What transport services does udp provide?
udp provides "connectionless" transmission services. The Chinese name of UDP is User Datagram Protocol. It is a connectionless transport layer protocol in the OSI reference model. It provides simple and unreliable transaction-oriented information transmission services; UDP provides applications with a way to send encapsulated data without establishing a connection. IP packet method.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
UDP provides connectionless transmission service. It does not need to establish a connection with the other party and can send datagrams directly. UDP only encapsulates the data transmitted by the application to the IP layer into datagrams and then sends them out. There is no need to establish a connection, no connection management, and no handshake protocol before sending data, so it is much faster than TCP. However, UDP also has its own shortcomings. It cannot guarantee the reliability of data transmission, so if important data is transmitted, the unreliability of UDP must be taken into consideration.
udp protocol introduction
The Internet protocol set supports a connectionless transmission protocol called the User Datagram Protocol (UDP, User Datagram Protocol). UDP provides a way for applications to send encapsulated IP packets without establishing a connection. RFC 768 describes UDP.
UDP is the abbreviation of User Datagram Protocol. The Chinese name is User Datagram Protocol. It is a connectionless transport layer protocol in the OSI (Open System Interconnection) reference model that provides transaction-oriented Simple Unreliable Message Delivery Service, IETF RFC 768 is the official specification of UDP. The protocol number of UDP in IP packets is 17.
The UDP protocol is used to process data packets like the TCP protocol. In the OSI model, both are located at the transport layer, which is the upper layer of the IP protocol. UDP has the disadvantage of not providing data packet grouping, assembly, and inability to sort data packets. That is to say, after a message is sent, it is impossible to know whether it has arrived safely and completely. UDP is used to support network applications that need to transmit data between computers. Numerous client/server network applications, including network video conferencing systems, require the use of UDP protocol. The UDP protocol has been used for many years since its inception. Although its initial glory has been overshadowed by some similar protocols, UDP is still a very practical and feasible network transport layer protocol even today.

Content
UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol in the OSI reference model. It is mainly used for packetization. In sequential arrival transmission, the checking and sorting of packet transmission order is completed by the application layer, providing a simple and unreliable transaction-oriented information transmission service. The UDP protocol is basically the interface between the IP protocol and the upper layer protocol. The UDP protocol is suitable for multiple applications running on the same device.
UDP provides connectionless communication and does not guarantee the reliability of transmitted data packets. It is suitable for transmitting a small amount of data at a time. The reliability of UDP transmission is responsible for the application layer. Commonly used UDP port numbers are: 53 (DNS), 69 (TFTP), and 161 (SNMP). UDP protocols include: TFTP, SNMP, NFS, DNS, and BOOTP.
UDP messages do not have reliability guarantee, sequence guarantee, flow control field, etc., and their reliability is poor. However, because the UDP protocol has fewer control options, it has small delay during data transmission and high data transmission efficiency. It is suitable for applications that do not require high reliability, or applications that can guarantee reliability, such as DNS, TFTP, and SNMP. wait.
Function
To identify multiple destination addresses on a given host, while allowing multiple applications to work on the same host and do so independently For the sending and receiving of data packets, the User Datagram Protocol UDP is designed.
UDP uses the underlying Internet protocol to transmit messages, and like IP provides unreliable connectionless packet transmission services. It does not provide functions such as packet arrival confirmation, sorting, and flow control.
UDP Helper can realize the relay and forwarding of broadcast messages of the specified UDP port, that is, convert the broadcast messages of the specified UDP port into unicast messages and send them to the specified server, playing the role of relay.
Extended knowledge:
The Internet's transport layer has two main protocols that complement each other. Connectionless is UDP, which does little in particular except give applications the ability to send packets and allow them to architect their own protocols at the required level. The connection-oriented one is TCP, which does almost everything.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What transport services does udp provide?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1374
1374
 52
52
 How to implement asynchronous communication using PHP and UDP protocols
Jul 30, 2023 pm 07:31 PM
How to implement asynchronous communication using PHP and UDP protocols
Jul 30, 2023 pm 07:31 PM
How to use PHP and UDP protocols to implement asynchronous communication In modern Internet applications, asynchronous communication has become a very important method. By using asynchronous communication, user requests can be processed concurrently without blocking the main thread, improving system performance and response speed. As a popular back-end programming language, PHP how to use UDP protocol to achieve asynchronous communication? This article will introduce how to use the UDP protocol in PHP to implement simple asynchronous communication, and attach specific code examples. 1. Introduction to UDP protocolU
 What are the UDP port numbers?
Feb 23, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
What are the UDP port numbers?
