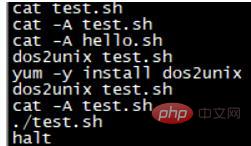
Only after normal login and exit, the system will write the commands in the cache to the file.
Historical commands can be saved up to 1000, which can be modified in /etc/profile:

This is the parameter:
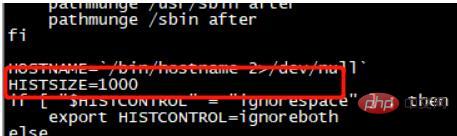
If the maximum number is exceeded, the oldest record will be deleted.
After modification, execute source /etc/profile to make the environment variables take effect.
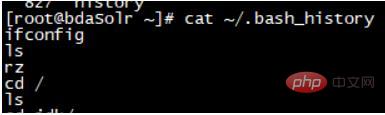
This command actually modifies the file /root/.bash_history:

Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the linux view history command?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




