What are the jquery search methods?
The search methods are: 1. parent(), which can find the parent element of the current element; 2. parents(), which can find the ancestor elements of the current element; 3. children(), which can find the children of the current element. element; 4. find(), which can find descendant elements of the current element; 5. contents(); 6. siblings(); 7. next(); 8. nextAll(); 9. nextUntil(); 10. prev( ); 11. prevUntil() and so on.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, jquery3.6 version, Dell G3 computer.
In order to operate elements more flexibly, in addition to selectors, jQuery also provides us with two ways in the form of "methods": one is "filter method"; the other is "find method". The filtering method and the search method are actually a supplement to the jQuery selector.
Filtering method refers to further filtering the selected elements. The search method mainly uses the currently selected element as the base point to find the parent element, child element or sibling element of this element.
In jQuery, for the search method, we can divide it into the following three situations.
Find ancestor elements
Find descendant elements
Find sibling elements
jQuery Finds Ancestor Elements
In jQuery, if you want to find the ancestor elements of the current element (parent element, parent element, etc.) , we have the following 3 methods.
(1)parent()
(2)parents()
(3 ) parentsUntil()
1, parent()
In jQuery, we can use the parent() method to find the " parent element". Note that elements have only one parent element.
Syntax:
$.parent(selector)
Description:
selector is an optional parameter, which is a selector used to find parent elements that meet the conditions. When the parameter is omitted, it means that the parent element does not need to meet any conditions; when the parameter is not omitted, it means that the parent element does not need to meet the condition.
Example: parent() without parameters
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
table, tr, td{border:1px solid silver;}
td
{
width:40px;
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
text-align:center;
}
</style>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("td").hover(function () {
$(this).parent().css("background-color", "silver");
}, function () {
$(this).parent().css("background-color", "white");
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>4</td>
<td>8</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>16</td>
<td>32</td>
<td>64</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>128</td>
<td>256</td>
<td>512</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>By default, the preview effect is as shown below.

When the mouse moves over a certain cell, the preview effect is as shown below.

Analysis:
$(this).parent() means selecting the parent element (tr) of the current td element, but the parent element (table) does not will be selected.
Example: parent() with parameters
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
table, tr, td{border:1px solid silver;}
td
{
width:40px;
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
text-align:center;
}
</style>
<script ></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("td").hover(function () {
$(this).parent(".select").css("background-color", "silver")
}, function () {
$(this).parent(".select").css("background-color", "white")
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>4</td>
<td>8</td>
</tr>
<tr class="select">
<td>16</td>
<td>32</td>
<td>64</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>128</td>
<td>256</td>
<td>512</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>By default, the preview effect is as shown below.

When the mouse moves over the td element of class="select", the preview effect is as shown in the figure below.

Analysis:
$(this).parent(".select") means selecting the parent element of the current td element ( tr), and the parent element must contain the class name "select".
2. parents()
In jQuery, we can use the parents() method to find the "ancestor elements" of the current element. Note that elements can have multiple ancestor elements
The two methods parent() and parents() are easy to distinguish. Among them, parent() is a singular number, so there is only one element to be searched for, which is the parent element. parents() is a plural number, so there are multiple elements to be searched, that is, all ancestor elements (including parent elements, grandfather elements, etc.).
Syntax:
$().parents(selector)
Description:
selector is an optional parameter, which is a selector used to find ancestor elements that meet the conditions. When the parameter is omitted, it means that the ancestor element does not need to meet any conditions; when the parameter is not omitted, it means that the ancestor element needs to meet the condition.
Example: Find all ancestor elements
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
var parents = $("span").parents();
var result = [];
$.each(parents, function(){
var item = this.tagName.toLowerCase();
result.push(item);
});
console.log(result.join(","));
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>
<strong>
<span>绿叶学习网</span>
</strong>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>The console output is as shown below.

