
What is template compilation? The following article will talk about template compilation in Vue and discuss the principles of template compilation. I hope it will be helpful to you!

vue provides template syntax that allows us to declaratively describe the binding relationship between state and DOM, such as <p>{{name}} </p>
<p></p>.
Template compilation refers to the process in which the template is compiled into a render function. The function of the render function is to generate a new vnode based on the latest status each time it is executed.
The compilation process is: Template as input-> Template compilation stage->Generate rendering function
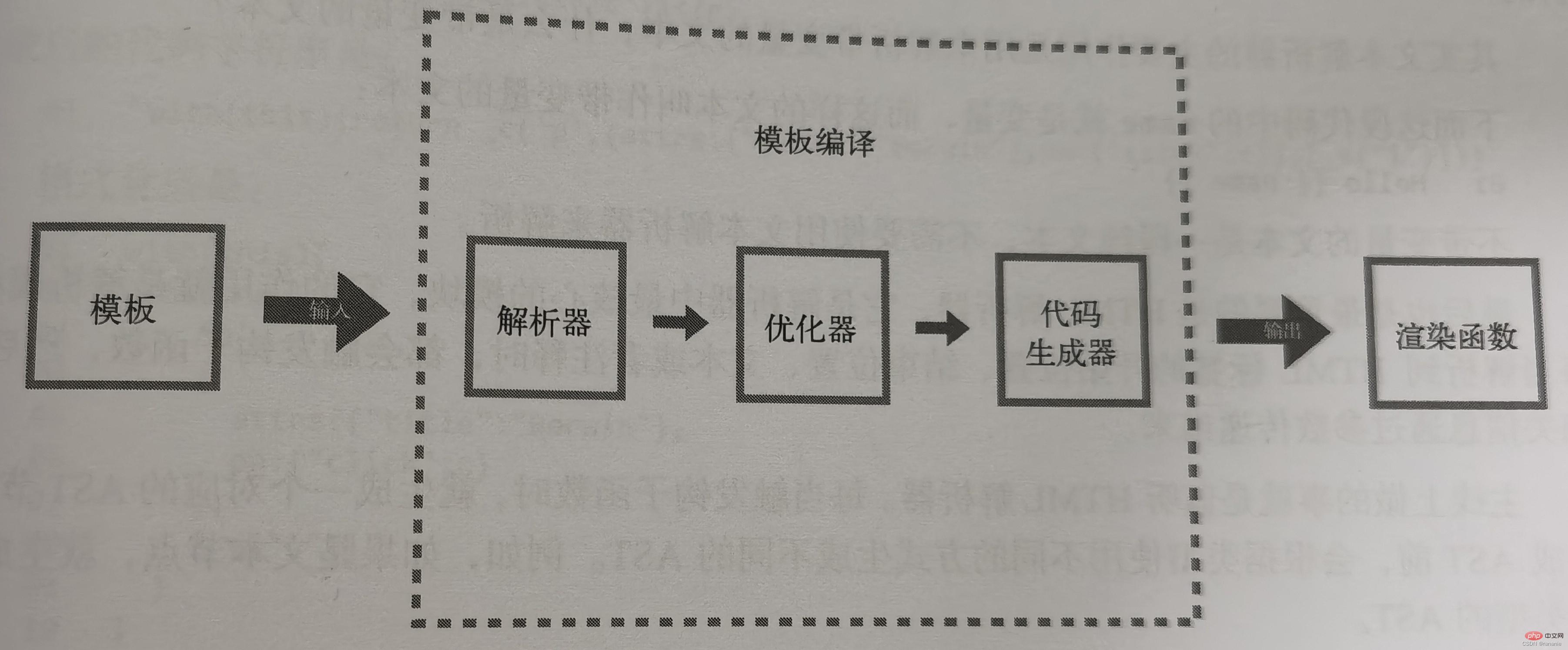
: Parse the template into AST (Abstract Syntax Tree)
: Traverse AST to mark static nodes, because static Nodes are immutable. There is no need to create new virtual nodes for labeled static nodes. You can directly clone existing virtual nodes.
: Use AST to generate rendering functions. Convert AST into code string. Put the code string into the rendering function and export it for use by the outside world.
el, template, render, $mount
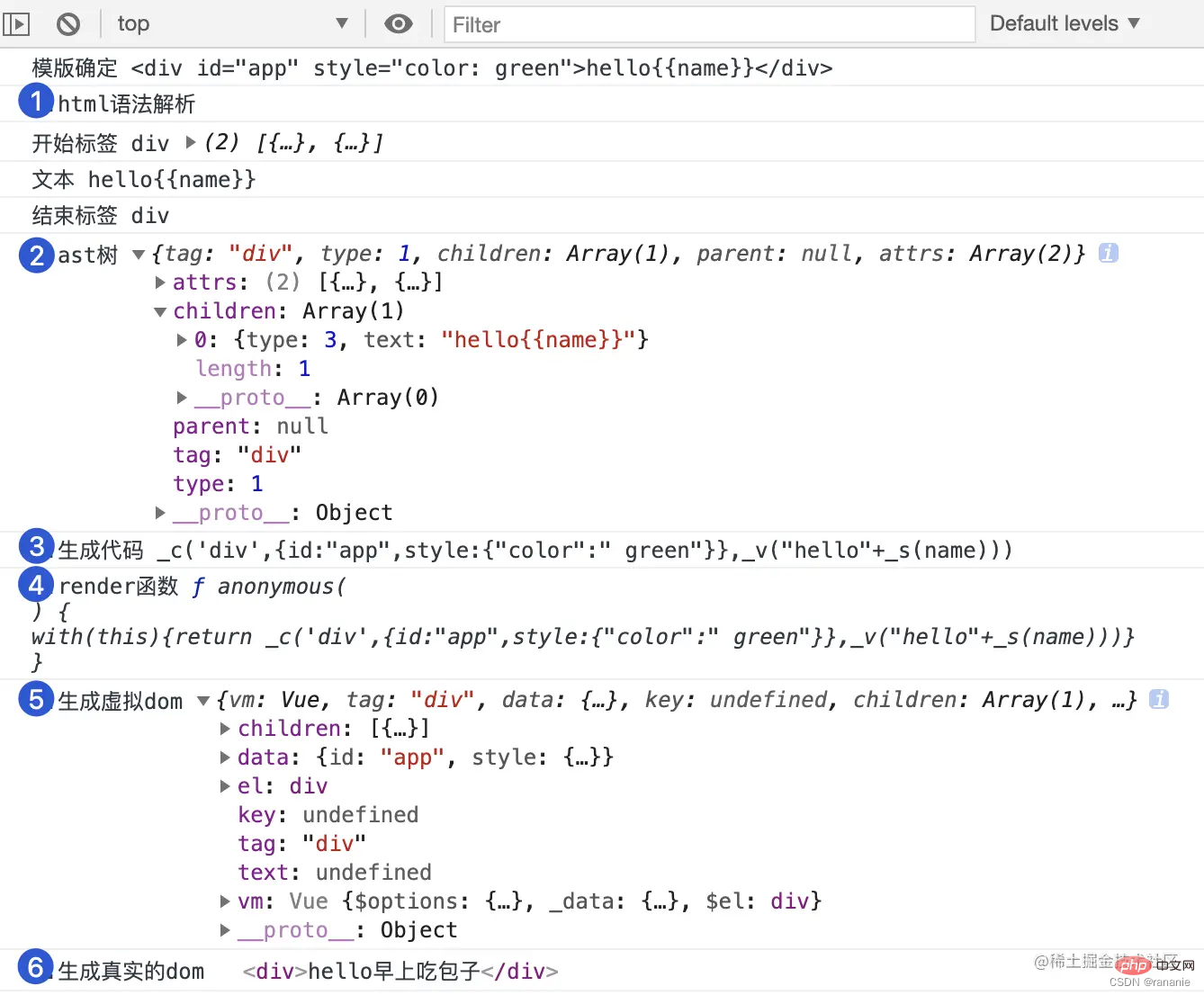
//复杂案例
let vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data() {
return {
a: 1,
b: [1]
}
},
render(h) {
return h('div', { id: 'hhh' }, 'hello')
},
template: `<div id='hhh' style="aa:1;bb:2"><a>{{xxx}}{{ccc}}</a></div>`
}).$mount('#app')
console.log(vue)
//脚手架创建的案例
let vue = new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')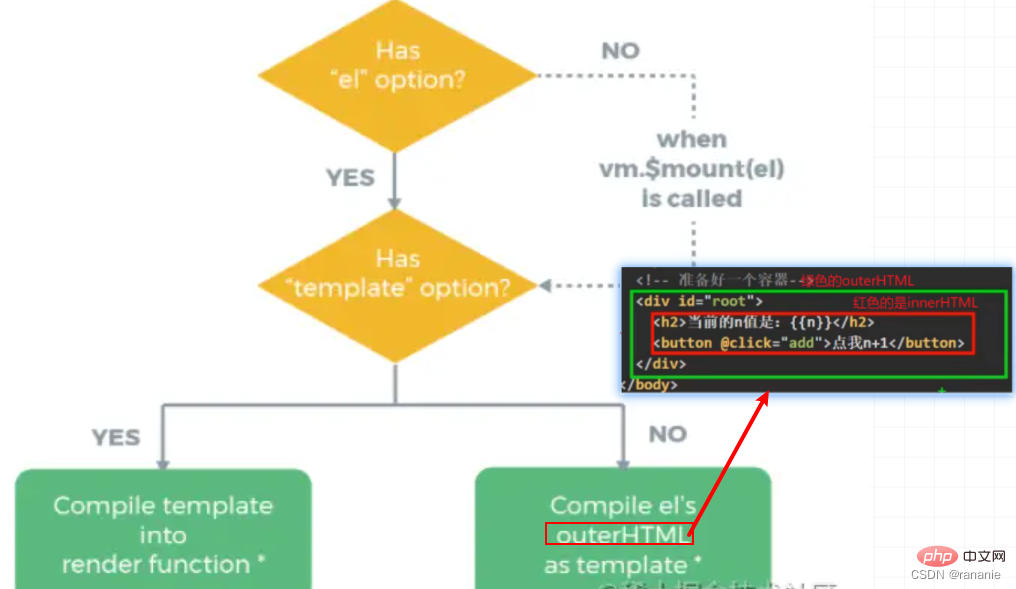
#1) Which root node to render to : Determine whether there is an el attribute. If there is, get the el root node directly. If not, get it when calling $mount. Root node
2) Which template to render to the root node: Whether to call the render function to pass in the templaterender: h => h(App ) ->
<div>
<p>{{name}}</p>
</div>{
tag: "div"
type: 1, //节点类型
staticRoot: false,
static: false,
plain: true,
parent: undefined, //存放父节点
attrsList: [],
attrsMap: {},
children: [ //存放孩子节点
{
tag: "p"
type: 1,
staticRoot: false,
static: false,
plain: true,
parent: {tag: "div", ...},
attrsList: [],
attrsMap: {},
children: [{
type: 2,
text: "{{name}}",
static: false,
expression: "_s(name)"
}]
}
]
}The principle of the parser is to intercept the template string in small sections, each time Intercepting a small string will trigger different hook functions according to the type of the intercepted string until the template string is intercepted. Then use the stack to determine the hierarchical relationship
