 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What is the use of Linux read command?
What is the use of Linux read command?
What is the use of Linux read command?
In Linux, the read command is used to read keyboard input. It can read a line of data from the standard input and assign the value of each field of the input line to a shell variable. When using redirection , you can read a line of data in the file, the syntax is "read [parameter] [name ...]".

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
Linux read command introduction
The read command in Linux reads a line from the standard input and converts each field of the input line Values assigned to shell variables.
Syntax
read [-ers] [-a aname] [-d delim] [-i text] [-n nchars] [-N nchars] [-p prompt] [-t timeout] [-u fd] [name ...]
Parameters
| Description | |
|---|---|
| is followed by a variable, which will be considered as an array, and then assigned a value. By default, spaces are used as delimiters. | |
| is followed by an identifier. In fact, only the first character after it is useful as a sign of the end. | |
| is followed by a prompt message, that is, the prompt message is printed before input. | |
| You can use the command completion function when typing. | |
| followed by a number defines the length of the input text, which is very practical. | |
| Shield \. If this option is not available, \ will be used as an escape character. If so, \ will be a normal character. | |
| Quiet mode, no longer displayed on the screen when entering characters, such as entering a password when logging in. | |
| followed by the number of seconds defines the waiting time for entering characters. | |
| Followed by fd, read from the file descriptor, which can be newly opened by exec. |
Description
The read internal command is used to read a single line of data from standard input. This command can be used to read keyboard input, and when using redirection, can read a line of data from a file.read command usage example
1. Simple reading
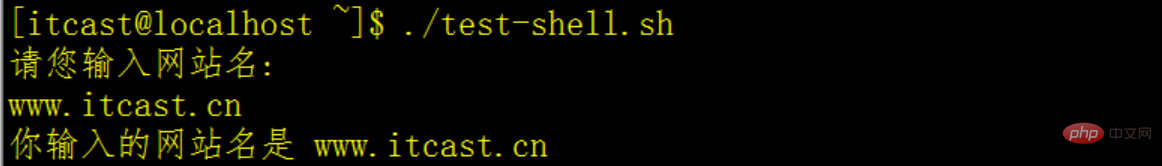
#!/bin/bash echo "请您输入网站名: " #读取从键盘的输入 read website echo "你输入的网站名是 $website" exit 0 #退出
2. Read the file
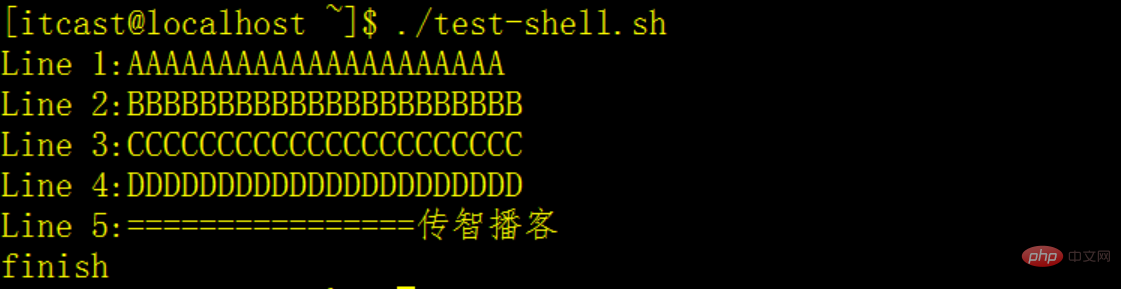
Every time you call the read command, "one line" of text in the file will be read. When the file has no readable lines, the read command exits with a non-zero status. We can use the cat command to transfer the results directly to the while command containing the read command. The content of the test file test.txt is as follows:AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAThe script is as follows, you can put the script into xxx.sh for executionBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD
=========== ===== Chuanzhi Podcast
#!/bin/bash count=1 cat test.txt | while read line # cat 命令的输出作为read命令的输入,read读到>的值放在line中 do echo "Line $count:$line" count=$[ $count + 1 ] # 注意中括号中的空格。 done echo "finish" exit 0
3. Example:
read 1987name 从标准输入读取输入并赋值给变量1987name。 read first last 从标准输入读取输入到第一个空格或者回车,将输入的第一个单词放到变量first中,并将该行其他的输入放在变量last中。 read 从标准输入读取一行并赋值给特定变量REPLY。 read -a arrayname 把单词清单读入arrayname的数组里。 read -p "text" 打印提示(text),等待输入,并将输入存储在REPLY中。 read -r line 允许输入包含反斜杠。 read -t 3 指定读取等待时间为3秒。 read -n 2 var 从输入中读取两个字符并存入变量var,不需要按回车读取。 read -d ":" var 用定界符“:”结束输入行。
Add an example of not allowing the password to be displayed when entering the password in the terminal.
方法1: #!/bin/bash read -p "输入密码:" -s pwd echo echo password read, is "$pwd" 方法2: #!/bin/bash stty -echo read -p "输入密码:" pwd stty echo echo echo 输入完毕。
-echo prohibits output from being sent to the terminal, while option echo allows output to be sent.
$ before the variable name. Otherwise, echo will directly output the variable name.
Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the use of Linux read command?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
This article describes how to effectively monitor the SSL performance of Nginx servers on Debian systems. We will use NginxExporter to export Nginx status data to Prometheus and then visually display it through Grafana. Step 1: Configuring Nginx First, we need to enable the stub_status module in the Nginx configuration file to obtain the status information of Nginx. Add the following snippet in your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or its include file): location/nginx_status{stub_status
 How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
This article introduces two methods of configuring a recycling bin in a Debian system: a graphical interface and a command line. Method 1: Use the Nautilus graphical interface to open the file manager: Find and start the Nautilus file manager (usually called "File") in the desktop or application menu. Find the Recycle Bin: Look for the Recycle Bin folder in the left navigation bar. If it is not found, try clicking "Other Location" or "Computer" to search. Configure Recycle Bin properties: Right-click "Recycle Bin" and select "Properties". In the Properties window, you can adjust the following settings: Maximum Size: Limit the disk space available in the Recycle Bin. Retention time: Set the preservation before the file is automatically deleted in the recycling bin
 How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
To restart the Apache server, follow these steps: Linux/macOS: Run sudo systemctl restart apache2. Windows: Run net stop Apache2.4 and then net start Apache2.4. Run netstat -a | findstr 80 to check the server status.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 The importance of Debian Sniffer in network monitoring
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
The importance of Debian Sniffer in network monitoring
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Although the search results do not directly mention "DebianSniffer" and its specific application in network monitoring, we can infer that "Sniffer" refers to a network packet capture analysis tool, and its application in the Debian system is not essentially different from other Linux distributions. Network monitoring is crucial to maintaining network stability and optimizing performance, and packet capture analysis tools play a key role. The following explains the important role of network monitoring tools (such as Sniffer running in Debian systems): The value of network monitoring tools: Fast fault location: Real-time monitoring of network metrics, such as bandwidth usage, latency, packet loss rate, etc., which can quickly identify the root cause of network failures and shorten the troubleshooting time.
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud



