What does onboard memory mean?
Onboard memory refers to the memory integrated on the motherboard itself. It is directly welded to the motherboard of the computer and cannot be replaced. Onboard means "integrated", which refers to functions or hardware integrated into the motherboard chip, including onboard graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, RAID, etc. Generally, the functions of onboard hardware are relatively simple and cannot completely replace independent hardware; however, purchasing them can control the purchase cost.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
Onboard memory: refers to the memory integrated on the motherboard itself. It is directly welded to the motherboard of the computer and cannot be replaced.
Onboard is generally used as an adjective, which means "integrated". Refers to the functions or hardware integrated in the motherboard chip, mainly including onboard graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, RAID, etc. Generally, onboard hardware functions are relatively simple and cannot completely replace independent hardware. But purchasing can control the cost of purchasing. Buy according to your needs. For example, for office use, you can choose onboard graphics cards, sound cards, and netbooks, which can greatly save the purchase cost!
Memory is one of the important components in the computer. It is a bridge to communicate with the CPU. . All programs in the computer run in the memory, so the performance of the memory has a great impact on the computer.

Extended information:
Memory is a place where programs and data are temporarily stored, such as when we use WPS processing When writing a document, when you type characters on the keyboard, it is stored in the memory. When you choose to save, the data in the memory will be stored in the hard (disk) disk.
Memory generally uses semiconductor storage units, including random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), and cache (CACHE).
Why do thin and light notebooks almost always have onboard memory?
The main reason why thin and light laptops lose scalability is to leave more space for heat dissipation, and the second reason is to make the machine thinner and lighter. Not for cost reasons as you might imagine. Under normal circumstances (such as LPDDR4 onboard vs. DDR4 dual slot), the R&D cost of dual-slot products will be even lower.
In addition, sacrificing thinness and lightness for expandability is not something you want. If the appearance looks too silly, big, black and thick, consumers will simply vote to buy another product with their money.
There are several scalability solutions for thin and light notebooks, which actually have their own pros and cons:
-
Dual hard drive and dual memory:
stands for Combat 66. The result is that the machine is very thick and heavy. The machine only has 25w of performance release, which is significantly different from the 70w of current 14-inch high-performance products. Moreover, the D4 memory performance will also drag down the core display and do high-performance The machines dare not and cannot play like this
Single hard drive and dual slots:
represents combat X, using dual-slot D5 memory , however, the price of D5 memory is now so high that the price of the whole machine cannot be brought down. This machine will probably not sell very well this year...
Single hard drive, onboard slot memory:
represents the products ThinkPad T14 and ASUS Warrior 15. The first is the inevitable choice faced by this type of machine. Should you have 16 onboard and one empty slot, or should you have 8 onboard and 8 slots? The former is single-channel when purchased, and its performance is severely limited. The latter, once upgraded, is an asymmetric dual-channel that is tasteless and a pity to discard.
Dual hard drive onboard memory:
Personally, I think that on the basis of providing 32G memory configuration, it is the most suitable solution at this stage. 32G memory can meet the memory needs of most people during the life cycle of a thin and light all-round notebook, and the price is acceptable. Secondly, it maintains the scalability of the hard drive. Compared with memory, the gap in user demand for hard drives is significantly larger, which can be made up for by self-upgrading.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What does onboard memory mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Printer has insufficient memory and cannot print the page Excel or PowerPoint error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
Printer has insufficient memory and cannot print the page Excel or PowerPoint error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
If you encounter the problem of insufficient printer memory when printing Excel worksheets or PowerPoint presentations, this article may be helpful to you. You may receive a similar error message stating that the printer does not have enough memory to print the page. However, there are some suggestions you can follow to resolve this issue. Why is printer memory unavailable when printing? Insufficient printer memory may cause a memory not available error. Sometimes it's because the printer driver settings are too low, but it can also be for other reasons. Large file size Printer driver Outdated or corrupt Interruption from installed add-ons Misconfiguration of printer settings This issue may also occur because of low memory settings on the Microsoft Windows printer driver. Repair printing
 Large memory optimization, what should I do if the computer upgrades to 16g/32g memory speed and there is no change?
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Large memory optimization, what should I do if the computer upgrades to 16g/32g memory speed and there is no change?
