
How to use non-single file components in Vue? The following article will introduce you to the use of non-single file components in Vue. I hope it will be helpful to you!

A collection of local function generations and resources that implement an application (simply put: A small box that integrates html, js, css, and resources)
Understanding: a collection of codes used to achieve local (specific) functional effects
Why: the function of an interface Very complex
Function: reuse coding, simplify project coding, and improve operating efficiency
Components are divided into non-single file components and single file components. Generally, single file components are commonly used. [Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial, web front-end development]
2.1 Three steps to use components
(1)How to define a component?
Create usingVue.extend(options), where options It is almost the same as the options passed in when new Vue(options). But there is a slight difference. There is no need to write the el attribute in the component, because the component directly serves the Vue instance, so there is no need to write it in the component, and after the component is written, it not only serves one place, as shown here Reusability of components, so components cannot write el.
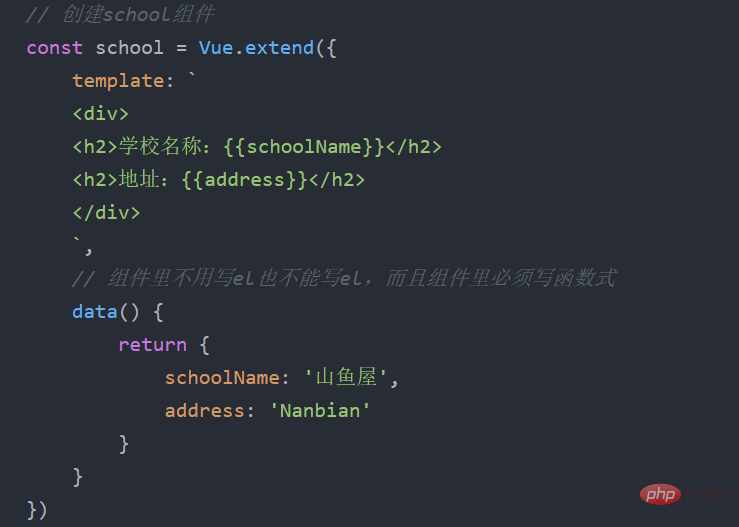
(2) How to register a component?
1. Local registration: Pass in the components option when relying on new Vue 2. Global registration: rely on Vue.component('Component name, component)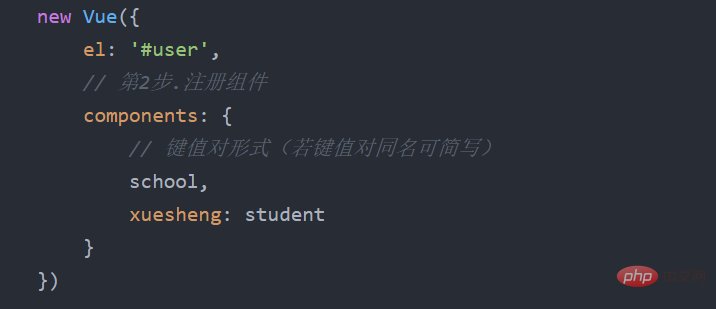
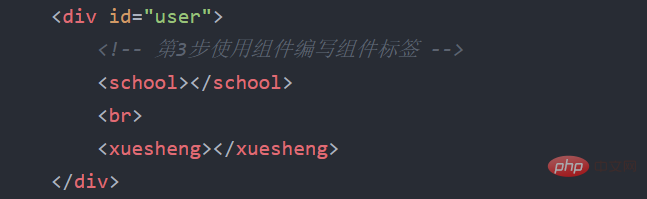
(3) How to use componentsWriting component labels (using components)
The following is to create non- The whole process of single file component
(4)Why does data have to be written as a function?
Avoid reference relationships between data when components are reused.
Note: Use template to configure the component structure.
<body>
<div id="user">
<!-- 第3步使用组件编写组件标签 -->
<school></school>
<br>
<xuesheng></xuesheng>
</div>
<div class="user2">
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 第一步:创建组件
// 创建school组件
const school = Vue.extend({
template: `
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
`,
// 组件里不用写el也不能写el,而且组件里必须写函数式
data() {
return {
schoolName: '山鱼屋',
address: 'Nanbian'
}
}
})
// 创建student组件
const student = Vue.extend({
template: `
<div>
<h2>学生名称:{{studentName}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<button @click = 'showName'>点我出名</button>
</div>
`,
// 组件里不用写el也不能写el,而且组件里必须写函数式
data() {
return {
studentName: '山鱼屋',
age: 20
}
},
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.studentName)
}
},
})
// 创建全局组件
const hello = Vue.extend({
template: `
<div>
<h2>你好呀!{{name}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
name: 'shanyu',
}
}
})
// 注册全局的组件
Vue.component('hello', hello);
// 创建vm
new Vue({
el: '#user',
// 第2步.注册组件
components: {
// 键值对形式(若键值对同名可简写)
school,
xuesheng: student
}
})
new Vue({
el: '.user2',
})
</script>1) About component names
Composed of one word: the first way of writing (the first letter is lowercase): school, the second way of writing (the first letter is capitalized) School
Multiple words: the first way of writing (kebab-case Naming): my-school, the second way of writing (Came1Case naming): MySchool (Requires Vue scaffolding support)
Note:
(1), the component name is exhausted It is possible to avoid existing element names in HTML, such as h2 and H2.
(2). You can use the name configuration item to specify the name of the component as it appears in the developer tools.
