What encoding format is flac?
FLAC is a lossless audio compression encoding and a digital music file format; unlike other lossy compression encodings such as MP3 and AAC, it does not destroy any original audio information, so music can be restored CD sound quality. FLAC is lossless compression, which means that no information will be lost after the audio is compressed with FLAC encoding. After the FLAC file is restored to a WAV file, the content will be the same as the WAV file before compression.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
flac is one of the currently popular digital music file formats.
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec), Chinese can be interpreted as lossless audio compression coding.
FLAC is a well-known set of free audio compression codes, which is characterized by lossless compression. Unlike other lossy compression codes such as MP3 and AAC, it does not destroy any original audio information, so it can restore the sound quality of music discs.

FLAC is free and supports most operating systems, including Windows, systems developed based on Unix Like kernels (Linux, BSD, Solaris, IRIX, AIX, etc.) , BeOS, OS/2, Amiga. And FLAC provides a build system on the development tools autotools, MSVC, Watcom C, and Project Builder.
Features
Lossless compression: The encoded audio (PCM) data does not have any information loss, and the decoded output audio is consistent with the encoder's Every byte of input is the same. Each data frame has a 16-bit CRC check code of the current frame, which is used to monitor data transmission errors. For the entire audio data, an MD5 tag for the original uncompressed audio data is also stored in the file header, which is used to verify the data during decoding and testing. When a computer plays a WAV file, it sends the PCM data in the WAV file directly to the sound card. When the computer plays FLAC, it needs to first decode the FLAC into PCM data and then send it to the sound card. It just adds a decoding link, just like decompressing a RAR file. The PCM data is no different from the WAV before compression.
Fast: FLAC pays more attention to the speed of decoding. Decoding only requires integer operations and has very low computational speed requirements compared to most encoding methods. Real-time decoding can be easily achieved on very common hardware.
Hardware support: Because FLAC provides free decoding examples and has low decoding complexity, FLAC was the only lossless compression encoding with widespread and good hardware support until 2012.
Can be used for streaming media: Each data frame of FLAC contains all the information required for decoding. The current frame is decoded without reference to the data frames preceding or following it. FLAC uses a synchronization code and CRC (similar to encoding formats such as MPEG) so that the decoder can have minimal time delay when positioning jumps in the data stream.
Can be positioned: FLAC supports fast sampling and precise positioning. This is not only beneficial for playback, but also makes FLAC files easier to edit.
Flexible metadata: New types of metadata data blocks can be defined and implemented without affecting the use of old data streams and decoders. Existing metadata types include tags, cue tables, and positioning tables. Registered applications can define their own dedicated metadata types (Annotation: This is similar to the MIDI standard).
Ideal for archiving applications: FLAC is an open encoding format, and without any data loss, you can convert it to any other format you need. In addition to the CRC and MD5 tags of each data frame to ensure data integrity, flac (Annotation: the command line encoding tool provided by the FLAC project) also provides a verify option when using this option for encoding. , while encoding, the encoded data will be decoded immediately and compared with the original input data. Once a difference is found, it will exit and give an alarm.
Facilitates backing up CDs: FLAC has a "CUE table" metadata data block used to save the CD's content list and the index points of all audio tracks. You can save a CD to a single file and import the CD's cue table, so that a FLAC file can completely record all the information of the entire CD. In other words, you can embed CUE files that are usually stored separately into FLAC in the file. When your original CD is damaged, you can use this file to restore an exact copy of the CD.
Anti-damage: Due to the frame structure of FLAC, once the data stream is damaged, the loss will be limited to the damaged data frame. Usually only a short fragment is lost. When many other lossless audio compression formats encounter damage, one damage will cause the loss of all subsequent data.

Expand knowledge: analyze the difference
FLAC is different from MP3. MP3 is a lossy audio compression encoding, but FLAC is a lossless compression, which means that no information will be lost after the audio is compressed with FLAC encoding. After the FLAC file is restored to a WAV file, the content will be the same as the WAV file before compression.
This compression method is similar to ZIP, but the compression rate of FLAC is greater than ZIP and RAR, because FLAC is a compression method specially designed for the characteristics of PCM audio.
And you can use the player to play FLAC compressed files directly, just like you usually play MP3 files (there are already many car players and home audio equipment that support FLAC, you can find these equipment manufacturers on the FLAC website the link to).