Analysis:
("span").parents() returns a collection of jQuery objects, in this example , we use .each() to traverse all ancestor elements of the span element. For the .each() method, we will introduce it in detail in subsequent chapters. Some friends will ask: "To get the tag name of an element, shouldn't you use (this).tagName? Why is this.tagName used here?"
$(this) is a jQuery object , which calls jQuery methods or properties, such as click(), keyup(), etc. this is a DOM object, which calls methods or properties of the DOM object, such as this.id, this.value, etc. Since the tagName attribute belongs to the DOM object, we use this.tagName here.
3、parentsUntil()
在jQuery中,parentsUntil()方法是parents()方法的一个补充,它可以查找“指定范围”的所有祖先元素,相当于在parents()方法返回的集合中截取一部分。
语法:
$().parentsUntil(selecotr)
说明:
selector是一个可选参数,它是一个选择器,用来选择符合条件的祖先元素。
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<script ></script>
<script>
$(function(){
var parents = $("span").parentsUntil("div");
var result = [];
$.each(parents, function(){
var item = this.tagName.toLowerCase();
result.push(item);
});
console.log(result.join(","));
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>
<strong>
<span>绿叶学习网</span>
</strong>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>控制台输出结果如下图所示。

分析:
在实际开发中,我们一般只会用到parent()方法和parents()这两个,极少用到parentsUntil()。因此对于parentsUntil()方法,我们了解一下就行。
jQuery查找后代元素
在jQuery中,如果想要查找当前元素的后代元素(子元素、孙元素等),我们有以下3种方法:
- (1)children()
- (2)find()
- (3)contents()
1、children()
在jQuery中,我们可以使用children()方法来查找当前元素的“子元素”。注意,children()方法只能查找子元素,不能查找其他后代元素。
语法:
$().children(selector)
说明:
selector是一个可选参数,它是一个选择器,用来查找符合条件的子元素。当参数省略,表示选择所有子元素;当参数不省略时,表示选择符合条件的子元素。
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<style lang="">
p{margin:6px 0;}
</style>
<script ></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#wrapper").hover(function(){
$(this).children(".select").css("color", "red");
},function(){
$(this).children(".select").css("color", "black");
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrapper">
<p>子元素</p>
<p>子元素</p>
<div>
<p>孙元素</p>
<p>孙元素</p>
</div>
<p>子元素</p>
<p>子元素</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>默认情况下,预览效果如下图所示。

当鼠标移到id="wrapper"的div元素上面,此时预览效果如下图所示。

分析:
$(this).children(".select")表示获取当前元素下的class="select"的子元素。我们可以发现,class="select"的孙元素却不会被选中。
2、find()
在jQuery中,我们可以使用find()方法来查找当前元素的“后代元素”。注意,find()方法不仅能查找子元素,还能查找其他后代元素。
语法:
$().find(selector)
说明:
selector是一个可选参数,它是一个选择器,用来查找符合条件的后代元素。当参数省略,表示选择所有后代元素;当参数不省略时,表示选择符合条件的后代元素。
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<style lang="">
p{margin:6px 0;}
</style>
<script ></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#wrapper").hover(function(){
$(this).find(".select").css("color", "red");
},function(){
$(this).find(".select").css("color", "black");
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrapper">
<p>子元素</p>
<p>子元素</p>
<div>
<p>孙元素</p>
<p>孙元素</p>
</div>
<p>子元素</p>
<p>子元素</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>默认情况下,预览效果如下图所示。

当鼠标移到id="wrapper"的div元素上面,此时预览效果如下图所示。

分析:
$(this).find(".select")表示不仅会选取当前元素下的class="select"的子元素,还会选取class="select"的孙元素。
3、contents()
在jQuery中,我们可以使用contents()方法来获取子元素及其内部文本。contents()方法和children()方法相似,不同的是,contents()返回的jQuery对象中不仅包含子元素,还包含文本内容。而children()方法返回的jQuery对象中只会包含子元素,不包含文本内容。
在实际开发中,我们极少会用到contents()方法,因此小伙伴们不需要深入了解,这里简单认识一下即可。
jQuery查找兄弟元素
兄弟元素,指的是该元素在同一个父元素下的同级元素。
在jquery中,查询同级元素一般有七个方法:siblings()、next()、nextAll()、nextUntil()、prev()、prevAll()、prevUntil()
siblings()方法,主要用于获得指定元素的同级所有元素
next()方法,主要用于获得指定元素的下一个同级元素
nextAll()方法,主要用于获得指定元素的下一个同级的所有元素
nextUntil()方法,主要用于获得指定元素的下一个同级元素,这个同级元素必须为指定元素与nextUntil()方法所设置元素之间的元素
prev()方法,主要用于获得指定元素的上一级同级元素
prevAll()方法,主要用于获得指定元素上一级所有的同级元素
prevUntil()方法,主要用于获得指定元素的上一个同级元素,这个同级元素必须为指定元素与prevUntil()方法所设置元素之间的元素
siblings()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" ></script>
</head>
<body>
<div><span>Hello</span></div>
<p class="selected">Hello Again</p>
<p>And Again</p>
<script>
$("p").siblings(".selected").css("background", "yellow");
</script>
</body>
</html>
next()方法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" ></script> </head> <body> <ul> <li>list item 1</li> <li>list item 2</li> <li class="third-item">list item 3</li> <li>list item 4</li> <li>list item 5</li> </ul> <script> $('li.third-item').next().css('background-color', 'red'); </script> </body> </html>

