 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 A thorough understanding of MySql master-slave synchronization in one article
A thorough understanding of MySql master-slave synchronization in one article
A thorough understanding of MySql master-slave synchronization in one article
This article brings you relevant knowledge about MySql, including mainly introducing the master-slave synchronization of MySQL and its working principle, etc. Friends who are interested can take a look at it together. Welcome to collect and learn!
1 Introduction
Hello everyone, Mysql is the most commonly used database for everyone. The following is to share the knowledge points of mysql master-slave synchronization for everyone to consolidate. Mysql basic knowledge, if there are any mistakes, please correct me.
2 Overview of MySql master-slave synchronization
MySQL master-slave synchronization, namely MySQL Replication, can synchronize data from one database server to multiple database servers. The MySQL database comes with a master-slave synchronization function. After configuration, it can realize master-slave synchronization in various schemes based on database and table structures.
Redis is a high-performance in-memory database, but it is not the protagonist today; MySQL is a relational database based on disk files. Compared with Redis, the reading speed will be slower, but it is powerful. Can be used to store persistent data. In actual work, we often use Redis as a cache in conjunction with MySQL. When there is a data access request, it will first be searched from the cache. If it exists, it will be taken out directly. If it does not exist, the database will be accessed again. This improves the performance. The efficiency of reading also reduces the access pressure on the back-end database. Using a cache architecture like Redis is a very important part of a high-concurrency architecture.
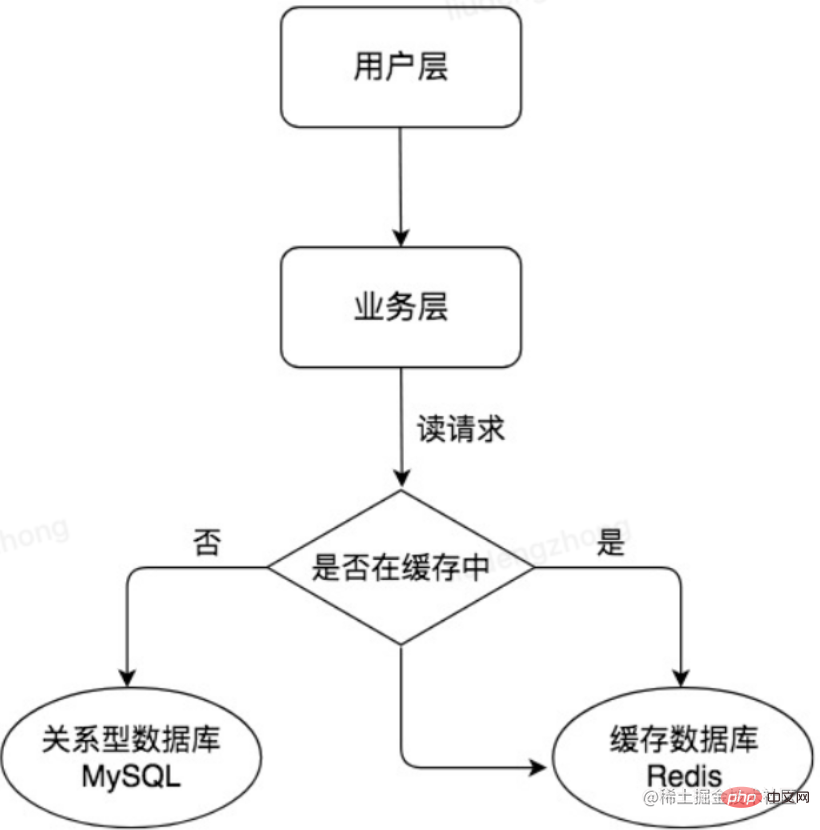
As the business volume continues to grow, the pressure on the database will continue to increase. Frequent changes in the cache are also strongly dependent on the data query results, resulting in low data query efficiency. High load, too many connections, etc. For e-commerce scenarios, there are often many typical scenarios of more reading and less writing. We can use a master-slave architecture for MySQL and separate reading and writing, so that the master server (Master) handles write requests and the slave server (Slave) handles read requests. This can further improve the concurrent processing capabilities of the database. As shown in the picture below:
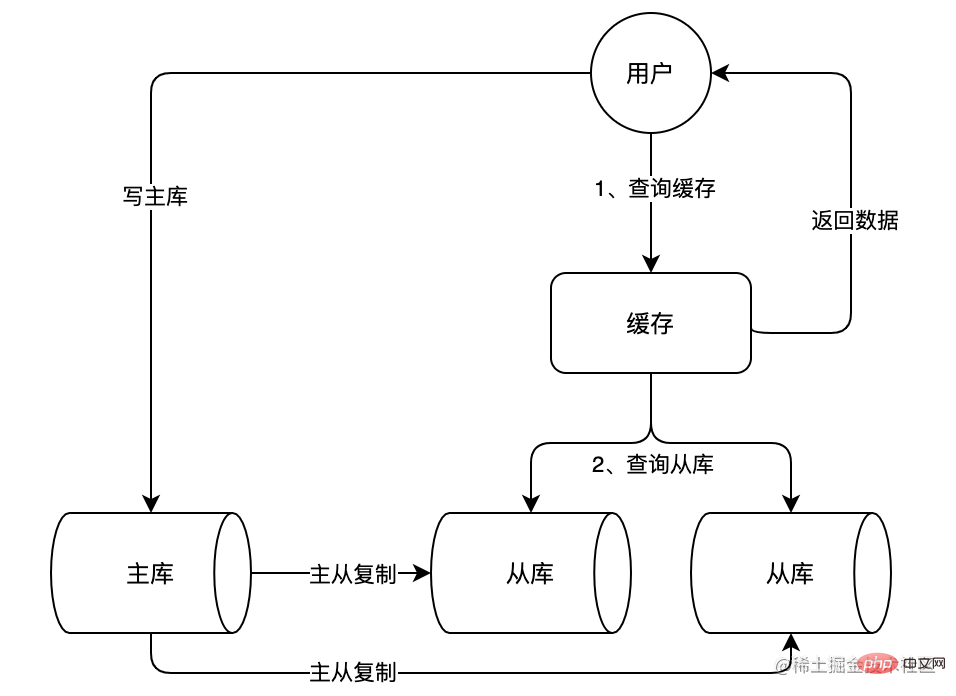