The internal part of the parser is also divided into several sub-parsers, such as HTML parser, text parser, etc.The role of the HTML parser is to parse HTML. In the process of parsing HTML, various hook functions are continuously triggered.
{{}}
How to determine the level between DOM relation? Using the stack When triggering the hook function of the start tag, if the current tag is not a self-closing tag,
pushentersstack. When the hook function of the end tag is triggered,
pop comes out from the stack
Benefits of marking static subtrees
优化器的内部实现主要分两步用递归的方式将所有节点添加 static 属性,true表示是静态的,false表示不是静态的。
静态根节点也是静态节点
如果一个静态根节点的子节点只有一个文本节点或没有子节点,那么不会标记成静态根节点,即使他们是,因为优化成本大于收益
怎么判断是否静态节点?
在将模板字符串解析成AST的时候,会根据不同的文本类型设置一个 type
| type | 说明 | 是否时静态节点 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 元素节点 | 进行一些排除 |
| 2 | 带遍历的动态文本节点 | 不是 |
| 3 | 不带遍历的纯文本节点 | 是 |
代码生成器的作用:将AST转化成渲染函数中的代码字符串
<div>
<p>{{name}}</p>
</div>
//生成的render渲染函数
{
render: `with(this){return _c('div',[_c('p',[_v(_s(name))])])}`
}
//格式化后
with(this){
return _c(
'div',
[
_c(
'p',
[
_v(_s(name))
]
)
]
)
}生成代码字符串是一个递归的过程,从顶向下依次处理每一个AST节点。
节点有三种类型,分别对应三种不同的创建方法与别名。
| 类型 | 创建方法 | 别名 |
|---|---|---|
| 元素节点 | createElement | _c |
| 文本节点 | createTextVNode | _v |
| 注释节点 | createEmptyVNode | _e |
渲染函数可以生成VNode的原因:渲染函数其实是执行了createElement,而createElement可以创建VNode。
代码字符串的拼接过程
递归AST来生成字符串,最先生成根节点,然后在子节点字符串生成后,将其拼接在根节点的参数中,子节点的子节点拼接在子节点的参数中,一层层拼接。
The above is the detailed content of Vue learning talks about template compilation principles. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!