
This article will take you to learn Node together and give an in-depth introduction to the use of Express and routing modules. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Express is based on the Node.js platform, fast, An open and minimalist web development framework. The function of Express is similar to the built-in http module of Node.js. is specially used to create a web server. The essence of Express: It is a third-party package on npm that provides a convenient way to quickly create a web server. Its Chinese website is: Express Chinese website. Of course, you can create a web server using the built-in http module without using Express, but the http module is extremely complicated to use and the development efficiency is extremely low. Express is further encapsulated based on the built-in http module, which can greatly improve development efficiency. For front-end programmers, the two most common servers are:
Web website server (a server that specializes in providing external Web page resources);API interface server(API interface server specially provided to external parties). Using Express, you can quickly and easily create a Web website server and API interface server. [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial, Programming teaching]
Installation and use of Expressnpm install express
Create a basic server: with built-in http Common server comparisons of modules http built-in module writing// 导入 express 模块
const express = require('express')
// 创建 web 服务器
const app = express()
// 调用 app.listen(端口号,启动成功后的回调函数),启动服务器
app.listen(8081,()=>{
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1:8081');
})
Monitoring GET requests: Through the app.get() method, you can monitor the client's GET request, the specific syntax format is as follows: // 参数1:客户端请求的URL地址
// 参数2:请求对应的处理函数
// req:请求对象(包含请求相关属性和方法);res:响应对象(包含响应相关的属性和方法)
app.get('请求的URL',function(req,res){/*处理函数*/})
Monitor POST request: Through the app.post() method, you can monitor the client's POST request, the specific syntax The format is as follows: // 参数1:客户端请求的URL地址
// 参数2:请求对应的处理函数. req:请求对象(包含请求相关属性和方法);res:响应对象(包含响应相关的属性和方法)
app.post('请求的URL',function(req,res){/*处理函数*/})
// 导入 express 模块
const express = require('express')
// 创建 Web 服务器
const app = express()
// get请求
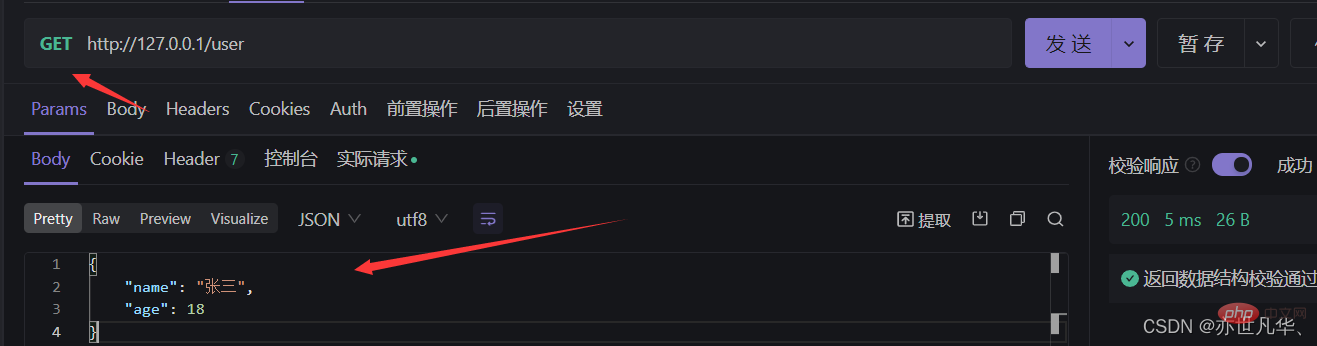
app.get('/user',(req,res)=>{
// 向客户端响应一个 json 对象
res.send({name:'张三',age:18})
})
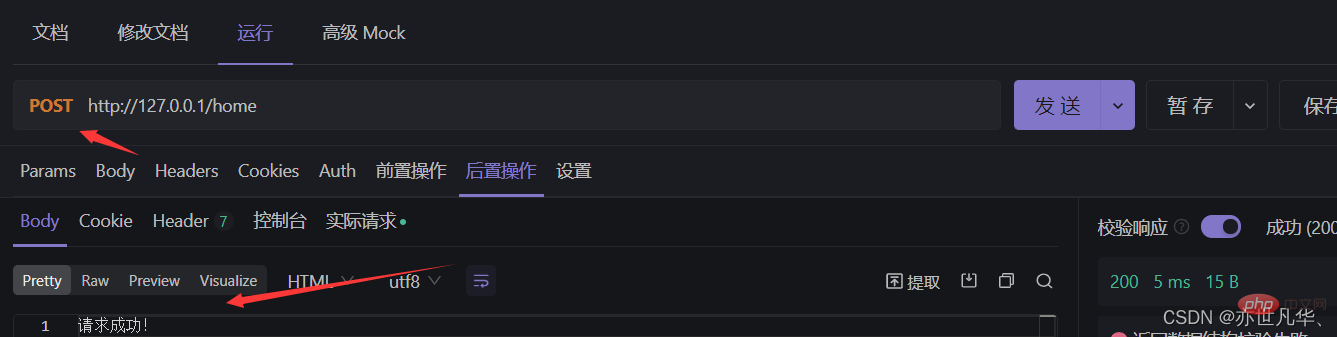
// post请求
app.post('/home',(req,res)=>{
// 向客户端响应一个 文本字符串
res.send('请求成功!')