In the above picture, you can see that we have added two slave libraries. These two slave libraries can withstand a large number of read requests together and share the main load. library pressure. The slave database will continuously synchronize data from the master database through master-slave replication to ensure that the data in the slave database is consistent with the data in the master database.
Next, let’s take a look at the functions of master-slave synchronization and how master-slave synchronization is implemented.
3 The role of master-slave synchronization
Generally speaking, not all systems need to design a master-slave architecture for the database, because the architecture itself has a certain cost Yes, if our purpose is to improve the efficiency of high concurrent access to the database, then we should first optimize the SQL statements and indexes to give full play to the maximum performance of the database; secondly, adopt a caching strategy, such as using caching tools such as Redis and MongoDB, through which The advantage of high performance is to store data in an in-memory database to improve reading efficiency. Finally, the database adopts a master-slave architecture to separate reading and writing. The cost of system use and maintenance gradually increases according to the upgrade of the architecture.
Getting back to the subject, master-slave synchronization can not only improve the throughput of the database, but also has the following three aspects:
3.1 Read and write separation
We can synchronize data through master-slave replication, and then improve the concurrent processing capabilities of the database through read-write separation. To put it simply, our data is placed in multiple databases, one of which is the Master database, and the rest are Slave databases. When the data in the main database changes, the data will be automatically synchronized to the slave database, and our program can read data from the slave database, that is, using a read-write separation method. E-commerce applications are often "read more and write less", and the separation of reading and writing can achieve higher concurrent access. Originally, all read and write pressures were borne by one server. Now, multiple servers jointly handle read requests, reducing the pressure on the main database. In addition, load balancing can be performed on the slave servers, so that different read requests can be evenly distributed to different slave servers according to policies, making reading smoother. Another reason for smooth reading is to reduce the impact of lock tables. For example, if we let the main library be responsible for writing, when a write lock occurs in the main library, it will not affect the query operation of the slave library.
3.2 Data Backup
Master-slave synchronization is also equivalent to a data hot backup mechanism, which is backed up under the normal operation of the main database without affecting the provision of data services.
