
Browser caching is an important direction in front-end optimization. By caching static resources, the loading time of the page can be reduced, the load on the server can be reduced, and the user experience can be improved. This article will introduce the basic principles of browser caching and common caching strategies, and implement them using code under the koa framework of nodejs.

The basic principle of browser caching is to cache static resources (such as CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) Local, when the page requests these resources again, they are obtained directly from the local instead of downloading them from the server again. This can reduce page loading time and reduce server load, improving user experience.
In the HTTP protocol, browser caching can be implemented through two mechanisms: strong caching and negotiated caching. [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial]
Expires field:
Cache-Control (alternative)
public: All content is cached (both clients and proxy servers can be cached)
private: Only cached to private cache ( Client)
no-cache: Confirm with the server whether the returned response has been changed before using the response to satisfy subsequent requests for the same URL. Therefore, if the appropriate validation token (ETag) is present, no-cache initiates a round-trip communication to validate the cached response, and can avoid downloading if the resource has not been changed.
no-store: The value is not cached
must-revalidation/proxy-revalidation: If the cached content is invalidated, the request must be sent to the server Re-authentication
max-age=xxx: The cached content will expire after xxx seconds. This option can only be used in http1.1, than last-Modified Higher priority
last-Modified (last modified date)
last-Modified: Saved on the server , record the date when the resource was last modified (it cannot be accurate to seconds. If it is modified multiple times within a few seconds, it may cause an error to hit the cache)
if-modified-since: Save In the client, the request is carried and compared with the last-Modified of the server. If it is the same, it will directly hit the cache and return the 304 status code
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
// 设置 expires方案
const setExpires = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
const expires = new Date(Date.now() + 60 * 1000);
ctx.set('Expires', expires.toUTCString());
await next();
}
// Cache-Control方案(优先执行)
const setCacheControl = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
ctx.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=60');
await next();
}
// Last-Modified方案
const setLastModified = async (ctx, next) => {
// 获取资源最后修改时间
const lastModified = new Date('2021-03-05T00:00:00Z');
// 设置 Last-Modified 头
ctx.set('Last-Modified', lastModified.toUTCString());
await next();
}
const response = (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
}
// 跟Last-Modified方案相对应
const lastModifiedResponse = (ctx) => {
// 如果资源已经修改过,则返回新的资源
if (ctx.headers['if-modified-since'] !== ctx.response.get('Last-Modified')) {
response(ctx)
} else ctx.status = 304;
}
app.get('/getMes', setExpires, response);
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server started on port 3000'));Etag/if-None-Match
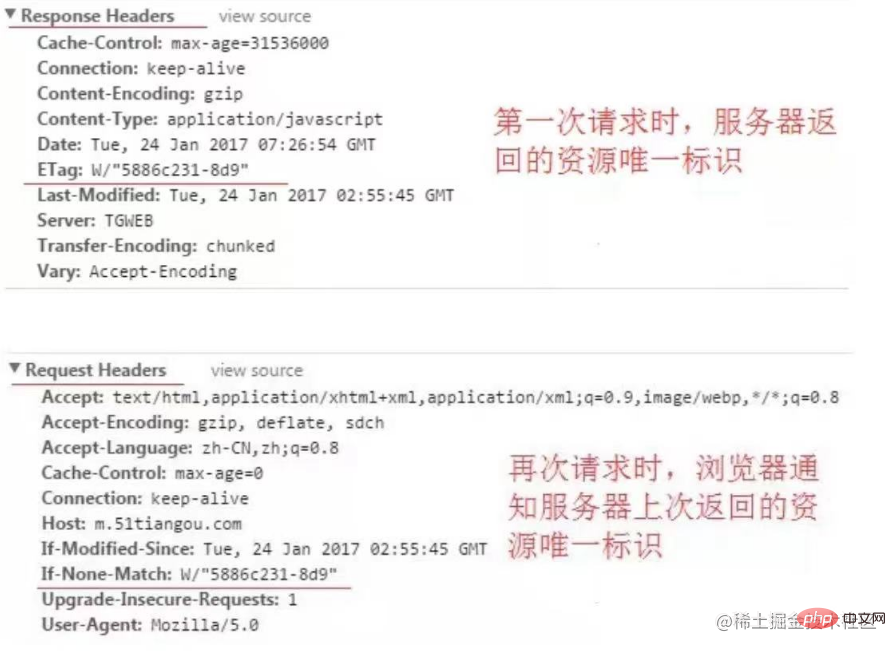
Last_Modified and if- Modified-Since
last-Modified: Saved in the server, records the date when the resource was last modified (it cannot be accurate to seconds. If it is modified multiple times within a few seconds, it may cause errors. Hit cache)
if-modified-since: Saved in the client, the request is carried and compared with the last-Modified of the server. If the same, the cache will be directly hit and a 304 status code will be returned.
