What does 32-bit machine refer to the computer's CPU?
32-bit machine refers to the computer's CPU that can process 32-bit binary data at the same time. The word length of the CPU indicates the CPU's ability to process data each time, which is always in multiples of 8, such as 16-bit, 32-bit, 64-bit, etc.; while the CPU of a 32-bit computer can process up to 32-bit data at a time, that is 4-byte data, for example, its EAX register is 32-bit. Of course, 32-bit computers can usually handle 16-bit and 8-bit data.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
32-bit machine refers to the computer's CPU that can process 32-bit binary data at the same time. The word length of the CPU indicates the CPU's ability to process data each time. It is always in multiples of 8, such as 16-bit, 32-bit, 64-bit, etc.
The number of bits in a computer refers to the maximum number of bits that the CPU can process at one time. The CPU of a 32-bit computer can process up to 32 bits of data at a time, which is 4 bytes of data, while a 64-bit CPU can process 64 bits of data at a time, which is 8 bytes of data.
The CPU of a 32-bit computer can process up to 32-bit data at a time. For example, its EAX register is 32-bit. Of course, a 32-bit computer can usually process 16-bit and 8-bit data. When Intel upgraded from the 16-bit 286 to the 386, in order to be compatible with the 16-bit system, it first launched the 386SX. This kind of CPU has an internal budget of 32 bits and external data transmission of 16 bits. Until the 386DX, all CPUs were 32-bit internally and externally.

Expand knowledge:
Central processing unit (CPU, central processing unit), as the computing and control core of the computer system, is The final execution unit for information processing and program execution. Since its creation, CPU has made great progress in logical structure, operating efficiency and function extension.
32-bit CPU can only process 32 bits, or 4 bytes of data at a time; while a 64-bit CPU can process 64 bits, or 8 bytes of data at a time. If we edit the 128-bit instructions in units of 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit: the old 16-bit CPU (such as Intel 80286 CPU) requires 8 instructions, the 32-bit CPU requires 4 instructions, and 64-bit CPU only needs two instructions. Obviously, under the same operating frequency, the processing speed of 64-bit CPU is faster than that of 16-bit and 32-bit.
You can compare 32-bit and 64-bit CPUs. The number of 64-bit code streams has not changed, and its width changes with the width of the instruction code; while the width of the data stream has doubled. Although in theory a 64-bit system can process twice the amount of data in one clock cycle as a 32-bit system, there is usually a gap between theory and reality.
It should be noted that the CPU not only needs registers with a wide enough bit width, but also a sufficient number of registers to ensure large amounts of data processing. Therefore, in order to accommodate more data, the registers and internal data channels must also be doubled, so the number of registers in a 64-bit CPU is generally twice that of a 32-bit CPU.
However, although the number of register bits has increased, the instruction registers for executing instructions are all the same, that is, the data flow is doubled but the instruction flow remains unchanged. In addition, increasing the number of data bits can also expand the dynamic range. In the commonly used decimal system, you can only get up to 10 integers (in the case of one digit). This is because there are only 10 different symbols from 0 to 9 to express the corresponding meanings. If you want to express numbers above 10, you need to Add one digit and two digits (00-99) to represent 100 numbers.
The calculation formula of the decimal dynamic range can be obtained: DR=10^n (n represents the number of digits). In the binary system, we can get the corresponding formula: DR=2^n, then 32-bit can reach 2^32=4.3×109, and after upgrading to 64-bit, it can reach 2^64=1.8×1019. The dynamic range has been expanded by 4.3 billion times.
Tip: Expanding the dynamic range can improve the accuracy of the data in the register to a certain extent. For example, when using a 32-bit system to process meteorological simulation computing tasks, when the processed data exceeds the maximum dynamic range that 32-bit can provide, the system will appear such as Overflow (exceeding the largest positive integer) or Underflow (below the minimum Negative integer) error message, so the data in the register cannot be guaranteed to be accurate.
In addition to computing power, compared with 32-bit CPUs, the advantage of 64-bit CPUs is also reflected in the system's control of memory. Since addresses use special integers, an ALU (arithmetic logic unit) and registers of a 64-bit CPU can handle larger integers, which means larger addresses.