3.3 High Availability
Data backup is actually a redundant mechanism. Through this redundancy method, the high availability of the database can be exchanged. When the server fails, , downtime and other unavailable situations, failover can be quickly performed and the slave database can act as the master database to ensure the normal operation of the service. You can learn about the high availability SLA indicators of the e-commerce system database.
4 The principle of master-slave synchronization
Speaking of the principle of master-slave synchronization, we need to understand an important log file in the database, which is the Binlog binary file, which records events that update the database. In fact, the principle of master-slave synchronization is based on Binlog. Data is synchronized.
In the process of master-slave replication, the operation will be based on three threads. One is the binlog dump thread, located on the master node. The other two threads are the I/O thread and the SQL thread. They are respectively Located on the slave node, as shown below:
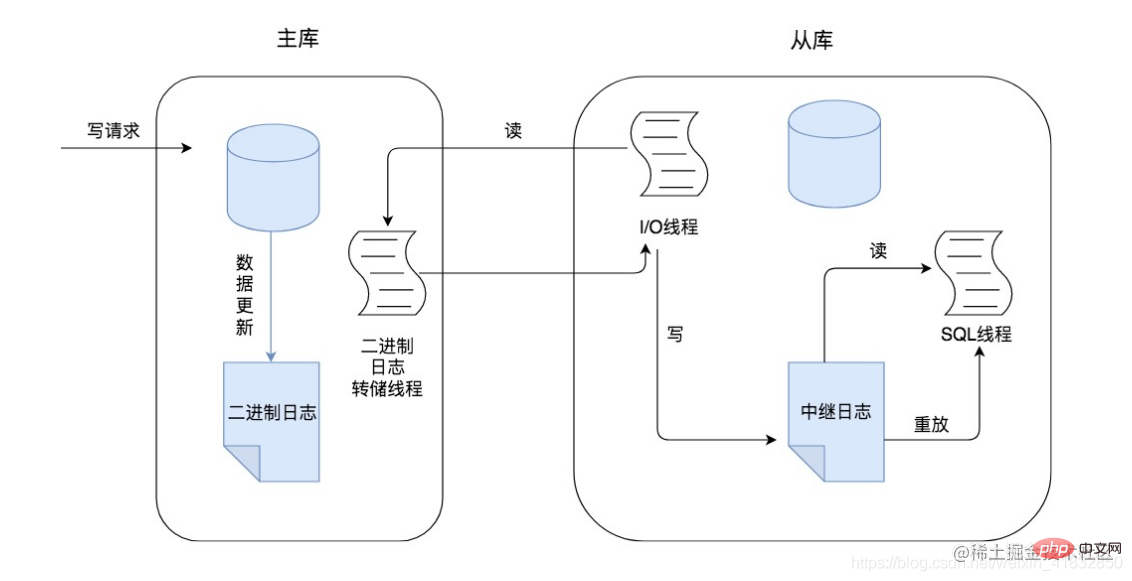
- When the master node receives a write request, the write request may be an addition, deletion, or modification operation. At this time, the update operations of the write request will be recorded in the binlog log.
- The master node will copy the data to the slave node, such as the slave01 node and slave02 node in the figure. In this process, each slave node must first be connected to the master node. When the slave When a node is connected to the master node, the master node will create a binlog dump thread for each slave node to send binlog logs to each slave node.
- The binlog dump thread will read the binlog log on the master node, and then send the binlog log to the I/O thread on the slave node. When the main library reads events, it will lock the Binglog. After the reading is completed, the lock will be released.
- After the I/O thread on the slave node receives the binlog log, it will first write the binlog log to the local relaylog, and the binlog log will be saved in the relaylog.
- The SQL thread on the slave node will read the binlog log in the relaylog, parse it into specific additions, deletions and modification operations, and put these operations performed on the master node into Do it again on the slave node to achieve the effect of data restoration, so that the data consistency between the master node and the slave node can be ensured.
