 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What types of file times are there in Linux?
What types of file times are there in Linux?
What types of file times are there in Linux?
Linux has three types of file times: 1. Access time (atime). If a file is read once, its access time will change; 2. Modification time (mtime), which refers to the last time the file content was modified. Modification time; 3. Status change time (ctime), when the status of the file is changed, the status time will change accordingly.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
In Linux, the time of a file is an important attribute of the file. There are three main times of the file in Linux, namely modification time, access time and status time:
Access time
(atime: access time): Read the content of the file once, and atime will be updated. For example, use more, cat and other commands on this file. In addition, the ls and stat commands will not modify the access time of the file.Modification time
(mtime:modifiy time):mtime is the time when the file content was last modified. For example, save the file after vi. The time listed by ls -l is this time.State change time
(ctime: change time): ctime changes with the content of the i node when writing a file, changing owner, permissions or link settings What changes is the time when the i node of the file was last modified. If the file attributes are modified once through the chmod and chown commands, this time will be updated.
Attribute description
| File time attribute | Description | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mtime | Modification time | The time when the file content was last modified, we often use The file time displayed by the ls -l command is this time. When the file content is modified, its mtime will change accordingly. |
| atime | Access time | When a read operation is performed on a file, its access time will change. For example, cat, more and other operations, but the stat and ls commands will not affect atime. |
| ctime | State time | When the status of the file is changed, the status time will change accordingly. For example, when using chmod, chown, etc. to change file attributes, the ctime of the file will be changed. |
Check the file time
Generally, according to the time attribute of the file, you can combine it with the find command to query the desired results
For example, query files updated within the last 2 hoursfind / -mtime -2
How to view Linux file attributes:
ls -lc filenameList the ctime (last status change time) of the filels -lu filenameList the atime (last status change time) of the file Access time)ls -l filenameList the mtime (last modification time) of the filestat filenameSee the three time attributes of the file at once
Create a new fileWhen touching file, ctime, atime, and mtime are the same; when After using vi to write information to a file, you must first access the file, so atime changes. When the file content changes, all ctime and mtime also change; ctime will change when using the chmod command.
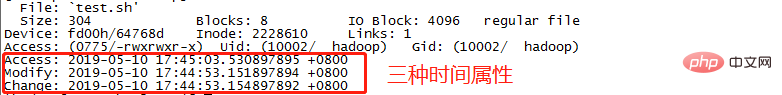
General operations that affect the three time attributes:
cat, less, more, etc. only access files and do not modify them. File operations will only modify the value of atime.
The operations of chmod and chown to modify file permissions, owners, and groups will modify the values of atime and ctime.
vi and other operations that modify the file content will modify the values of atime, ctime, and mtime.
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What types of file times are there in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Android TV Box gets unofficial Ubuntu 24.04 upgrade
Sep 05, 2024 am 06:33 AM
Android TV Box gets unofficial Ubuntu 24.04 upgrade
Sep 05, 2024 am 06:33 AM
For many users, hacking an Android TV box sounds daunting. However, developer Murray R. Van Luyn faced the challenge of looking for suitable alternatives to the Raspberry Pi during the Broadcom chip shortage. His collaborative efforts with the Armbia
 deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
DeepSeek is a powerful intelligent search and analysis tool that provides two access methods: web version and official website. The web version is convenient and efficient, and can be used without installation; the official website provides comprehensive product information, download resources and support services. Whether individuals or corporate users, they can easily obtain and analyze massive data through DeepSeek to improve work efficiency, assist decision-making and promote innovation.
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 BitPie Bitpie wallet app download address
Sep 10, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
BitPie Bitpie wallet app download address
Sep 10, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
How to download BitPie Bitpie Wallet App? The steps are as follows: Search for "BitPie Bitpie Wallet" in the AppStore (Apple devices) or Google Play Store (Android devices). Click the "Get" or "Install" button to download the app. For the computer version, visit the official BitPie wallet website and download the corresponding software package.
 BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet is a cryptocurrency exchange that provides a variety of trading services including spot trading, contract trading and derivatives. Founded in 2018, the exchange is headquartered in Singapore and is committed to providing users with a safe and reliable trading platform. BITGet offers a variety of trading pairs, including BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT and XRP/USDT. Additionally, the exchange has a reputation for security and liquidity and offers a variety of features such as premium order types, leveraged trading and 24/7 customer support.
 Detailed explanation: Shell script variable judgment parameter command
Sep 02, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
Detailed explanation: Shell script variable judgment parameter command
Sep 02, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The system variable $n is the parameter passed to the script or function. n is a number indicating the number of parameters. For example, the first parameter is $1, and the second parameter is $2$? The exit status of the previous command, or the return value of the function. Returns 0 on success, 1 on failure $#Number of parameters passed to the script or function $* All these parameters are enclosed in double quotes. If a script receives two parameters, $* is equal to $1$2$0The name of the command being executed. For shell scripts, this is the path to the activated command. When $@ is enclosed in double quotes (""), it is slightly different from $*. If a script receives two parameters, $@ is equivalent to $1$2$$the process number of the current shell. For a shell script, this is the process I when it is executing
 Zabbix 3.4 Source code compilation installation
Sep 04, 2024 am 07:32 AM
Zabbix 3.4 Source code compilation installation
Sep 04, 2024 am 07:32 AM
1. Installation environment (Hyper-V virtual machine): $hostnamectlStatichostname:localhost.localdomainIconname:computer-vmChassis:vmMachineID:renwoles1d8743989a40cb81db696400BootID:renwoles272f4aa59935dcdd0d456501Virtualization:microsoftOperatingSystem:CentOS Linux7(Core)CPEOSName:cpe:
 Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi OKX, the world's leading digital asset exchange, has now launched an official installation package to provide a safe and convenient trading experience. The OKX installation package of Ouyi does not need to be accessed through a browser. It can directly install independent applications on the device, creating a stable and efficient trading platform for users. The installation process is simple and easy to understand. Users only need to download the latest version of the installation package and follow the prompts to complete the installation step by step.





