What is es6 callback hell?
In es6, callback hell is multi-layer callback functions nested in each other, that is, callback functions nested in callback functions; it is an operation that occurs to achieve sequential execution of code, and it will cause us The code is very poorly readable and difficult to maintain later. Promise is used in es6 to solve the problem of callback hell.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
##Preface
Before we formally understand “callback hell”, we first understand two concepts:1. Callback function
When a function is passed as a parameter to another parameter, and it will not be executed immediately, the function can only be executed when certain conditions are met. This kind of function is called Callback. There are callback functions in the timers and Ajax that we are familiar with:setTimeout(function(){ //function(){console.log('执行了回调函数')}就是回调函数,它只有在3秒后才会执行
console.log('执行了回调函数');
},3000) //3000毫秒function(){console.log('The callback function was executed')}, in Execute after 3 seconds.
//1.创建异步对象
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest();
//2.绑定监听事件(接收请求)
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
//此方法会被调用4次
//最后一次,readyState==4
//并且响应状态码为200时,才是我们要的响应结果 xhr.status==200
if(xhr.readyState==4 && xhr.status==200){
//把响应数据存储到变量result中
var result=xhr.responseText;
console.log(result);
}
}
//3.打开链接(创建请求)
xhr.open("get","/demo/ajaxDemo",true);
//4.发送请求
xhr.send();xhr.onreadystatechange, which is executed after xhr.send() sends the request and gets the response.
2. Asynchronous tasks
The corresponding concept is "synchronous tasks". Synchronous tasks are queued for execution on the main thread, and only the previous task is executed. to perform the next task. Asynchronous tasks do not enter the main thread, but enter the asynchronous queue. Whether the previous task is completed does not affect the execution of the next task. Similarly, take the timer as an example of an asynchronous task:setTimeout(function(){
console.log('执行了回调函数');
},3000)
console.log('111');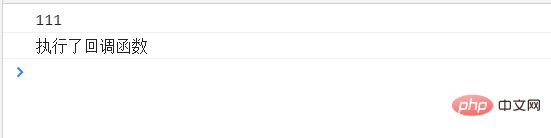 This kind of task that does not block the execution of subsequent tasks is called an asynchronous task.
This kind of task that does not block the execution of subsequent tasks is called an asynchronous task.
1. What is callback hell?
Based on the above, we can draw a conclusion: there is a code for asynchronous tasks, which cannot be guaranteed to be executed in order. So what if we have to execute the code in order? For example, if I want to say a sentence, the word order must be as follows: In martial arts, peace should be valued, martial ethics should be respected, and no fighting should be avoided. I have to do this to ensure that the order is correct:
setTimeout(function () { //第一层
console.log('武林要以和为贵');
setTimeout(function () { //第二程
console.log('要讲武德');
setTimeout(function () { //第三层
console.log('不要搞窝里斗');
}, 1000)
}, 2000)
}, 3000)
2. How to solve callback hell
1.Promise
Promise is in js A native object is a solution for asynchronous programming that can replace the traditional callback function solution.- The Promise constructor receives a function as a parameter. The asynchronous task we need to process is unloaded in the function body. The two parameters of the function are resolve and reject. When the asynchronous task is successfully executed, the resolve function is called to return the result, otherwise reject is called.
- The then method of the Promise object is used to receive the response data when the processing is successful, and the catch method is used to receive the corresponding data when the processing fails.
- The chain programming of Promise can guarantee the execution order of the code. The premise is that every time after than is processed, a Promise object must be returned so that it can be received at the next then data.
function fn(str){
var p=new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
//处理异步任务
var flag=true;
setTimeout(function(){
if(flag){
resolve(str)
}
else{
reject('操作失败')
}
})
})
return p;
}
fn('武林要以和为贵')
.then((data)=>{
console.log(data);
return fn('要讲武德');
})
.then((data)=>{
console.log(data);
return fn('不要搞窝里斗')
})
.then((data)=>{
console.log(data);
})
.catch((data)=>{
console.log(data);
}) But the biggest problem with Promise is code redundancy. The original asynchronous task is encapsulated by Promise, regardless of Using than for all operations will result in everything being then...then...then... at first glance, which is not conducive to code maintenance.
But the biggest problem with Promise is code redundancy. The original asynchronous task is encapsulated by Promise, regardless of Using than for all operations will result in everything being then...then...then... at first glance, which is not conducive to code maintenance.
async keyword, which is A keyword is placed in front of the declared function, indicating that the function is an asynchronous task and will not block the execution of subsequent functions:
async function fn(){
return '不讲武德';
}
console.log(fn()); You can see that when the async function returns data, it is automatically encapsulated into a Promise object.