5 How to solve the data consistency problem of master-slave synchronization
As you can imagine, if the data we want to operate are all stored in the same database, then the When the data is updated, a write lock can be added to the record, so that data inconsistency will not occur when reading. But at this time, the role of the slave library is to back up data, without separation of reading and writing, so as to share the pressure of the main library. Therefore, we also need to find a way to solve the problem of data inconsistency in master-slave synchronization when separating reading and writing, that is, to solve the problem of data replication between master and slave. If the slave follows data consistency To divide from weak to strong, there are the following three replication methods.5.1 Fully synchronous replication
First of all, fully synchronous replication means that after the master database completes a transaction, all slave databases must also complete the transaction. Only then can the processing results be returned to the client; therefore, although the data consistency of fully synchronous replication is guaranteed, the master library needs to wait for all slave libraries to complete a transaction, and the performance is relatively low. As shown below: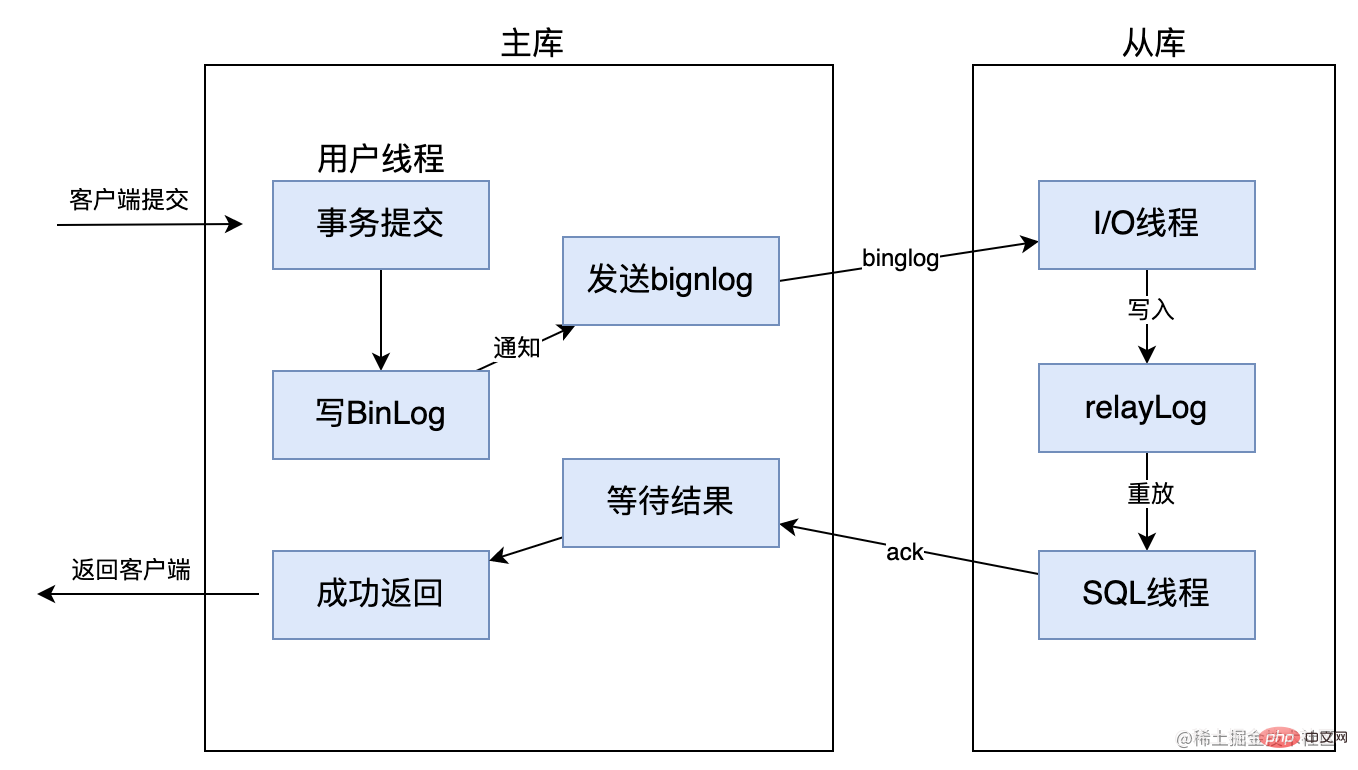
5.2 Asynchronous replication
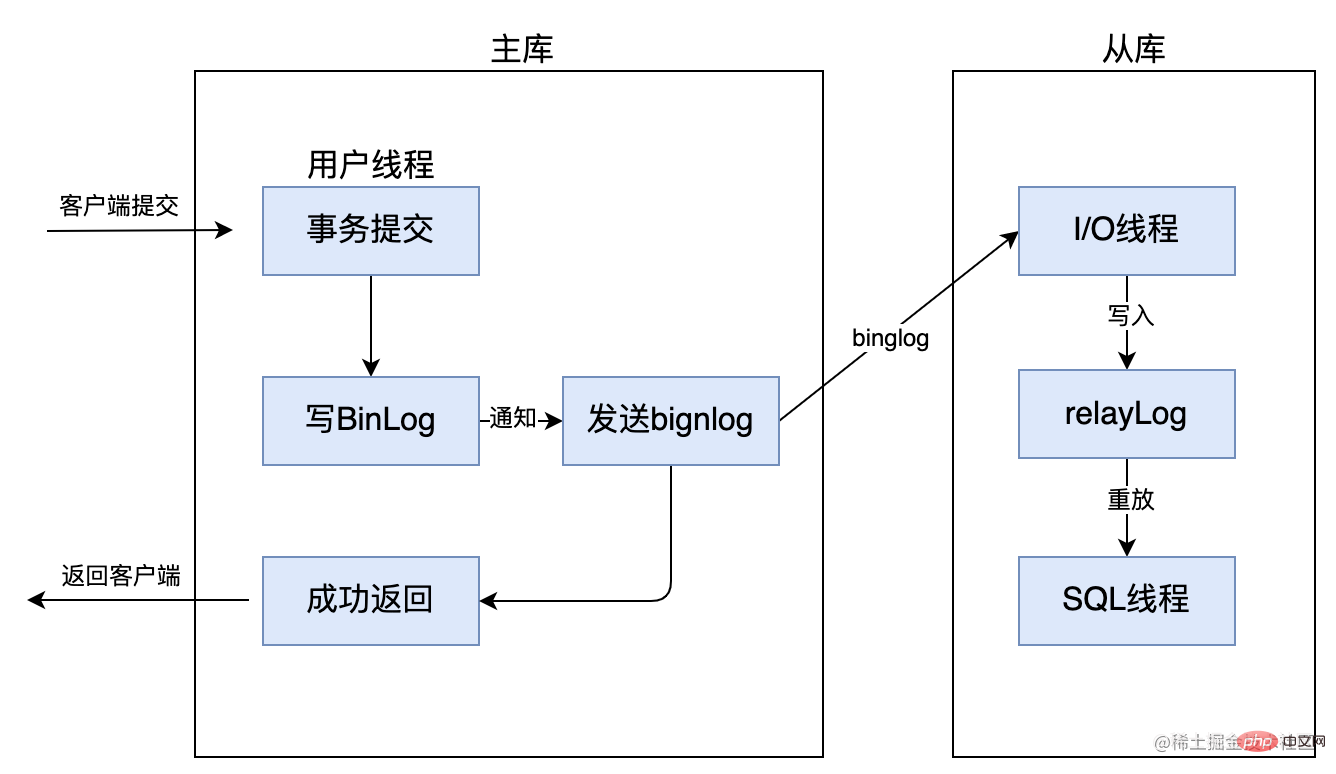
Asynchronous replication means that when the main library submits things, the binlog dump thread will be notified to send The binlog log is sent to the slave library. Once the binlog dump thread sends the binlog log to the slave library, there is no need to wait for the slave library to complete the transaction synchronously. The master library will return the processing results to the client. Because the main library only needs to complete the transaction by itself, it can return the processing results to the client without caring about whether the slave library has completed the transaction. This may lead to short-term master-slave data inconsistencies, such as If you query the new data just inserted in the master database immediately from the slave database, you may not be able to query it.Furthermore, if the main database crashes after submitting the transaction, the binlog may not have time to be synchronized to the slave database. At this time, if the master-slave node is switched for recovery failure, data loss will occur. Therefore, although asynchronous replication has high performance, it is the weakest in terms of data consistency.
Mysql master-slave replication adopts asynchronous replication by default.
5.3 Semi-synchronous replication
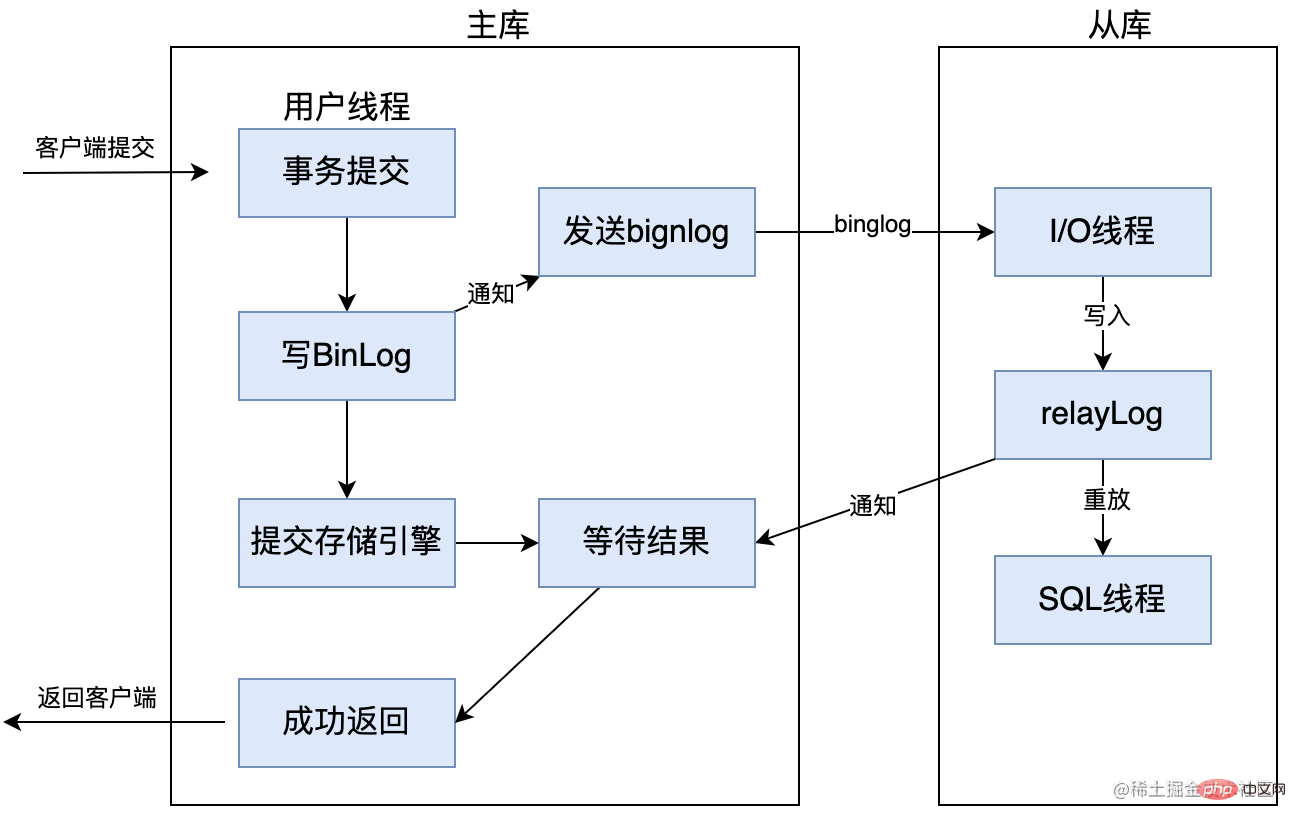
After MySQL version 5.5, semi-synchronous replication is supported. The principle is that after the client submits COMMIT, the result is not returned directly to the client, but rather waits for at least one slave library to receive the Binlog and write it to the relay log before returning it to the client. The advantage of this is that it improves the consistency of the data. Of course, compared with asynchronous replication, it increases the delay of at least one more network connection and reduces the efficiency of writing to the main database.
In the MySQL5.7 version, a rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_for_slave_count parameter has also been added. We can set the number of slave libraries that need to respond. The default is 1, which means that as long as one slave library responds, it can return to the client. If you increase this parameter, you can improve the strength of data consistency, but it will also increase the time the master database waits for the slave database to respond.
