What does linux snmp service mean?
In Linux, the SNMP service refers to the Simple Network Management Protocol. It is a network management standard protocol widely used in TCP/IP networks. It provides a central computer running network management software (i.e. Network management workstation) to monitor and manage a standardized management framework (method) for computer networks. SNMP services enable network administrators to manage network performance, identify and resolve network problems, and plan for network growth.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is SNMP service?
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a network management standard protocol (application layer protocol) widely used in TCP/IP networks. It provides a central computer running network management software. (i.e. network management workstation) to monitor and manage the standardized management framework (method) of computer networks. Currently, three versions of SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 have been promulgated, which are widely used in network equipment such as network switches, routers, and printers.
SNMP is a standard protocol specially designed for managing network nodes (servers, workstations, routers, switches, HUBS, etc.) in IP networks. It is an application layer protocol. SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, identify and resolve network problems, and plan for network growth. Network management systems are notified of network problems by receiving random messages (and event reports) via SNMP.
The predecessor of SNMP is Simple Gateway Monitoring Protocol (SGMP), which is used to manage communication lines. Subsequently, people made great modifications to SGMP, especially adding SMI and MIB that conform to the Internet definition. The improved protocol is the famous SNMP. The SNMP network management framework based on TCP/IP is the current standard in the industry and consists of three main parts, namely the management information structure SMI (Structure of Management Information), the management information base MIB and the management protocol SNMP.
SMI defines the organization and identification of information used by the SNMP framework, and provides templates for MIB to define management objects and use management objects.
MIB defines a collection of management objects that can be accessed through SNMP.
The SNMP protocol is an application layer protocol that defines how the network manager reads and writes the MIB object of the agent process.
Configuring the SNMP service of Linux
1. Install the SNMP service
1) Check whether the snmp rpm package has been installed on the system
The following are the rpm packages required to install the snmp service:
libsensors3-2.10.6-55.el5.i386.rpm lm_sensors-2.10.6-55.el5.i386.rpm net-snmp-libs-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm net-snmp-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm net-snmp-utils-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm
Recommended to http://rpm. pbone.net/Download these rpm packages. This website is relatively comprehensive and contains various versions of packages.
Use command: $ rpm -qa|grep snmp
Check whether net-snmp-utils-5.3.2.2-5.el5, net-snmp-libs is installed -5.3.2.2-5.el5, net-snmp-5.3.2.2-5.el5 three rpm packages
Use command: $ rpm -qa|grep libsen
Check whether libsensors3-2.10.6-55.el5 is installed
Use command: $ rpm -qa|grep lm
Check whether lm_sensors-2.10.6 is installed -55.el5
Note:
(1) There is a certain order for the installation of these packages, and there will be a prompt during installation. For example, when installing
net-snmp-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm, you will be prompted that net-snmp-libs-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm must be installed first.
(2) net-snmp-utils-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm is not a package that must be installed, but installing it will bring a lot of help. It provides many tools, such as You can use the snmptranslate command to view oid, and you can use the snmpget, snmpwalk commands, etc.
(3)net-snmp-libs-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm、net-snmp-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm、
net The three packages -snmp-utils-5.3.2.2-5.el5.i386.rpm have certain version requirements and must be of the same version, otherwise the installation will not succeed. I am using the 5.3.2.2-5.el5 version here. You can also download other versions of rpm packages, but please note that the versions must be consistent. During installation, you will also be prompted as to which version of the package is necessary. You can download it according to the prompts. Required package.
2) Install the above rpm packages
If the above packages are not installed in the system, install them first.
Use command: rpm –ivh package name
After installation, use command: $ rpm -qa|grep snmp to check whether it has been installed Successful installation.
YUM installation:
yum install -y net-snmp net-snmp-utils
3) Start snmp service
If the installation is successful, you can use the command:
$ service snmpd start
Prompt :Starting snmpd: [ OK ], then the snmp service is started successfully.
You can set the snmp service to start automatically at boot, thus eliminating the trouble of manual startup.
Use the command: $ chkconfig snmpd on to set the snmpd service to start automatically at boot.
Then use the command: $ chkconfig --list | grep snmpd to check whether the setting has been successful.
4) Verify the snmp service
(1) Use the snmpwalk command to view the host name of the localhost of this machine
(2) Use the snmptranslate command, Check whether the snmp tool can use
(3) to test whether the remote host can obtain data.
我这里登陆了另外一台Linux主机,该主机也按照上面的步骤安装好snmp服务及snmp工具。通过这台主机,获取远端主机的数据,这时需指定远端主机的IP地址
修改 SNMP 配置文件
1)配置文件路径
2)修改配置文件

