How to declare read-only constants in es6
In es6, you can use the const keyword to declare read-only constants, the syntax is "const constant name = constant value;"; once declared, the constant must be initialized and the initialized value cannot be changed. Constants declared by const belong to the block scope and are subject to the "temporary dead zone". They will not create any global properties on the window and cannot be reassigned or redeclared.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
In es6, you can use the const keyword to declare read-only constants.
es6 const keyword
const declares a read-only constant. Once declared, a constant must be initialized and the initialized value cannot be changed.
const PI = 3.1415; PI // 3.1415 PI = 3; // TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.
const constants comply with the following rules:
belongs to the block scope.
is subject to the "temporary dead zone".
It does not create any global properties on window.
Not reassignable.
Cannot be redeclared.
const Once a variable is declared, it must be initialized immediately.
const foo; // SyntaxError: Missing initializer in const declaration
The above code indicates that for const, if you just declare without assigning a value, an error will be reported.
The scope of const is the same as that of the let command: it is only valid within the block-level scope where it is declared.
if (true) {
const MAX = 5;
}
MAX // Uncaught ReferenceError: MAX is not definedThe constants declared by the const command are not promoted. There is also a temporary dead zone and can only be used after the declared position.
if (true) {
console.log(MAX); // ReferenceError
const MAX = 5;
}The above code is called before the constant MAX is declared, and an error is reported.
Constant declared by const cannot be declared repeatedly like let.
var message = "Hello!"; let age = 25; // 以下两行都会报错 const message = "Goodbye!"; const age = 30;
The essence of const
What const actually guarantees is not that the value of the variable cannot be changed, but that the data stored in the memory address pointed to by the variable cannot be changed. For simple types of data (numeric values, strings, Boolean values), the value is stored at the memory address pointed to by the variable, and is therefore equivalent to a constant. But for composite type data (mainly objects and arrays), the memory address pointed to by the variable only stores a pointer to the actual data. Const can only guarantee that this pointer is fixed (that is, it always points to another fixed address) , as for whether the data structure it points to is variable, it is completely out of control. Therefore, you must be very careful when declaring an object as a constant.
const foo = {};
// 为 foo 添加一个属性,可以成功
foo.prop = 123;
foo.prop // 123
// 将 foo 指向另一个对象,就会报错
foo = {}; // TypeError: "foo" is read-onlyIn the above code, the constant foo stores an address, which points to an object. What is immutable is only this address, that is, foo cannot be pointed to another address, but the object itself is mutable, so new properties can still be added to it.
Here is another example.
const a = []; a.push('Hello'); // 可执行 a.length = 0; // 可执行 a = ['Dave']; // 报错
In the above code, the constant a is an array. The array itself is writable, but if another array is assigned to a, an error will be reported.
If you really want to freeze the object, you should use the Object.freeze method.
const foo = Object.freeze({});
// 常规模式时,下面一行不起作用;
// 严格模式时,该行会报错
foo.prop = 123;In the above code, the constant foo points to a frozen object, so adding new attributes will not work, and an error will be reported in strict mode.
In addition to freezing the object itself, the properties of the object should also be frozen. Below is a function that completely freezes an object.
var constantize = (obj) => {
Object.freeze(obj);
Object.keys(obj).forEach( (key, i) => {
if ( typeof obj[key] === 'object' ) {
constantize( obj[key] );
}
});
};【Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, programming video】
The above is the detailed content of How to declare read-only constants in es6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
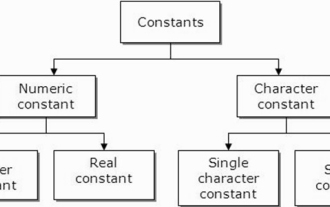 What are constants in C language? Can you give an example?
Aug 28, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
What are constants in C language? Can you give an example?
Aug 28, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
A constant is also called a variable and once defined, its value does not change during the execution of the program. Therefore, we can declare a variable as a constant referencing a fixed value. It is also called text. Constants must be defined using the Const keyword. Syntax The syntax of constants used in C programming language is as follows - consttypeVariableName; (or) consttype*VariableName; Different types of constants The different types of constants used in C programming language are as follows: Integer constants - For example: 1,0,34, 4567 Floating point constants - Example: 0.0, 156.89, 23.456 Octal and Hexadecimal constants - Example: Hex: 0x2a, 0xaa.. Octal
 How to create a constant in Python?
Aug 29, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
How to create a constant in Python?
Aug 29, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
Constants and variables are used to store data values in programming. A variable usually refers to a value that can change over time. A constant is a type of variable whose value cannot be changed during program execution. There are only six built-in constants available in Python, they are False, True, None, NotImplemented, Ellipsis(...) and __debug__. Apart from these constants, Python does not have any built-in data types to store constant values. Example An example of a constant is demonstrated below - False=100 outputs SyntaxError:cannotassigntoFalseFalse is a built-in constant in Python that is used to store boolean values
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
For browser compatibility. As a new specification for JS, ES6 adds a lot of new syntax and API. However, modern browsers do not have high support for the new features of ES6, so ES6 code needs to be converted to ES5 code. In the WeChat web developer tools, babel is used by default to convert the developer's ES6 syntax code into ES5 code that is well supported by all three terminals, helping developers solve development problems caused by different environments; only in the project Just configure and check the "ES6 to ES5" option.
 In Java, is it possible to define a constant using only the final keyword?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
In Java, is it possible to define a constant using only the final keyword?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
A constant variable is a variable whose value is fixed and only one copy exists in the program. Once you declare a constant variable and assign a value to it, you cannot change its value again throughout the program. Unlike other languages, Java does not directly support constants. However, you can still create a constant by declaring a variable static and final. Static - Once you declare a static variable, they will be loaded into memory at compile time, i.e. only one copy will be available. Final - Once you declare a final variable, its value cannot be modified. Therefore, you can create a constant in Java by declaring the instance variable as static and final. Example Demonstration classData{&am
 How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
Steps: 1. Convert the two arrays to set types respectively, with the syntax "newA=new Set(a);newB=new Set(b);"; 2. Use has() and filter() to find the difference set, with the syntax " new Set([...newA].filter(x =>!newB.has(x)))", the difference set elements will be included in a set collection and returned; 3. Use Array.from to convert the set into an array Type, syntax "Array.from(collection)".
 How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
In es5, you can use the for statement and indexOf() function to achieve array deduplication. The syntax "for(i=0;i<array length;i++){a=newArr.indexOf(arr[i]);if(a== -1){...}}". In es6, you can use the spread operator, Array.from() and Set to remove duplication; you need to first convert the array into a Set object to remove duplication, and then use the spread operator or the Array.from() function to convert the Set object back to an array. Just group.
 What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
In es6, the temporary dead zone is a syntax error, which refers to the let and const commands that make the block form a closed scope. Within a code block, before a variable is declared using the let/const command, the variable is unavailable and belongs to the variable's "dead zone" before the variable is declared; this is syntactically called a "temporary dead zone". ES6 stipulates that variable promotion does not occur in temporary dead zones and let and const statements, mainly to reduce runtime errors and prevent the variable from being used before it is declared, resulting in unexpected behavior.