nextAll()方法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" ></script> </head> <body> <ul> <li>list item 1</li> <li>list item 2</li> <li class="third-item">list item 3</li> <li>list item 4</li> <li>list item 5</li> </ul> <script> $('li.third-item').nextAll().css('background-color', 'red'); </script> </body> </html>

nextUntil()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" ></script>
<style>
.siblings * {
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("li.start").nextUntil("li.stop").css({
"color": "red",
"border": "2px solid red"
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:500px;" class="siblings">
<ul>ul (父节点)
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
<li class="start">li (类名为"start"的兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的下一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的下一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的下一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li class="stop">li (类名为"stop"的兄弟节点)</li>
</ul>
</div>
<p>在这个例子中,我们返回在类名为“star”和类名为“stop”的 li元素之间的所有下一个兄弟元素。</p>
</body>
</html>
prev()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" ></script>
<style>
.siblings * {
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("li.start").prev().css({
"color": "red",
"border": "2px solid red"
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:500px;" class="siblings">
<ul>ul (父节点)
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li class="start">li (类名为"start"的li节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>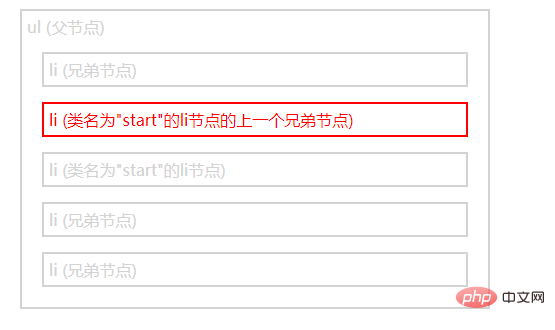
prevAll()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.10.2.min.js"></script>
<style>
.siblings * {
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("li.start").prevAll().css({
"color": "red",
"border": "2px solid red"
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:500px;" class="siblings">
<ul>ul (parent)
<li>li (类名为"start"的li的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li class="start">li (类名为"start"的li节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
</ul>
</div>
<p>在这个例子中,我们返回类名称为“star”的li元素之前的所有兄弟元素。</p>
</body>
</html>
prevUntil()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" ></script>
<style>
.siblings * {
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("li.start").prevUntil("li.stop").css({
"color": "red",
"border": "2px solid red"
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:500px;" class="siblings">
<ul>ul (父节点)
<li class="stop">li (类名为"stop"的兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (类名为"start"的li节点的上一个兄弟节点)</li>
<li class="start">li (类名为"start"的li节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
<li>li (兄弟节点)</li>
</ul>
</div>
<p>在这个例子中,我们返回在类名为“star”和“stop”的li元素之间的所有上一个兄弟元素,。</p>
</body>
</html>【推荐学习:jQuery视频教程、web前端视频】
The above is the detailed content of What are the jquery search methods?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference method: Quick start guide jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used in website development. It simplifies JavaScript programming and provides developers with rich functions and features. This article will introduce jQuery's reference method in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers get started quickly. Introducing jQuery First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the HTML file. It can be introduced through a CDN link or downloaded
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery? In front-end development, we often encounter the need to manipulate the height attributes of elements. Sometimes, we may need to dynamically change the height of an element, and sometimes we need to remove the height attribute of an element. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to remove the height attribute of an element and provide specific code examples. Before using jQuery to operate the height attribute, we first need to understand the height attribute in CSS. The height attribute is used to set the height of an element
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM manipulation and event handling in web pages. In jQuery, the eq() method is used to select elements at a specified index position. The specific usage and application scenarios are as follows. In jQuery, the eq() method selects the element at a specified index position. Index positions start counting from 0, i.e. the index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on. The syntax of the eq() method is as follows: $("s
 Introduction to how to add new rows to a table using jQuery
Feb 29, 2024 am 08:12 AM
Introduction to how to add new rows to a table using jQuery
Feb 29, 2024 am 08:12 AM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library widely used in web development. During web development, it is often necessary to dynamically add new rows to tables through JavaScript. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to add new rows to a table, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the HTML page. The jQuery library can be introduced in the tag through the following code:





