How many types of cpu interfaces are there?
There are 14 types: Socket 478, Socket 775, Socket 754, Socket 939, Socket 940, Socket 603, Socket 604, Socket A, Socket B, Socket 423, Socket 370, SLOT 1, SLOT 2, SLOT A. Among them, Socket 478 is the interface type used by the early Pentium 4 series processors, with a pin number of 478.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The cpu interface generally refers to the cpu pins.
The pin-type interface is used to correspond to the corresponding slot type on the motherboard. Different types of CPU interfaces vary in the number of jacks, volume, and shape, and cannot be plugged into each other.
cpu interface type
Socket 478
The original Socket 478 interface was the early Pentium 4 The interface type used by the series processors has 478 pins. The Socket 478 Pentium 4 processor is very small and its pin arrangement is extremely compact. Intel's Pentium 4 series and P4 Celeron series both use this interface, and this kind of CPU has gradually withdrawn from the market.
However, Intel launched a new Socket 478 interface in early 2006. This interface is a dedicated interface for Intel's Core architecture processors Core Duo and Core Solo, which is similar to the early desktop version of the Pentium 4 series. Compared with the Socket 478 interface, although the number of pins is the same as 478, their pin definitions and important parameters such as voltage are completely different, so the two are not compatible with each other. With Intel's processors fully shifting to the Core architecture, more and more processors will use the new Socket 478 interface in the future. For example, the upcoming Celeron M of the Core architecture will also use this interface.
Socket 775
Socket 775, also known as Socket T, is the interface corresponding to the Intel LGA775 packaged CPU. There are LGA775 packages that use this interface. Single-core Pentium 4, Pentium 4 EE, Celeron D and dual-core Pentium D and Pentium EE CPUs. Different from the previous Socket 478 interface CPU, the bottom of the Socket 775 interface CPU does not have traditional pins, but is replaced by 775 contacts, that is, not pin type but contact type, through the 775 in the corresponding Socket 775 slot. The contact pins transmit signals. The Socket 775 interface can not only effectively improve the signal strength of the processor and increase the processor frequency, but also improve the yield rate of processor production and reduce production costs. As Socket 478 gradually fades out, Socket 775 has become the standard interface for Intel desktop CPUs.
Socket 754
Socket 754 is the CPU interface when the AMD64-bit desktop platform was initially released in September 2003. It has 754 CPU pins and only supports single-channel DDR memory. . This interface is used in low-end models of Athlon 64 and high-end models of Sempron for desktop platforms, as well as Mobile Sempron, Mobile Athlon 64 and Turion 64 for mobile platforms. As AMD fully shifts to support DDR2 memory starting in 2006, Socket 754 on the desktop platform will gradually be replaced by Socket AM2, thus unifying AMD's desktop processor interfaces. At the same time, Socket 754 on the mobile platform will also gradually be replaced by Socket AM2. Replaced by Socket S1 with 638 CPU pins and supporting dual-channel DDR2 memory. Socket 754 completed its historical mission at the end of 2007 and was eliminated. Its lifespan is much longer than that of Socket 939, which was once claimed to replace itself.
Socket 939
Socket 939 is a 64-bit desktop platform interface standard launched by AMD in June 2004. It has 939 CPU pins and supports dual-channel DDR memory. . This interface is used in the Opteron 1XX series for the entry-level server/workstation market and the Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX and Athlon 64 X2 for the desktop market. In addition, some Semprons designed for OEM manufacturers also use the Socket 939 interface. Socket 939 processors cannot be plugged into the old Socket 940 sockets, but Socket 939 still uses the same CPU fan system mode. As AMD began to fully shift to support DDR2 memory in 2006, Socket 939 was replaced by Socket AM2. It completed its historical mission in early 2007 and was eliminated. Its lifespan from launch to elimination was less than 3 years.
Socket 940
Socket 940 is the earliest released interface standard for AMD64-bit CPU. It has 940 CPU pins and supports dual-channel ECC DDR memory. This interface was used by servers/workstations such as Opteron and the original Athlon 64 FX. With the new Athlon 64 FX and some Opteron 1XX series switching to the Socket 939 interface, Socket 940 has become the dedicated interface for the entire Opteron 2XX series, the entire Opteron 8XX series, and some Opteron 1XX series. As AMD fully shifts to support DDR2 memory starting in 2006, Socket 940 will gradually be replaced by Socket F, completing its historical mission and being eliminated.
Socket 603
Socket 603 is used more professionally and is used in Intel’s high-end server/workstation platforms. The CPUs using this interface are Xeon MP and early Xeon , with 603 CPU pins. CPUs with Socket 603 interface are compatible with Socket 604 slots.
Socket 604
Similar to Socket 603, Socket 604 is still used in Intel's high-end server/workstation platform. The CPUs using this interface are 533MHz and 800MHz FSB Xeon. CPUs with Socket 604 interface are not compatible with Socket 603 slots.
Socket A
The Socket A interface, also called Socket 462, is the socket interface for AMD's Athlon XP and Duron processors. The Socket A interface has 462 slots and can support 133MHz FSB.
Socket B
Intel will start using the new LGA 1366 interface in the next generation 45nm Nehalem series processors. Also known as Socket B, it gradually replaces the LGA 775 that has been popular for many years. As can be seen from the name, LGA 1366 has about 600 more pins than LGA 775A. These pins will be used for QPI bus, three 64bit DDR3 memory channels and other connections. The interface of Bloomfield, Gainestown and Nehalem processors is LGA 1366, which is 20% larger than Penryn, which uses LGA 775 interface. The larger the processor die, the greater the heat generated, so a CPU cooler with better heat dissipation is needed. Moreover, there is an extra metal plate on the back of the processor (similar in appearance to the LGA 775 interface), which is used to better fix the processor and heat sink. LGA 1366 also puts forward new requirements for the motherboard voltage regulation module (VMR), and the version will be upgraded from 11 to 11.1.
Socket 423
The Socket 423 slot is the standard interface of the original Pentium 4 processor. The appearance of Socket 423 is similar to the previous Socket type slots, corresponding to The CPU pin count is 423. With the popularity of DDR memory, Intel developed the i845 chipset that supports SDRAM and DDR memory. The CPU socket was also changed to Socket 478, and the Socket 423 interface disappeared.
Socket 370
The Socket 370 architecture was developed by Intel to replace the SLOT architecture. It looks very similar to Socket 7 and also uses a zero-plug force slot. The corresponding The CPU is 370 pins. Intel's famous "Copper Mine" and "Tualatin" series of CPUs use this interface.
SLOT 1
SLOT 1 is a CPU interface developed by Intel to replace Socket 7 and applied for a patent. In this way, other manufacturers will not be able to produce products with SLOT 1 interface. The CPU with the SLOT1 interface is no longer the familiar square shape, but has become a flat rectangular parallelepiped, and the interface has also become a golden finger instead of a pin. SLOT 1 is a slot designed by Intel for the Pentium II series CPU. It integrates the Pentium II CPU, its related control circuits, and the second-level cache on a daughter card. This interface has been eliminated.
SLOT 2
SLOT 2 is more professional and is used in high-end servers and graphics workstation systems. The CPU used is also very expensive Xeon series. Slot 2 is longer than SLOT 1. With the Slot 2 design, 8 processors can be used in one server at the same time. Moreover, the Pentium II CPU using the Slot 2 interface adopted the most advanced 0.25 micron manufacturing process at the time. Motherboard chipsets that support the SLOT 2 interface are 440GX and 450NX.
SLOT A
The SLOT A interface is similar to Intel's SLOT 1 interface and is used by AMD's K7 Athlon. In terms of technology and performance, SLOT A motherboard is fully compatible with various original peripheral expansion card devices. It does not use Intel's P6 GTL bus protocol, but Digital's Alpha bus protocol EV6. The EV6 architecture is a more advanced architecture that uses a multi-threaded point-to-point topology and supports a bus frequency of 200MHz.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of How many types of cpu interfaces are there?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
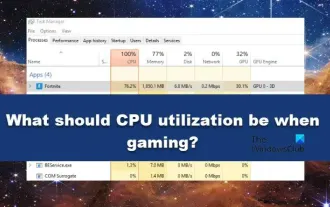 What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
It's common for games to slow down your computer because they consume a lot of resources. It's crucial to understand your CPU usage when gaming so you can avoid overloading it. Therefore, keeping track of appropriate CPU usage is key to keeping your gaming experience smooth. In this article, we'll look at the appropriate CPU usage you should achieve while your game is running. CPU utilization during gaming CPU utilization is an important indicator of processor workload and depends on the performance specifications of the CPU. More powerful CPUs generally have higher usage. A CPU with more cores and threads can improve the overall performance of your system. Multi-threading support helps unleash the full potential of your CPU. In games, CPU usage depends on processor utilization, which can affect the game
 How to set CPU performance to full in Win11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:42 PM
How to set CPU performance to full in Win11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:42 PM
Many users find that the computer is not running smoothly enough when using the Win11 system. They want to improve CPU performance, but they don't know how to do it. The following will introduce in detail how to set the CPU performance to the highest level in Win11 system to make your computer more efficient. Setting method: 1. Right-click "This PC" on the desktop and select "Properties" in the option list. 2. After entering the new interface, click "Advanced System Settings" in "Related Links". 3. In the window that opens, click the "Advanced" tab at the top, then click the & at the bottom of "Performance"
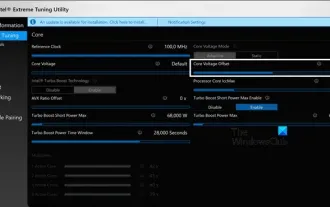 How to undervolt and overclock your CPU using Intel XTU
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to undervolt and overclock your CPU using Intel XTU
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:06 AM
Intel XTU is a powerful application that allows you to easily manage your computer's performance. You can fix overheating issues by adjusting the CPU voltage, or boost performance by overclocking. In this article, we'll look at how you can take advantage of Intel XTU to optimize your computer's performance, whether that's adjusting voltage or overclocking. What effect do undervolting and overclocking have on the CPU? Before we move on to learning how to undervolt and overclock a CPU, we first have to understand what they are. Undervolting refers to gradually reducing the voltage required by the CPU. This process helps reduce heat emissions, as high voltage results in higher temperatures. By reducing the voltage supply to the CPU, the temperature can be effectively reduced. If your laptop starts to slow down after getting hot, you should solve the problem promptly.