The maximum addressing space of traditional 32-bit CPU is 4GB, which makes many large-scale data processing programs that require large-capacity memory appear to be stretched thin at this time, forming a bottleneck in operating efficiency. The 64-bit processor can theoretically reach 18 million TB (1TB = 1024GB), which will be able to completely solve the bottleneck phenomenon encountered by 32-bit computing systems.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What does 32-bit machine refer to the computer's CPU?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
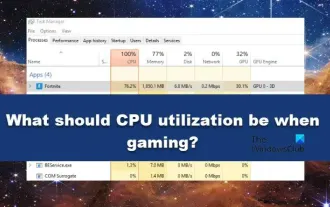 What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
It's common for games to slow down your computer because they consume a lot of resources. It's crucial to understand your CPU usage when gaming so you can avoid overloading it. Therefore, keeping track of appropriate CPU usage is key to keeping your gaming experience smooth. In this article, we'll look at the appropriate CPU usage you should achieve while your game is running. CPU utilization during gaming CPU utilization is an important indicator of processor workload and depends on the performance specifications of the CPU. More powerful CPUs generally have higher usage. A CPU with more cores and threads can improve the overall performance of your system. Multi-threading support helps unleash the full potential of your CPU. In games, CPU usage depends on processor utilization, which can affect the game
 How to set CPU performance to full in Win11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:42 PM
How to set CPU performance to full in Win11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:42 PM
Many users find that the computer is not running smoothly enough when using the Win11 system. They want to improve CPU performance, but they don't know how to do it. The following will introduce in detail how to set the CPU performance to the highest level in Win11 system to make your computer more efficient. Setting method: 1. Right-click "This PC" on the desktop and select "Properties" in the option list. 2. After entering the new interface, click "Advanced System Settings" in "Related Links". 3. In the window that opens, click the "Advanced" tab at the top, then click the & at the bottom of "Performance"
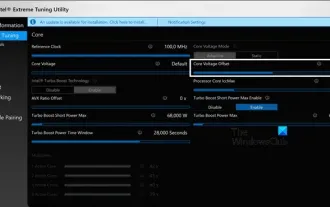 How to undervolt and overclock your CPU using Intel XTU
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to undervolt and overclock your CPU using Intel XTU
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:06 AM
Intel XTU is a powerful application that allows you to easily manage your computer's performance. You can fix overheating issues by adjusting the CPU voltage, or boost performance by overclocking. In this article, we'll look at how you can take advantage of Intel XTU to optimize your computer's performance, whether that's adjusting voltage or overclocking. What effect do undervolting and overclocking have on the CPU? Before we move on to learning how to undervolt and overclock a CPU, we first have to understand what they are. Undervolting refers to gradually reducing the voltage required by the CPU. This process helps reduce heat emissions, as high voltage results in higher temperatures. By reducing the voltage supply to the CPU, the temperature can be effectively reduced. If your laptop starts to slow down after getting hot, you should solve the problem promptly.
 The difference between boxed and bulk cpu
Jan 23, 2024 am 09:46 AM
The difference between boxed and bulk cpu
Jan 23, 2024 am 09:46 AM
The differences between boxed and bulk CPUs: 1. Quality; 2. Warranty period; 3. Fan; 4. Price; 5. Packaging; 6. Sales channels. Detailed introduction: 1. Quality, whether it is boxed or bulk, there is no difference in the quality of the CPU itself. They are all manufactured by the same manufacturer and undergo the same quality testing and quality control process; 2. Warranty period, boxed CPU A longer warranty period is usually provided, usually three years, while bulk CPUs usually only have a one-year warranty, this is because boxed CPUs are usually sold by official or authorized dealers, etc.
 How to increase the clock frequency of your computer's CPU
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to increase the clock frequency of your computer's CPU
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to Overclock Computer CPUs With the continuous advancement of technology, people's demand for computer performance is also getting higher and higher. An effective way to improve computer performance is to increase the CPU's operating frequency through overclocking. Overclocking allows the CPU to process data faster, providing higher computing power. So, how to overclock a computer CPU? The following will introduce you to the basic principles and specific operation methods of overclocking. First, let's understand how overclocking works. The operating frequency of the CPU is determined by the crystal oscillator on the motherboard
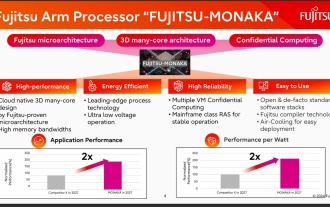 144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
According to news from this website on July 28, foreign media TechRader reported that Fujitsu introduced in detail the FUJITSU-MONAKA (hereinafter referred to as MONAKA) processor planned to be shipped in 2027. MONAKACPU is based on the "cloud native 3D many-core" architecture and adopts the Arm instruction set. It is oriented to the data center, edge and telecommunications fields. It is suitable for AI computing and can realize mainframe-level RAS1. Fujitsu said that MONAKA will achieve a leap in energy efficiency and performance: thanks to technologies such as ultra-low voltage (ULV) technology, the CPU can achieve 2 times the energy efficiency of competing products in 2027, and cooling does not require water cooling; in addition, the application performance of the processor It can also reach twice as much as your opponent. In terms of instructions, MONAKA is equipped with vector
 The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. First, we right-click the blank space of the taskbar and select the [Task Manager] option, or right-click the start logo, and then select the [Task Manager] option. 2. In the opened Task Manager interface, we click the [Services] tab on the far right. 3. In the opened [Service] tab, click the [Open Service] option below. 4. In the [Services] window that opens, right-click the [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] service, and then select the [Properties] option. 5. In the properties window that opens, change [Open with] to [Disabled], click [Apply] and then click [OK]. 6. Click the start logo, then click the shutdown button, select [Restart], and complete the computer restart.
 Leak reveals key specs of Intel Arrow Lake-U, -H, -HX and -S
Jun 15, 2024 pm 09:49 PM
Leak reveals key specs of Intel Arrow Lake-U, -H, -HX and -S
Jun 15, 2024 pm 09:49 PM
IntelArrowLakeisexpectedtobebasedonthesameprocessorarchitectureasLunarLake,meaningthatIntel'sbrandnewLionCoveperformancecoreswillbecombinedwiththeeconomicalSkymontefficiencycores.WhileLunarLakeisonlyavailableasava