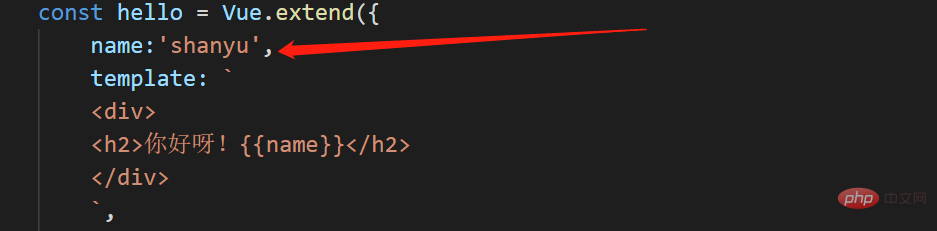
##2) About component tags
The first way of writing:3) Abbreviation
const school = Vue.extend(options) can be abbreviated as: const school = {options}
2.2The nesting of components
is similar to Russian matryoshka dolls, with large pieces nested inside small pieces (in fact, there is another one under the vm A component named app, which manages all components)<body>
<div id="user">
</div>
<script>
// 创建room组件
const room = {
template:
`<div>
<h2>
房间号{{num}}
</h2>
<h2>
puwei:{{pnum}}
</h2>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
num: '222',
pnum: '8'
}
}
}
// 创建students组件
const students = {
template:
`<div>
<h2>
姓名:{{name}}
</h2>
<h2>
学号:{{studentnum}}
</h2>
<room></room>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
name: '山鱼',
studentnum: '9657'
}
},
components: {
room
}
}
// 创建school组件
const school = {
template:
`<div>
<h2>
校名:{{sname}}
</h2>
<h2>
地址:{{address}}
</h2>
<students></students>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
sname: '山鱼学院',
address: '华山道9088号'
}
},
components: {
students
}
}
const app = {
template:
`
<school></school>
</div>`,
components: {
school
}
}
// 创建app组件
new Vue({
template:`<app></app>`,
el: '#user',
components: {
app,
}
})
</script>
</body>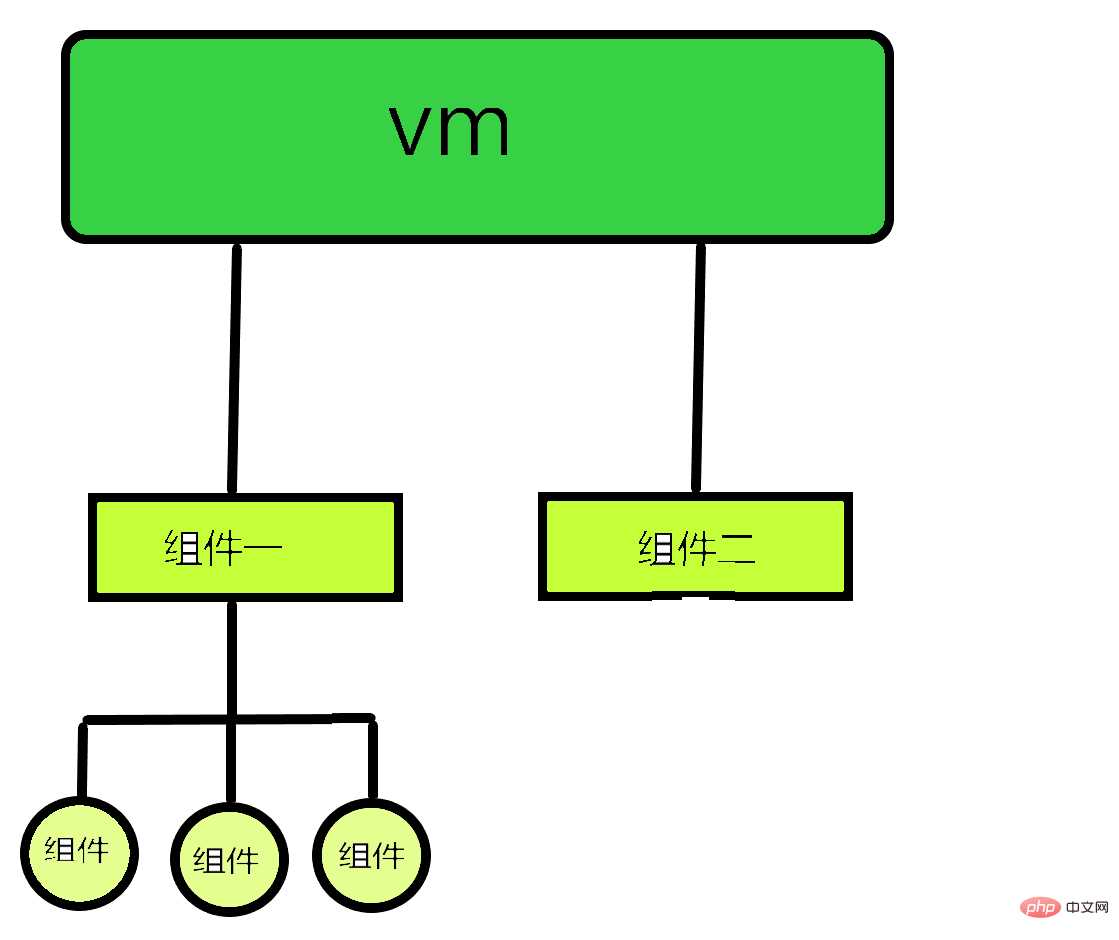
, which is not defined by the programmer but is generated by Vue.extend.
is returned (although the twins are very similar, they are not the same one anyway. People)
function, methods## in component configuration The function in #, the function in watch, and the two numbers in computed all have this [VueComponent instance object]. (2) data
function in new Vue(options) configuration, function inmethods, function in watch, The this of the functions in computed is [Vue instance object]. (Learning video sharing: vuejs introductory tutorial
,Basic programming video)
The above is the detailed content of An article to talk about the use of non-single file components in Vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!