However, semi-synchronous replication also has the following problems:
- The performance of semi-synchronous replication is different compared to asynchronous replication. Compared with asynchronous replication, which does not need to wait for a response from any slave library to receive data, semi-synchronous replication needs to wait for at least one response from the slave library to confirm receipt of the binlog log, which results in greater performance losses.
- The maximum time the master library waits for the response from the slave library is configurable. If the configured time is exceeded, semi-synchronous replication will become asynchronous replication. Then, the problem of asynchronous replication will also appear.
- In versions prior to MySQL 5.7.2, semi-synchronous replication had a phantom read problem.
When the main library successfully submits the transaction and is in the process of waiting for confirmation from the slave library, at this time, the slave library has not had time to return the processing results to the client, but because the main library storage engine has already submitted the transaction, , so other clients can read data from the main library.
However, if the main library suddenly hangs up in the next second, and the next request comes in at this time, because the main library hangs up, the request can only be switched to the slave library, because the slave library has not yet received the request from the master library. The database has synchronized the data, so of course this data cannot be read from the database. Compared with the result of reading the data in the previous second, the phenomenon of phantom reading is caused.
5.4 Enhanced semi-synchronous replication
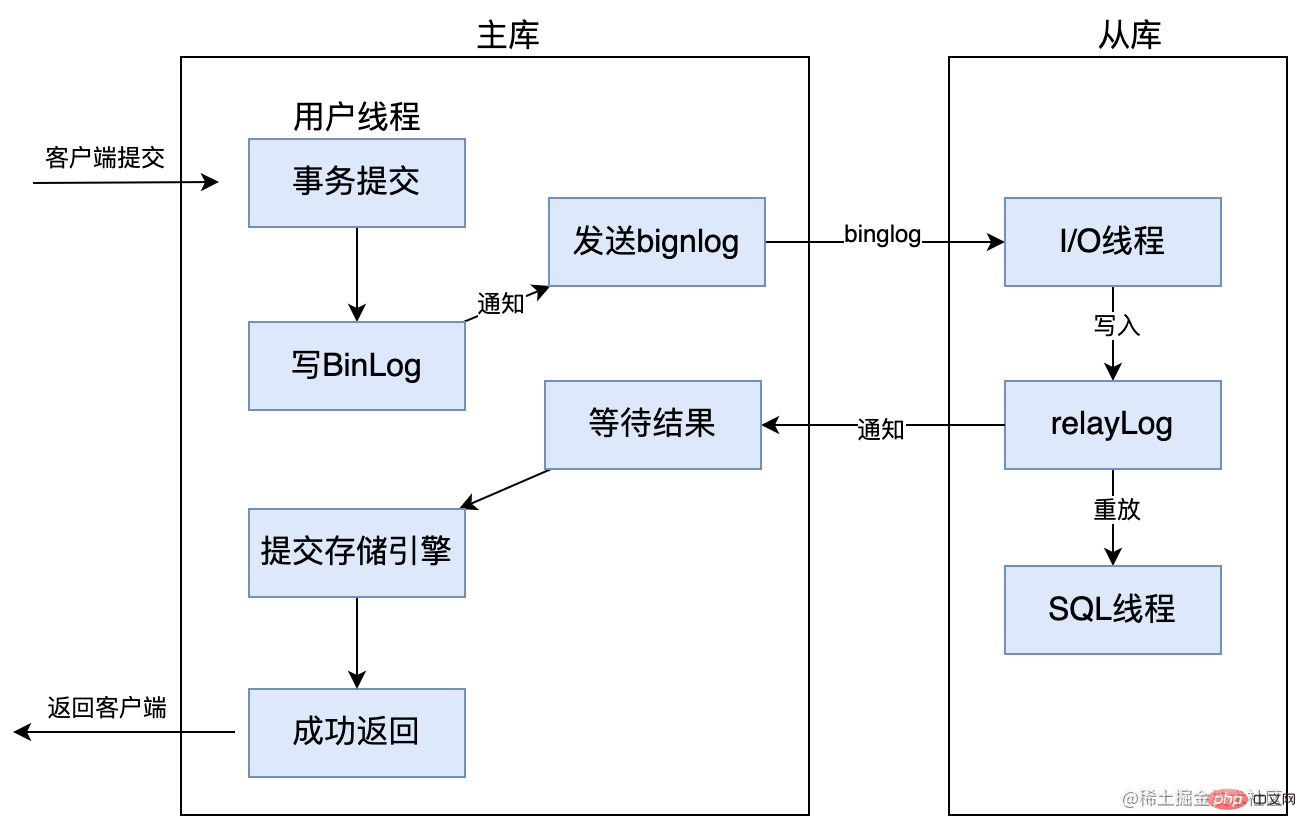
Enhanced semi-synchronous replication is an improvement made to semi-synchronous replication in versions after mysql 5.7.2. The principle is almost the same, and it mainly solves the problem of magic. Reading question.