ETag is the unique identifier assigned by the server to the resource, and Last-Modified is the last modified time of the resource as reported by the server.
ETag can be generated using any algorithm, such as hashing, while Last-Modified can only use a specific time format (GMT). The comparison of
ETag is a strong validator (exact-match validator) and requires an exact match, while the comparison of Last-Modified is a weak The validator (weak validator) only needs to be the same within the same second.
ETag is suitable for all types of resources, while Last-Modified is only suitable for resources that change infrequently, such as pictures, videos, etc. .
For resources that are updated frequently, ETag is more suitable because it can more accurately detect whether the resource has been modified; while for resources that are not updated frequently, Last-Modified is more suitable because It reduces server load and network traffic.
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
// 设置 eTag方案
const setExpires = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
const maxAge = 60;
ctx.set('Cache-Control', `public, max-age=${maxAge}`);
// 设置 ETag 头
const etag = 'etag-123456789';
ctx.set('ETag', etag);
await next();
}
// Last-Modified方案
const setLastModified = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
const maxAge = 60;
ctx.set('Cache-Control', `public, max-age=${maxAge}`);
// 设置 Last-Modified 头
const lastModified = new Date('2021-03-05T00:00:00Z');
ctx.set('Last-Modified', lastModified.toUTCString());
await next();
}
const response = (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
}
// 跟Etag方案对应
const etagResponse = (ctx) => {
// 如果 ETag 头未被修改,则返回 304
if (ctx.headers['if-none-match'] === ctx.response.get('ETag')) {
ctx.status = 304;
} else ctx.body = 'Hello World';
}
// 跟Last-Modified方案相对应
const lastModifiedResponse = (ctx) => {
// 如果资源已经修改过,则返回新的资源
if (ctx.headers['if-modified-since'] !== ctx.response.get('Last-Modified')) {
response(ctx)
} else ctx.status = 304;
}
app.get('/getMes', setExpires, response);
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server started on port 3000'));const Koa = require('koa');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const app = new Koa();
// 假设这是要缓存的资源
const content = 'Hello, world!';
app.use(async (ctx) => {
// 计算资源的哈希值
const hash = crypto.createHash('md5').update(content).digest('hex');
// 设置 ETag 头
ctx.set('ETag', hash);
// 判断客户端是否发送了 If-None-Match 头
const ifNoneMatch = ctx.get('If-None-Match');
if (ifNoneMatch === hash) {
// 如果客户端发送了 If-None-Match 头,并且与当前资源的哈希值相同,则返回 304 Not Modified
ctx.status = 304;
} else {
// 如果客户端没有发送 If-None-Match 头,或者与当前资源的哈希值不同,则返回新的资源
ctx.body = content;
}
});
app.listen(3000);The strong cache has not expired, data is read from the cache, cache-control priority is higher than last-Modified
The server returns a 304 status code if the cache is not invalidated, and the client reads data from the cache
If the cache is invalidated, resources and a 200 status code are returned
Strong cache usually caches static resources (such as CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) in the browser to reduce the loading time of the page and reduce the load on the server.
Negotiation cache is usually used to cache dynamic resources (such as HTML pages, API data, etc.) to reduce the load on the server and the consumption of network bandwidth.
In actual applications, strong caching and negotiation caching can be used alone or together. For some static resources, you can only use strong caching; for some dynamic resources, you can only use negotiation caching; for some frequently changing resources, you can use strong caching and negotiation caching in combination, which can not only reduce the load on the server, but also ensure timeliness. Get the latest resources.
Although it is implemented using back-end nodejs, I think the front-end should also know more or less about this knowledge so that the back-end can better understand it. to interact. How to implement the front-end will be discussed later?
For more node-related knowledge, please visit: nodejs tutorial!
The above is the detailed content of What is cache? How to implement it using node?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!