Feb 23, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
Common UDP port numbers are 53, 69, 161, 2049, 68, and 520. UDP uses port numbers to reserve their own data transmission channels for different applications: 1. Network File System (NFS), the port number is 2049; 2. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), the port number is 161; 3. Domain Name System (DNS) , the port number is 53; 4. Simple File Transfer System (TFTP), the port number is 69; 5. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), the port number is 68; 6. Routing Information Protocol, the port number is 520, etc.
 How does Java network programming use UDP for connectionless communication?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 12:51 PM
How does Java network programming use UDP for connectionless communication?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 12:51 PM
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a lightweight connectionless network protocol commonly used in time-sensitive applications. It allows applications to send and receive data without establishing a TCP connection. Sample Java code can be used to create a UDP server and client, with the server listening for incoming datagrams and responding, and the client sending messages and receiving responses. This code can be used to build real-world use cases such as chat applications or data collection systems.
 How to analyze UDP protocol
May 12, 2023 pm 02:49 PM
How to analyze UDP protocol
May 12, 2023 pm 02:49 PM
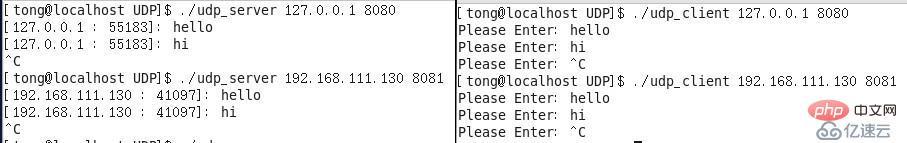
1. Socket: socket: ip address + port number. In the TCP/IP protocol, it uniquely identifies a process in network communication. Sockets are used to describe a one-to-one relationship between network connections. The TCP/IP protocol stipulates that network data flow should use big-endian byte order, that is, (memory) low address high byte (data). 2. UDP_SOCKET related UDP protocol----User Datagram Protocol (non-connection oriented)---SOCK_DGRAMh represents host, n represents network, l represents 32-bit long integer, and s represents 16-bit short integer. The IPv4 address format is defined in netinet/in.h, IPv4 address: sockadd
 What transport services does udp provide?
Feb 27, 2023 am 10:20 AM
What transport services does udp provide?
Feb 27, 2023 am 10:20 AM
UDP provides "connectionless" transport services. The Chinese name of UDP is User Datagram Protocol. It is a connectionless transport layer protocol in the OSI reference model. It provides simple and unreliable transaction-oriented information transmission services; UDP provides applications with a way to send encapsulated data without establishing a connection. IP packet method.
 What does UDP protocol mean?
Aug 08, 2023 pm 03:43 PM
What does UDP protocol mean?
Aug 08, 2023 pm 03:43 PM
UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol that provides a way to send data packets to the network, but does not guarantee the reliability, sequence and integrity of data packets, nor does it provide congestion control and flow control, etc. Function. Characteristics of UDP: 1. No connectivity, no need to establish a connection before sending data, data packets can be sent directly to the target host; 2. High efficiency, the header overhead is small, only 8 bytes; 3. Unreliability, It does not provide the reliability of data packets. After the data packet is sent, it will not be resent even if it is lost, nor does it guarantee the order of the data packets, etc.
 How to implement UDP programming for network communication based on UDP protocol in Java
May 17, 2023 pm 01:13 PM
How to implement UDP programming for network communication based on UDP protocol in Java
May 17, 2023 pm 01:13 PM
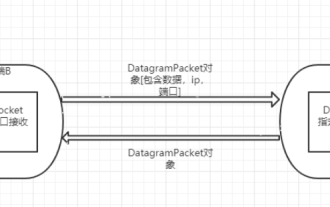
Basic introduction to UDP programming communication classes DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket [data packet/datagram] implement network programs based on the UDP protocol. UDP datagrams are sent and received through the datagram socket DatagramSocket. The system does not guarantee that the UDP datagram will be safely delivered to the destination, nor is it sure when it will arrive. The DatagramPacket object encapsulates a UDP datagram, which contains the IP address and port number of the sender and the IP address and port number of the receiver. Each datagram in the UDP protocol gives complete address information, so there is no need to establish a connection between the sender and the receiver. The two classes/objects at the core of the basic process Da
 Detailed explanation of why DNS uses UDP instead of TCP!
Mar 01, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Detailed explanation of why DNS uses UDP instead of TCP!
Mar 01, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
The main reason why DNS (DomainNameSystem) uses UDP (UserDatagramProtocol) instead of TCP (TransmissionControlProtocol) is for performance and efficiency considerations. The following explains in detail why DNS chooses to use the UDP protocol: Small requests and fast responses: DNS queries are usually small requests, requiring only a few bytes of data transfer. UDP is a connectionless protocol that does not require establishing a connection before communicating, but instead sends packets to the destination address and waits for a response. This makes UDP more suitable for fast response scenarios than TCP. Low latency: DNS queries generally require low latency to provide fast domain name resolution services.



