 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What three parts does the linux process include?
What three parts does the linux process include?
What three parts does the linux process include?
The three parts of the Linux process: 1. The process control block makes a program (including data) that cannot run independently in a multi-program environment become a basic unit that can run independently, and can be combined with other Processes that are executed concurrently; 2. Program segment is the program code segment in the process that can be executed by the process scheduler on the CPU; 3. Data segment is the data segment of a process, which can be the original processed by the program corresponding to the process. Data can also be intermediate or final data generated after program execution.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
1. Definition of process
A process (Process) is a program in the computer that performs a running activity on a certain data collection. It is a system The basic unit for resource allocation is the basis of the operating system structure.
In short, it is the execution process of program.
A process is an instance of a running program, that is, a task that is being executed.
The process has a life cycle. It is created as the program runs and terminates as the program ends.
The process is the smallest unit for allocating resources. As long as a process is created, [0-3G] of user space is allocated.
As long as the user executes a program, the kernel will create a task_struct (PCB) structure, which represents the current process.
Maintains its own set of file descriptors and buffers within the process. As soon as the process execution ends, all its resources will be reclaimed by the operating system.
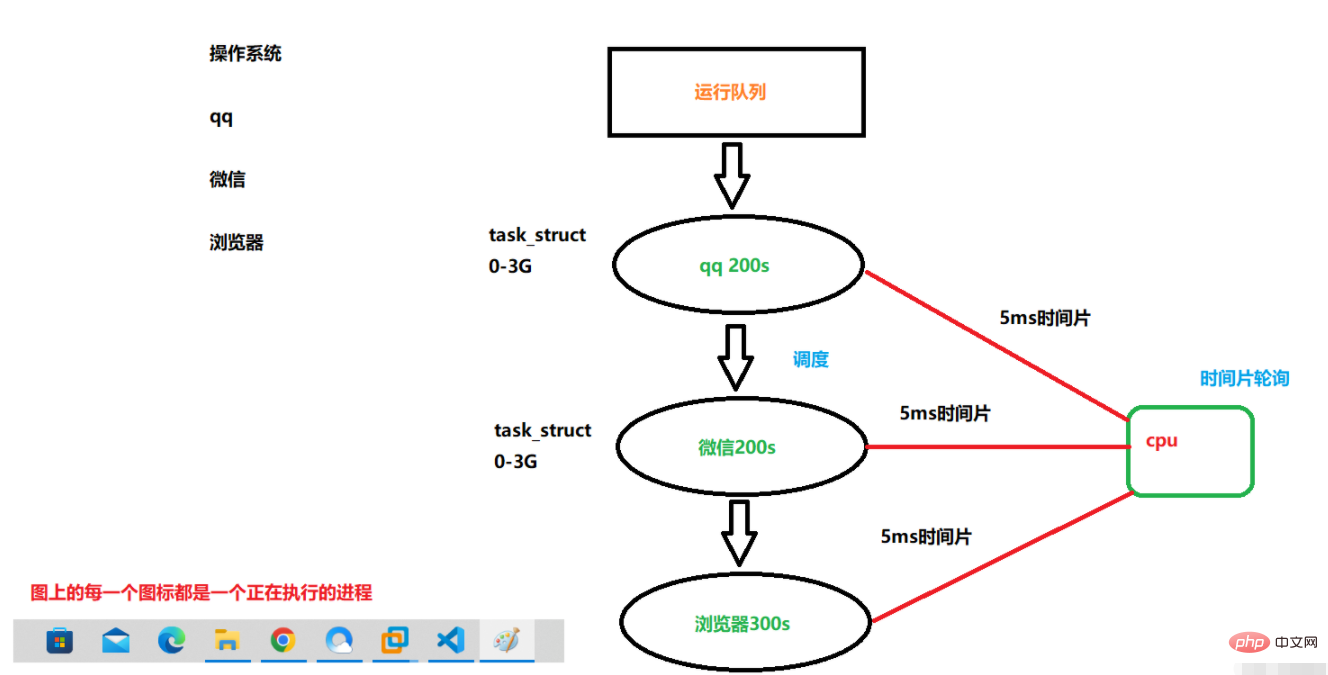
Time slice polling to achieve concurrency
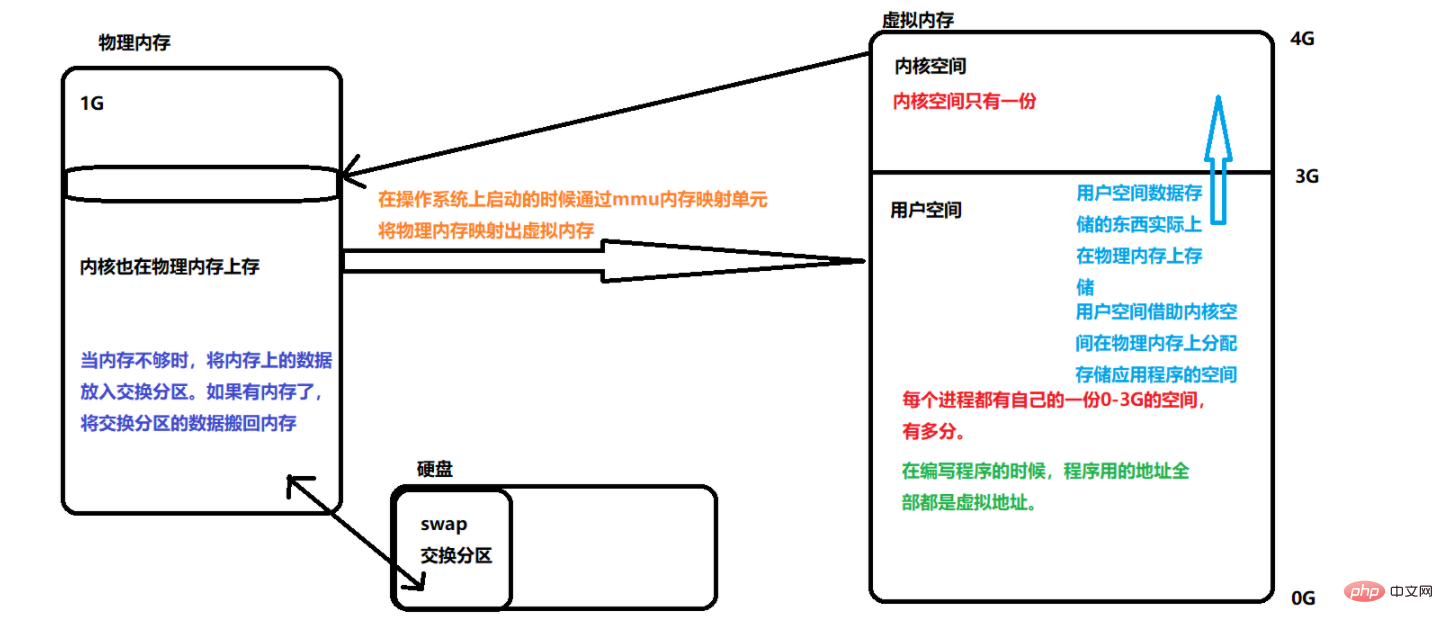
2. Characteristics of the process
Dynamicity: The essence of a process is the execution of a program in a multi-programming system. The process is dynamically generated and dies dynamically.
Concurrency: Any process can execute concurrently with other processes
Independence: A process is a basic unit that can run independently. It is also an independent unit for system resource allocation and scheduling;
Asynchronicity: Due to the mutual constraints between processes, the process has intermittent execution, that is, the processes are independent and unpredictable. Advance at a faster speed
Multiple different processes can contain the same program: a program constitutes different processes in different data sets and can obtain different results; but execution During the process, the program cannot be changed.
3. The composition and function of the process
The composition of the process consists of three parts: process control block PCB (task_struct), data segment , program segment.
Process control block: Make a program (including data) that cannot run independently in a multiprogramming environment become a basic unit that can run independently, and a process that can execute concurrently with other processes.
Program segment: It is the program code segment in the process that can be executed on the CPU by the process scheduler.
Data segment: The data segment of a process can be the original data processed by the program corresponding to the process, or the intermediate or final data generated after the program is executed.
4. Process control block
##4.1 Process control block definition
In order to describe the operation of the control process, the data structure in the system that stores the management and control information of the process is called the process control block (PCB Process Control Block). It is part of the process entity and is a part of the operating system. The most important record-keeping data structure. It is the most important data structure for process management and control. Each process has a PCB. When a process is created, the PCB is established and accompanies the entire process of running the process until the process is cancelled.