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What encoding format is flac?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What file format is mdf
Feb 11, 2022 pm 02:24 PM
What file format is mdf
Feb 11, 2022 pm 02:24 PM
The full name of mdf is "Mirror Disc File", which is a media disc image file. Its function is to package the contents of CD and DVD discs into disk images similar to ISO files, so that they can be spread on the network; MDF files are widely used, such as The release of software, games, videos, even operating systems, and more.
 How to write the qq mailbox format? What is the qq mailbox format?
Feb 22, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
How to write the qq mailbox format? What is the qq mailbox format?
Feb 22, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
QQ email: QQ number@qq.com, English QQ email: English or numbers@qq.com, foxmail email account: set up your own account@foxmail.com, mobile phone email account: mobile phone number@qq.com. Tutorial Applicable Model: iPhone13 System: IOS15.3 Version: QQ Mailbox 6.3.3 Analysis 1QQ mailbox has four formats, commonly used QQ mailbox: QQ number@qq.com, English QQ mailbox: English or numbers@qq.com, foxmail Email account: set up your own account@foxmail.com, mobile phone email account: mobile phone number@qq.com. Supplement: What is qq mailbox? 1 The earliest QQ mailbox was only between QQ users
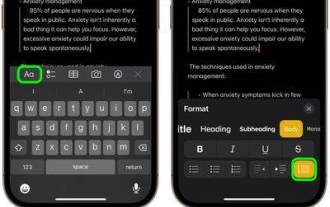 How to use block quotes in Apple Notes
Oct 12, 2023 pm 11:49 PM
How to use block quotes in Apple Notes
Oct 12, 2023 pm 11:49 PM
In iOS 17 and macOS Sonoma, Apple has added new formatting options for Apple Notes, including block quotes and a new Monostyle style. Here's how to use them. With additional formatting options in Apple Notes, you can now add block quotes to your notes. The block quote format makes it easy to visually offset sections of writing using the quote bar to the left of the text. Just tap/click the "Aa" format button and select the block quote option before typing or when you are on the line you want to convert to a block quote. This option applies to all text types, style options, and lists, including checklists. In the same Format menu you can find the new Single Style option. This is a revision of the previous "equal-width"
 What is the xlsx format file?
Jul 06, 2022 pm 03:28 PM
What is the xlsx format file?
Jul 06, 2022 pm 03:28 PM
xlsx is a table file for Microsoft's "Office Excel"; xlsx is a compressed file based on the "Office Open XML" standard that replaces the previous proprietary default file format, with an "x" added to the end of the traditional file extension, and can be opened by any " Any word processing software that uses .xlsx" files can convert this document into a ".xls" file.
 What is the file format of ink?
Feb 03, 2023 pm 02:32 PM
What is the file format of ink?
Feb 03, 2023 pm 02:32 PM
ink is the file format of a shortcut; a shortcut is a file object that is similar in function to a symbolic link, but is essentially different from a symbolic link; a shortcut is an ordinary file, not a symbol, and its extension is ".lnk" , so the shortcut can be copied, moved, changed or deleted; the shortcut can point to a file, folder or any other legal location in the system.
 What does fdf file mean?
Jan 31, 2023 am 10:24 AM
What does fdf file mean?
Jan 31, 2023 am 10:24 AM
FDF files are a format file similar to PDF files. They are a form data format used to export data from PDF form fields; FDF files are usually smaller than PDF files because they contain form field data rather than the entire form. The FDF file format can encapsulate text, fonts, formats, colors, and graphics and images independent of device and resolution in one file; it can also include electronic information such as hypertext links, sounds, and dynamic images, and supports special-length files and integration The degree of safety and reliability are high.
 How to open eml file
Feb 23, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
How to open eml file
Feb 23, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
eml file is an email file format that contains the original content and information of an email. Usually, the eml file is generated by an email client or email server and saves complete email data, including sender, recipient, subject, body, attachments, etc. To open eml files, you can use the following software: Mail client software: Most mail client software supports opening eml files directly, such as Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Mail, Thun
 What is the format of pptm?
Jan 11, 2021 pm 02:46 PM
What is the format of pptm?
Jan 11, 2021 pm 02:46 PM
pptm is a file format of PowerPoint in the office office suite. Its full name is "macro-enabled PowerPoint presentation". pptm files can only be opened with office software of version 2007 and above. If opened with other versions of software, problems such as inability to edit and incomplete images will occur.