You can see that when the async function returns data, it is automatically encapsulated into a Promise object.
async function fn() {
var flag = true;
if (flag) {
return '不讲武德';
}
else{
throw '处理失败'
}
}
fn()
.then(data=>{
console.log(data);
})
.catch(data=>{
console.log(data);
})
console.log('先执行我,表明async声明的函数是异步的');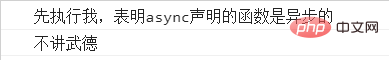
当把flag设置为false是,执行结果为: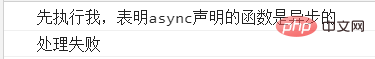
async关键字说完了,我们看看awai关键字
- await关键字只能在使用async定义的函数中使用
- await后面可以直接跟一个 Promise实例对象(可以跟任何表达式,更多的是跟一个返回Promise对象的表达式)
- await函数不能单独使用
- await可以直接拿到Promise中resolve中的数据。
//封装一个返回promise的异步任务
function fn(str) {
var p = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
var flag = true;
setTimeout(function () {
if (flag) {
resolve(str)
} else {
reject('处理失败')
}
})
})
return p;
}
//封装一个执行上述异步任务的async函数
async function test(){
var res1=await fn('武林要以和为贵'); //await直接拿到fn()返回的promise的数据,并且赋值给res
var res2=await fn('要讲武德');
var res3=await fn('不要搞窝里斗');
console.log(res1,res2,res3);
}
//执行函数
test();结果为: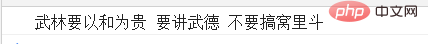
为什么叫await等待呢,因为当代码执行到async函数中的await时,代码就在此处等待不继续往下执行,知道await拿到Promise对象中resolve的数据,才继续往下执行,这样就保证了代码的执行顺序,而且使异步代码看起来更像同步代码。
总结
总结一下,当我们写代码遇到异步回调时,我们想让异步代码按照我们想要的顺序执行,如果按照传统的嵌套方式,就会出现回调地狱,这样的代码不利于维护,我们可以通过Promise对象进行链式编程来解决,这样尽管可以解决问题,但是ES7给我们提供了更加舒适的async/await语法糖,可以使得异步代码看起来更像是同步代码。
【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】
The above is the detailed content of What is es6 callback hell?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 How to reverse an array in ES6
Oct 26, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
How to reverse an array in ES6
Oct 26, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
In ES6, you can use the reverse() method of the array object to achieve array reversal. This method is used to reverse the order of the elements in the array, putting the last element first and the first element last. The syntax "array.reverse()". The reverse() method will modify the original array. If you do not want to modify it, you need to use it with the expansion operator "...", and the syntax is "[...array].reverse()".
 How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
Steps: 1. Convert the two arrays to set types respectively, with the syntax "newA=new Set(a);newB=new Set(b);"; 2. Use has() and filter() to find the difference set, with the syntax " new Set([...newA].filter(x =>!newB.has(x)))", the difference set elements will be included in a set collection and returned; 3. Use Array.from to convert the set into an array Type, syntax "Array.from(collection)".
 Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
For browser compatibility. As a new specification for JS, ES6 adds a lot of new syntax and API. However, modern browsers do not have high support for the new features of ES6, so ES6 code needs to be converted to ES5 code. In the WeChat web developer tools, babel is used by default to convert the developer's ES6 syntax code into ES5 code that is well supported by all three terminals, helping developers solve development problems caused by different environments; only in the project Just configure and check the "ES6 to ES5" option.
 What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
In es6, the temporary dead zone is a syntax error, which refers to the let and const commands that make the block form a closed scope. Within a code block, before a variable is declared using the let/const command, the variable is unavailable and belongs to the variable's "dead zone" before the variable is declared; this is syntactically called a "temporary dead zone". ES6 stipulates that variable promotion does not occur in temporary dead zones and let and const statements, mainly to reduce runtime errors and prevent the variable from being used before it is declared, resulting in unexpected behavior.
 Is require an es6 syntax?
Oct 21, 2022 pm 04:09 PM
Is require an es6 syntax?
Oct 21, 2022 pm 04:09 PM
No, require is the modular syntax of the CommonJS specification; and the modular syntax of the es6 specification is import. require is loaded at runtime, and import is loaded at compile time; require can be written anywhere in the code, import can only be written at the top of the file and cannot be used in conditional statements or function scopes; module attributes are introduced only when require is run. Therefore, the performance is relatively low. The properties of the module introduced during import compilation have slightly higher performance.
 How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
In es5, you can use the for statement and indexOf() function to achieve array deduplication. The syntax "for(i=0;i<array length;i++){a=newArr.indexOf(arr[i]);if(a== -1){...}}". In es6, you can use the spread operator, Array.from() and Set to remove duplication; you need to first convert the array into a Set object to remove duplication, and then use the spread operator or the Array.from() function to convert the Set object back to an array. Just group.
 Is es6 map ordered?
Nov 03, 2022 pm 07:05 PM
Is es6 map ordered?
Nov 03, 2022 pm 07:05 PM
The map is ordered. The map type in ES6 is an ordered list that stores many key-value pairs. The key names and corresponding values support all data types; the equivalence of key names is determined by calling the "Objext.is()" method. Implemented, so the number 5 and the string "5" will be judged as two types, and can appear in the program as two independent keys.