重启 SNMP 服务
snmp 服务名 snmpd.service
# 启动/停止/查看 snmp 服务 systemctl start/stop/status snmpd.service # 开启/禁用 snmp 自启动服务 systemctl enable/disable snmpd.service
使用 SNMP 软件获取 服务器信息
1)SNMP 中比较重要的配置
读写设备的密码: 在 SNMP 中称为
读Community和写Community
若使用 SNMP v3 协议版本,则密码设置比较复杂,需要密码配对-
被读取的内容 :类似于被读取的参数的寄存器/地址,在 SNMP 中称为
OIDOID的描述方式:类似IP地址,如1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.1.1
-
MIB文件:各厂商制作的,包含设备OID的配置文件
利用 SNMP 调试软件加载 MIB 文件,即可快速调试,读写设备的相关信息
MIB 文件中包含丰富内容:参数、参数的描述(帮助/含义)、参数的类型(数据类型)、参数的 OID 地址等
不同厂商可根据自己设备的特点,修改 MIB 文件,以添加专属的可用于 SNMP 协议的参数
加载错误的 MIB 文件,则 MIB 文件中记录的 OID 可能在设备中查询不到返回值
2)使用的 MIB 文件HOST-RESOURCE-MIB和UCD-SNMP
HOST-RESOURCE-MIB用于查看主机(服务器)的基础状态信息
主要包含.1.3.6.1.2.1.25中的信息,这部分内容大多数电脑、服务器都有UCD-SNMPLinux 和 Unix 系统通用的 MIB 描述文件
主要包含.1.3.6.1.4.1.2021中的信息
3)使用的 SNMP 软件

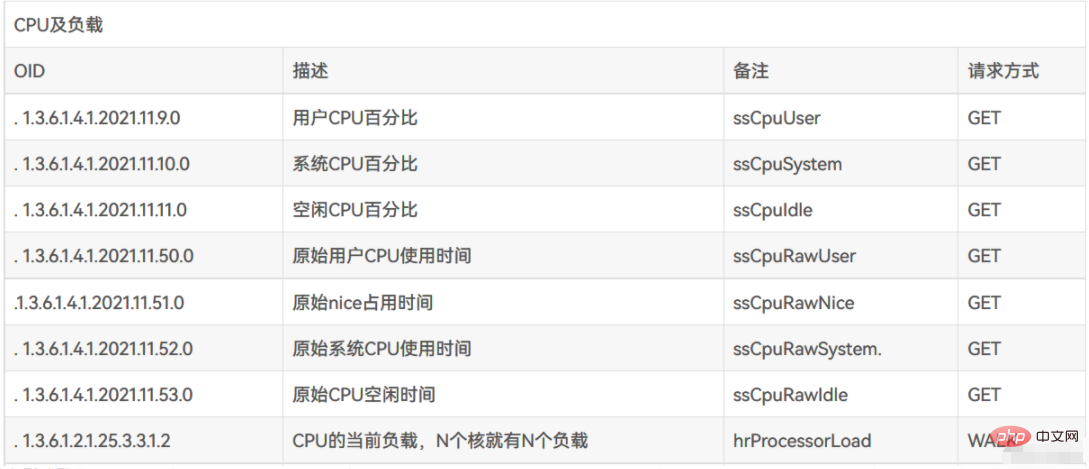
4)常用的 OID 地址

相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What does linux snmp service mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 36
36
 110
110
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.