})
app.listen(80,()=>{
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1:80');
})
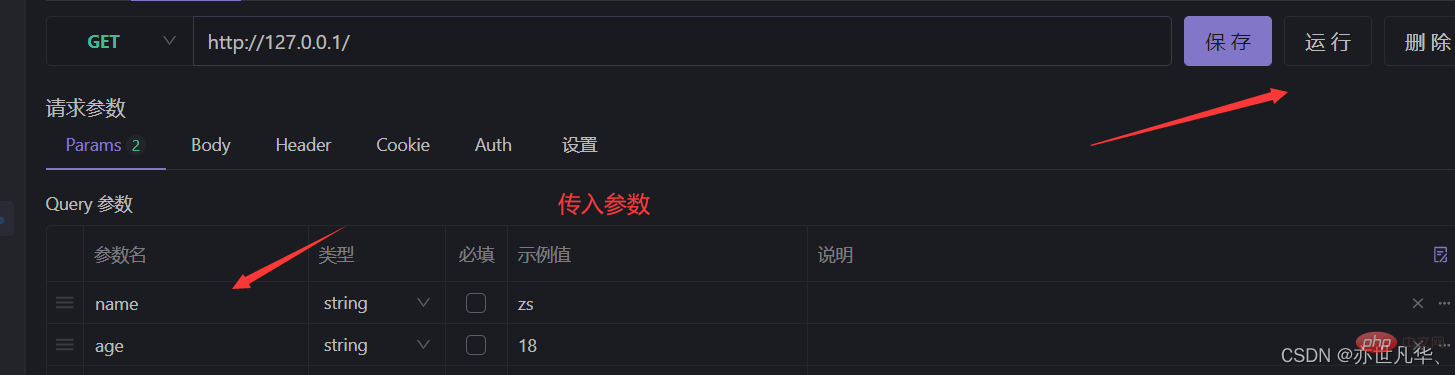
 Get the query parameters of the URL: Through the req.query object, you can access the parameters sent by the client to the server in the form of a query string:
Get the query parameters of the URL: Through the req.query object, you can access the parameters sent by the client to the server in the form of a query string:
app.get('/',(req,res)=>{
// 通过 req.query 可以获取到客户端发送过来的查询参数,默认情况下,req.query 是一个空对象
console.log(req.query);
res.send(req.query)
})
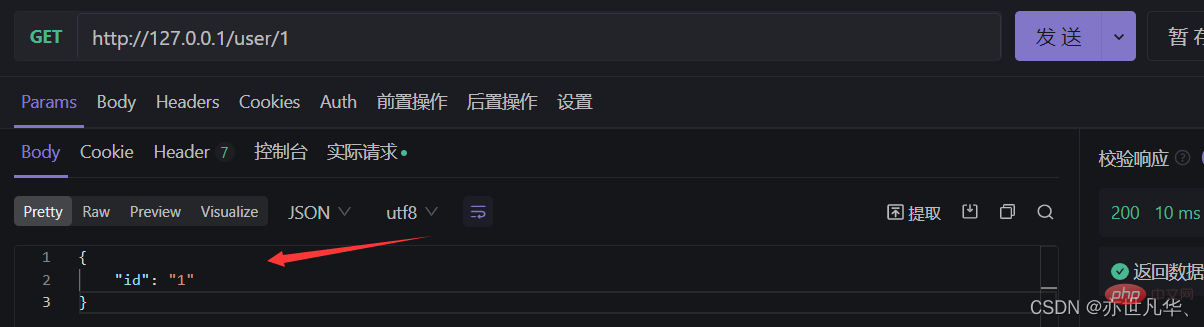
 Get the dynamic parameters in the URL: Through the req.params object, you can access the URL through: Matched dynamic parameters:
Get the dynamic parameters in the URL: Through the req.params object, you can access the URL through: Matched dynamic parameters:
// 这里的id是一个动态参数
app.get('/user/:id',(req,res)=>{
// req.params 是动态匹配到的 URL 参数,默认也是一个空对象
console.log(req.params);
res.send(req.params)
})
If you want to host multiple static resource directories, just call the express.static() function multiple times.