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
For mechanical hard drives or SATA solid-state drives, you will feel the increase in software running speed. If it is an NVME hard drive, you may not feel it. 1. Import the registry into the desktop and create a new text document, copy and paste the following content, save it as 1.reg, then right-click to merge and restart the computer. WindowsRegistryEditorVersion5.00[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\MemoryManagement]"DisablePagingExecutive"=d
 How to check memory usage on Xiaomi Mi 14Pro?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:19 PM
How to check memory usage on Xiaomi Mi 14Pro?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:19 PM
Recently, Xiaomi released a powerful high-end smartphone Xiaomi 14Pro, which not only has a stylish design, but also has internal and external black technology. The phone has top performance and excellent multitasking capabilities, allowing users to enjoy a fast and smooth mobile phone experience. However, performance will also be affected by memory. Many users want to know how to check the memory usage of Xiaomi 14Pro, so let’s take a look. How to check memory usage on Xiaomi Mi 14Pro? Introduction to how to check the memory usage of Xiaomi 14Pro. Open the [Application Management] button in [Settings] of Xiaomi 14Pro phone. To view the list of all installed apps, browse the list and find the app you want to view, click on it to enter the app details page. In the application details page
![Windows input encounters hang or high memory usage [Fix]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/170835409686241.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Windows input encounters hang or high memory usage [Fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
Windows input encounters hang or high memory usage [Fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
The Windows input experience is a key system service responsible for processing user input from various human interface devices. It starts automatically at system startup and runs in the background. However, sometimes this service may automatically hang or occupy too much memory, resulting in reduced system performance. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and manage this process in a timely manner to ensure system efficiency and stability. In this article, we will share how to fix issues where the Windows input experience hangs or causes high memory usage. The Windows Input Experience Service does not have a user interface, but it is closely related to handling basic system tasks and functions related to input devices. Its role is to help the Windows system understand every input entered by the user.
 Is there a big difference between 8g and 16g memory in computers? (Choose 8g or 16g of computer memory)
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
Is there a big difference between 8g and 16g memory in computers? (Choose 8g or 16g of computer memory)
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
When novice users buy a computer, they will be curious about the difference between 8g and 16g computer memory? Should I choose 8g or 16g? In response to this problem, today the editor will explain it to you in detail. Is there a big difference between 8g and 16g of computer memory? 1. For ordinary families or ordinary work, 8G running memory can meet the requirements, so there is not much difference between 8g and 16g during use. 2. When used by game enthusiasts, currently large-scale games basically start at 6g, and 8g is the minimum standard. Currently, when the screen is 2k, higher resolution will not bring higher frame rate performance, so there is no big difference between 8g and 16g. 3. For audio and video editing users, there will be obvious differences between 8g and 16g.
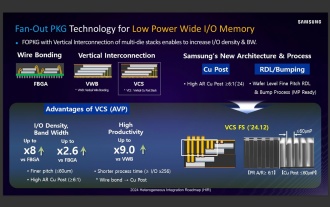 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
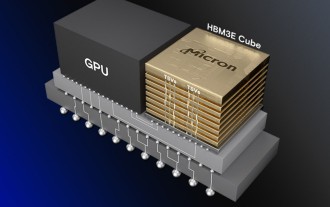 Micron: HBM memory consumes 3 times the wafer volume, and production capacity is basically booked for next year
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Micron: HBM memory consumes 3 times the wafer volume, and production capacity is basically booked for next year
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
This site reported on March 21 that Micron held a conference call after releasing its quarterly financial report. At the conference, Micron CEO Sanjay Mehrotra said that compared to traditional memory, HBM consumes significantly more wafers. Micron said that when producing the same capacity at the same node, the current most advanced HBM3E memory consumes three times more wafers than standard DDR5, and it is expected that as performance improves and packaging complexity intensifies, in the future HBM4 This ratio will further increase. Referring to previous reports on this site, this high ratio is partly due to HBM’s low yield rate. HBM memory is stacked with multi-layer DRAM memory TSV connections. A problem with one layer means that the entire
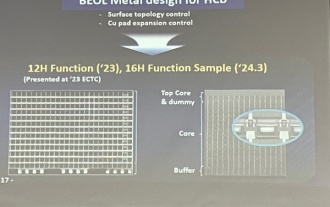 Samsung announced the completion of 16-layer hybrid bonding stacking process technology verification, which is expected to be widely used in HBM4 memory
Apr 07, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
Samsung announced the completion of 16-layer hybrid bonding stacking process technology verification, which is expected to be widely used in HBM4 memory
Apr 07, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
According to the report, Samsung Electronics executive Dae Woo Kim said that at the 2024 Korean Microelectronics and Packaging Society Annual Meeting, Samsung Electronics will complete the verification of the 16-layer hybrid bonding HBM memory technology. It is reported that this technology has passed technical verification. The report also stated that this technical verification will lay the foundation for the development of the memory market in the next few years. DaeWooKim said that Samsung Electronics has successfully manufactured a 16-layer stacked HBM3 memory based on hybrid bonding technology. The memory sample works normally. In the future, the 16-layer stacked hybrid bonding technology will be used for mass production of HBM4 memory. ▲Image source TheElec, same as below. Compared with the existing bonding process, hybrid bonding does not need to add bumps between DRAM memory layers, but directly connects the upper and lower layers copper to copper.



