What does the ipconfig command do?
The role of the ipconfig command: display all current TCP/IP network configuration values, and refresh the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings; this command can help users check the network status and view Numerous network information, such as delay, IP, host information, physical address information, etc. Without parameters, ipconfig displays the Internet Protocol version, IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The ipconfig command is a command in the DOS system. It can help users check the network status and see many network information you want to see, such as delay, IP, host information, physical address information, etc.
The role of the ipconfig command:
Display all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refresh the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings . Without parameters, ipconfig displays Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and IPv6 addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways for all adapters.
Syntax:
ipconfig [/allcompartments] [/all] [/renew [<adapter>]] [/release [<adapter>]] [/renew6[<adapter>]] [/release6 [<adapter>]] [/flushdns] [/displaydns] [/registerdns] [/showclassid <adapter>] [/setclassid <adapter> [<classID>]]
Parameters:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Display all adapters Complete TCP/IP configuration. Adapter can represent a physical interface (such as an installed network adapter) or a logical interface (such as a dial-up connection). | |
| Displays the contents of the DNS client resolver cache, which includes preloaded entries from the local Hosts file, as well as the most recently obtained name queries for computer resolution. Any resource records. The DNS Client service uses this information to quickly resolve frequently queried names before querying its configured DNS servers. | |
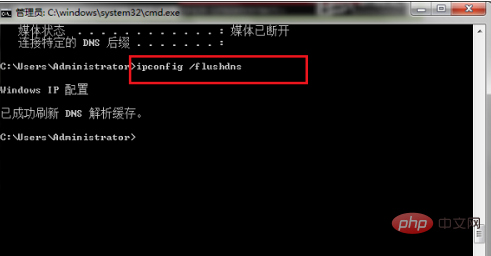
| Flush and reset the contents of the DNS client resolver cache. During DNS troubleshooting, you can use this procedure to discard negative cache entries in the cache, as well as any other entries that have been added dynamically. | |
| Initiates manual dynamic registration for the DNS name and IP address configured on the computer. You can use this parameter to troubleshoot failed DNS name registrations or to resolve dynamic update issues between the client and the DNS server without restarting the client computer. The DNS settings in the advanced properties of the TCP/IP protocol determine the names that are registered in DNS. | |
[ | Sends a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server to release the current DHCP configuration, and if not) specified Adapter discards the IP address configuration for all adapters (or, if the adapter parameter is included, the IP address configuration for a specific adapter). This parameter disables TCP/IP for adapters that are configured to automatically obtain an IP address. To specify Adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when using ipconfig without parameters. |
| adapter is discarded. ## Address configuration. This parameter disables TCP/IP for adapters configured to obtain an IP address automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when using ipconfig without parameters. | /Update
Renew (DHCP configuration for all adapters if no adapter is specified); if adapter parameters are included , renew the DHCP configuration for a specific | adapter. This parameter is available only on computers that have adapters configured to obtain IP addresses automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the The adapter name displayed when #ipconfig.##/renew6 | [
If no adapter is specified) Renew the DHCPv6 configuration for all adapters; if the adapter parameter is included, renews the DHCPv6 configuration for a specific Adapter. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters configured to obtain IPv6 addresses automatically. To specify Adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when using | ipconfigwithout parameters. /setclassid |
Configure the DHCP class ID for the specified adapter. To set the DHCP class ID for all adapters, use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in place of | Adapter. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters configured to obtain IP addresses automatically. If no DHCP class ID is specified, the current class ID is deleted. /showclassid |
Display the DHCP class ID of the specified adapter. To view the DHCP class IDs for all adapters, use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in place of | Adapter. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters configured to obtain IP addresses automatically. /? |
|
Note:
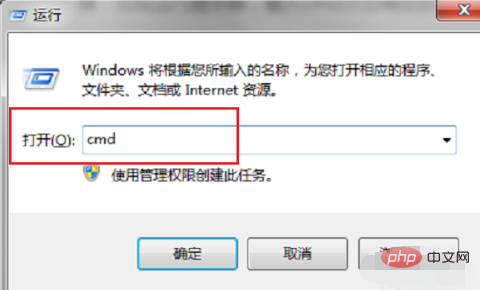
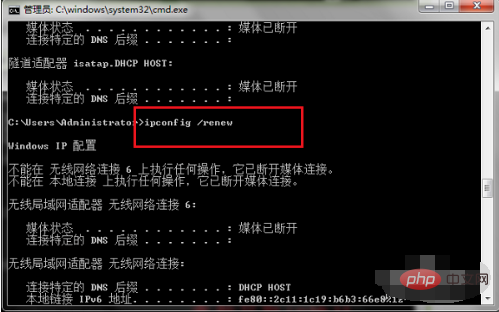
Example of using the ipconfig command Press the win R key on our computer, open Run, enter cmd, click OK, and enter the command Prompt, as shown below:
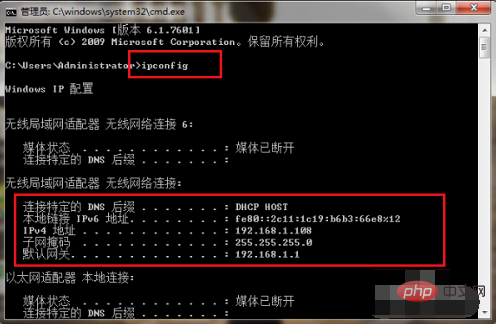
After entering the command prompt, we enter
Enter the
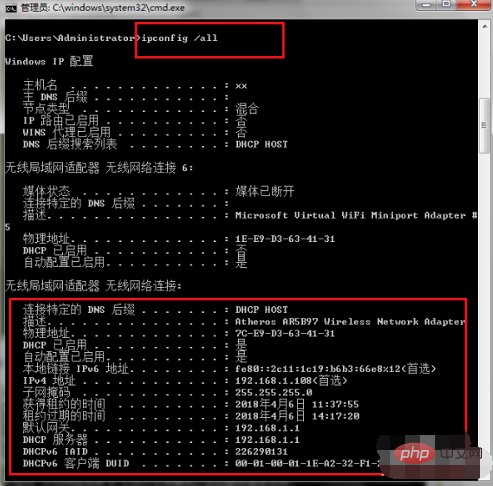
Enter the
Enter the
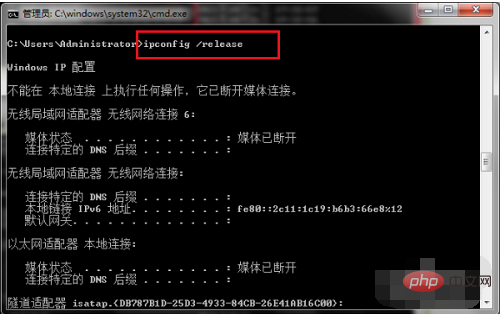
Enter the
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column! |
The above is the detailed content of What does the ipconfig command do?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52