app.use(express.static('test'))
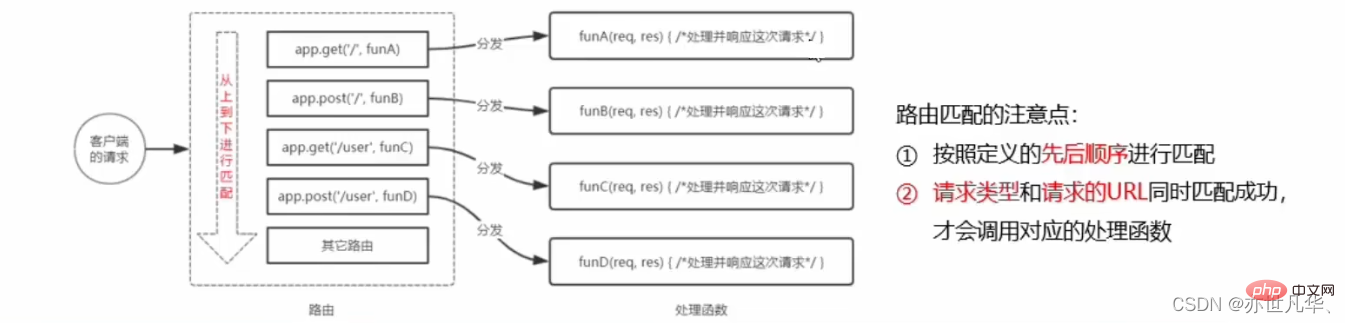
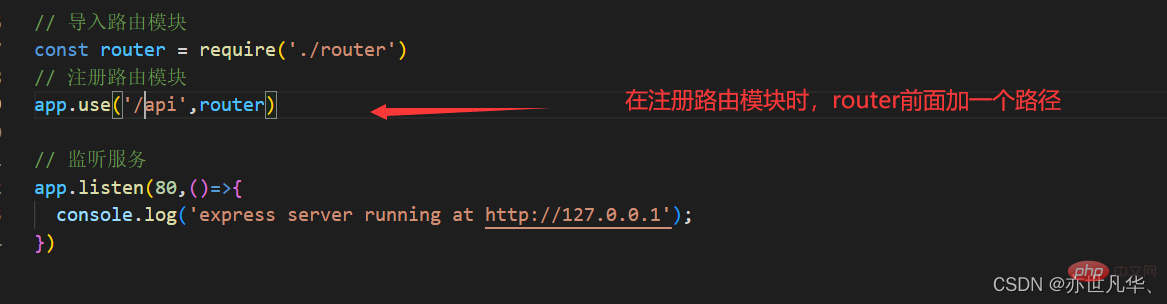
Note: Express looks for files in the specified static directory and provides external resource access paths, so static The directory name of the resource will not appear in the URL. If you want to mount the path prefix before hosting the static resource access path, you can use the following method: 在编写调试Node.js项目时,如果修改了项目代码,则需要手动频繁的close掉,然后重新启动非常的繁琐。我们可以使用 nodemon 这个工具,它能够监听项目文件的变动,当代码修改后,nodemon会自动帮助我们重启项目,极大地方便了开发与测试。 在终端运行如下命令,即可将 nodemon 安装为全局可用的工具: 安装完成之后,将之前的命令 node+文件名称 换成 nodemon+文件名称 即可自动重启项目进行监听,如下: 在Express中,路由指的是客户端的请求与服务器之间的映射关系。Express中的路由分三部分组成:请求的类型、请求的URL地址、处理函数。 每当一个请求到达服务器之后,需要先经过路由的匹配,只有匹配成功之后,才会调用对应的处理函数。在匹配时,会按照路由的顺序进行匹配,如果请求类型和请求的URL同时匹配成功,则Express会将这次请求转交到对应的function函数进行处理。 为了方便对路由进行模块化管理,Express不建议将路由直接挂载到app上,而是推荐将路由抽离为单独的模块。 创建路由模块: 注册路由模块: 如果想为路由模块添加前缀,方式也很简单,如下:(即可全局模块路径前有该前缀) 更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!// 在 express.static() 方法前面添加想要的路径前缀
app.use('text',express.static('test'))nodemon
npm install nodemon -g


Express路由
// 导入 express 模块
const express = require('express')
// 创建 Web 服务器
const app = express()
// 挂载路由
app.get('/',(req,res)=>{ res.send('hello world'); })
app.post('/',(req,res)=>{ res.send('hello ok'); })
// 监听服务
app.listen(80,()=>{
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1');
})模块化路由
// 导入 express 模块
const express = require('express')
// 创建 Web 服务器
const app = express()
// 挂载路由
app.get('/',(req,res)=>{ res.send('hello world'); })
app.post('/',(req,res)=>{ res.send('hello ok'); })
// 监听服务
app.listen(80,()=>{
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1');
})// 导入 express 模块
const express = require('express')
// 创建 服务器
const app = express()
// 导入路由模块
const router = require('./router')
// 注册路由模块
app.use(router)
// 监听服务
app.listen(80,()=>{
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1');
})
The above is the detailed content of An article explaining the Express and routing modules in Node in detail. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 what is nodejs
what is nodejs
 Nodejs implements crawler
Nodejs implements crawler
 What does java routing mean?
What does java routing mean?
 Commonly used codes in html language
Commonly used codes in html language
 The difference between front-end and back-end
The difference between front-end and back-end
 Introduction to the difference between javascript and java
Introduction to the difference between javascript and java
 What to do if the Bluetooth switch is missing in Windows 10
What to do if the Bluetooth switch is missing in Windows 10
 What is the difference between guid and mbr formats
What is the difference between guid and mbr formats
 wifi shows no ip assigned
wifi shows no ip assigned