After the master library is configured with the parameter rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point = AFTER_SYNC, before the storage engine commits the transaction, the master library must receive confirmation of completion of data synchronization from the slave library before submitting the transaction, thereby solving the phantom read problem. . Refer to the picture below:
6 Summary
Through the above content, we understand the master-slave synchronization of the Mysql database. If your The goal is only high concurrency of the database, so you can first consider optimization from aspects such as SQL optimization, indexing, and Redis cache data, and then consider whether to adopt a master-slave architecture.
In the configuration of the master-slave architecture, if we want to adopt a read-write separation strategy, we can write our own program or implement it through third-party middleware.
The advantage of writing your own program is that it is more independent. We can judge which queries to execute on the slave database. For high real-time requirements, we can also consider which queries can be executed on the main database. At the same time, the program directly connects to the database, reducing the middleware layer and reducing some performance losses.
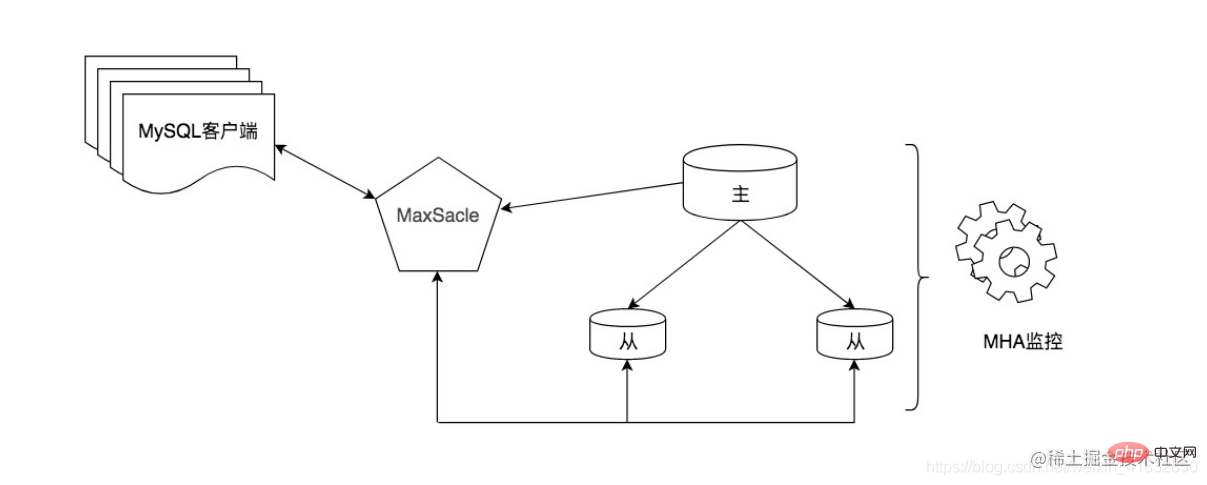
The method of using middleware has obvious advantages, it is powerful and easy to use. However, there will be some performance loss due to the addition of a middleware layer between the client and the database. At the same time, the price of commercial middleware is relatively high, and there is a certain learning cost. In addition, we can also consider using some excellent open source tools, such as MaxScale. It is MySQL data middleware developed by MariaDB. For example, in the figure below, MaxScale is used as the database proxy, and read-write separation is completed through routing and forwarding. At the same time, we can also use the MHA tool as a strongly consistent master-slave switching tool to complete the high-availability architecture of MySQL.
Recommended study: "MySQL Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of A thorough understanding of MySql master-slave synchronization in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.