 The difference between boxed and bulk cpu
Jan 23, 2024 am 09:46 AM
The difference between boxed and bulk cpu
Jan 23, 2024 am 09:46 AM
The differences between boxed and bulk CPUs: 1. Quality; 2. Warranty period; 3. Fan; 4. Price; 5. Packaging; 6. Sales channels. Detailed introduction: 1. Quality, whether it is boxed or bulk, there is no difference in the quality of the CPU itself. They are all manufactured by the same manufacturer and undergo the same quality testing and quality control process; 2. Warranty period, boxed CPU A longer warranty period is usually provided, usually three years, while bulk CPUs usually only have a one-year warranty, this is because boxed CPUs are usually sold by official or authorized dealers, etc.
 How to increase the clock frequency of your computer's CPU
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to increase the clock frequency of your computer's CPU
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to Overclock Computer CPUs With the continuous advancement of technology, people's demand for computer performance is also getting higher and higher. An effective way to improve computer performance is to increase the CPU's operating frequency through overclocking. Overclocking allows the CPU to process data faster, providing higher computing power. So, how to overclock a computer CPU? The following will introduce you to the basic principles and specific operation methods of overclocking. First, let's understand how overclocking works. The operating frequency of the CPU is determined by the crystal oscillator on the motherboard
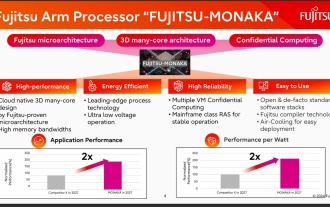 144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
According to news from this website on July 28, foreign media TechRader reported that Fujitsu introduced in detail the FUJITSU-MONAKA (hereinafter referred to as MONAKA) processor planned to be shipped in 2027. MONAKACPU is based on the "cloud native 3D many-core" architecture and adopts the Arm instruction set. It is oriented to the data center, edge and telecommunications fields. It is suitable for AI computing and can realize mainframe-level RAS1. Fujitsu said that MONAKA will achieve a leap in energy efficiency and performance: thanks to technologies such as ultra-low voltage (ULV) technology, the CPU can achieve 2 times the energy efficiency of competing products in 2027, and cooling does not require water cooling; in addition, the application performance of the processor It can also reach twice as much as your opponent. In terms of instructions, MONAKA is equipped with vector
 The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. First, we right-click the blank space of the taskbar and select the [Task Manager] option, or right-click the start logo, and then select the [Task Manager] option. 2. In the opened Task Manager interface, we click the [Services] tab on the far right. 3. In the opened [Service] tab, click the [Open Service] option below. 4. In the [Services] window that opens, right-click the [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] service, and then select the [Properties] option. 5. In the properties window that opens, change [Open with] to [Disabled], click [Apply] and then click [OK]. 6. Click the start logo, then click the shutdown button, select [Restart], and complete the computer restart.
 AM4 refuses to die, news says AMD will launch Ryzen 9 5900XT/7 5800XT: clocked at up to 4.8GHz
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
AM4 refuses to die, news says AMD will launch Ryzen 9 5900XT/7 5800XT: clocked at up to 4.8GHz
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
According to news from this website on June 1st, the source @CodeCommando tweeted today, sharing some screenshots of AMD’s upcoming presentation documents at the Computex2024 event. The content of the tweet was “AM4 will never die”, and the accompanying picture showed two new Ryzen5000XT series processors. The screenshots show the following two products: Ryzen 95900 Ryzen75800XT It is a faster variant of AMD's existing Ryzen75800X processor. Both processors are clocked up to 4.8G