The essence of PCB is a structure. The name of PCB is different in different operating systems. In Linux, the PCB is called task_struct, and the PCB is the only means of controlling the process. Each process has a process descriptor. This "process descriptor" is task_struct. A lot of information about process control is stored in task_struct.
- Identifier (pid): The unique identifier that describes this process and is used to distinguish other processes.
- Status: task status, exit code, exit signal, etc.
- Priority: relative to the priority of other processes (the smaller the number, the higher the priority).
- Program counter: The address of the next instruction to be executed in the program.
Memory pointers: including pointers to program code and process-related data, as well as pointers to memory blocks shared with other processes.
Context data: Saving the context is to save the value in the CPU register to the memory; restoring the context is to restore the register value in the memory to the CPU;
I/O status information: includes displayed I/O requests, I/O devices assigned to the process and a list of files being used by the process.
Accounting information: may include the total processor time, the total number of clocks used, time limits, accounting accounts, etc.
Other information
##5. The difference between process and program
- A process is an execution process of a program. It is dynamic, has a life cycle, and is stored in memory.
- The program is static and has no life cycle. Stored on disk, a program is an executable file.
- Processes can more truly describe concurrency, but programs cannot.
- Processes have the ability to create other processes, but programs do not.
- The same program can correspond to multiple processes.
6. The difference between processes and threads
Usually a process can contain several threads, and they can Using the resources owned by the process, in the operating system that introduces threads, the process is usually used as the basic unit for allocating resources, and the thread is used as the basic unit for independent running and independent scheduling. Since threads are smaller than processes, they are basically not With system resources, the overhead for its scheduling will be much smaller, and it can more efficiently increase the degree of concurrent execution among multiple programs in the system.7. Types of processes
There are three types of processes: interactive process, batch process, and daemon process- Interactive process: The interactive process is maintained by the shell and interacts with the user through the shell.
For example, a text editor is an interactive process.
- Batch process: The batch process will be placed in a queue in the kernel and run as the queue runs. Its priority is relatively low.
For example, the process of gcc compiling a program.
- Daemon process: The daemon process is a process running in the background. It starts when the system starts and terminates when the system terminates.
For example, various services on windows.
Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What three parts does the linux process include?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
The error log is located in /var/log/nginx (Linux) or /usr/local/var/log/nginx (macOS). Use the command line to clean up the steps: 1. Back up the original log; 2. Create an empty file as a new log; 3. Restart the Nginx service. Automatic cleaning can also be used with third-party tools such as logrotate or configured.



