What does it mean to format a data partition?
Formatting a data partition is to initialize the data partition in the specified disk. This operation usually causes all files in the existing partition to be cleared. Disk formatting involves two different procedures: low-level and high-level formatting. The former handles the characteristics of disk surface formatting and assigns disk sector numbers; after low-level formatting is completed, the hardware disk controller (disk controller) can see and use the results of low-level formatting; the latter handles "accompanied by Specific information written by the operating system".
The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, Dell G3 computer.
What does formatting the data partition mean?
Formatting the data partition is to initialize the data partition in the specified disk. Simply put, it means to All files in are cleared.
Format refers to an operation to initialize a disk or a partition in a disk. This operation usually results in all files in the existing disk or partition being deleted. Clear. Formatting is usually divided into low-level formatting and high-level formatting. Unless otherwise specified, formatting a hard drive usually refers to advanced formatting, while formatting a floppy disk usually includes both.

Types of formatting:
Disk formatting involves two different programs: Low-level with advanced formatting. The former handles the characteristics of disk surface formatting and assigns disk sector numbers; after low-level formatting is completed, the hardware disk controller (disk controller) can see and use the results of low-level formatting; the latter handles "accompanied by Specific information written by the operating system".
1. Low-level formatting
Low-Level Formatting (Low-Level Formatting) is also called low-level formatting or physical formatting (Physical Format). For some hard disk manufacturers Manufacturer, it is also called initialization. Initially, with the emergence of disks using coding schemes such as CHS addressing method, frequency modulation (FM), and modified frequency modulation (MFM), low-level formatting was used to refer to the division of disks into cylinders, tracks, and sectors. operate.
Nowadays, with the gradual withdrawal of floppy disks from daily use and the emergence of disks using new addressing methods and interfaces, this word has lost its original meaning. Most hard disk manufacturers will use low-level format ( Low-Level Formatting) is defined as the operation of creating hard disk sectors to enable the hard disk to have storage capabilities. Nowadays, people have certain misunderstandings about low-level formatting. In most cases, when low-level formatting is mentioned, it often refers to the zero-filling operation of the hard disk.
For a standard 1.44 MB floppy disk, low-level formatting will create 160 tracks (80 per side) on the floppy disk, 18 sectors per track, and each sector 512 bytes; 1,474,560 bytes in total. It should be noted that low-level formatting of floppy disks is usually supported by the system. Normally, the formatting operation of a floppy disk includes two parts: low-level formatting operation and high-level formatting operation.
2. Advanced formatting
Advanced formatting is also called logical formatting. It refers to the file system selected by the user (such as FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, NTFS, EXT2, EXT3, etc.), it is an operation to write specific data in a specific area of the disk to initialize the disk or disk partition and clear all files in the original disk or disk partition. Advanced formatting includes rewriting the corresponding area of the partition table in the master boot record, and carving out a piece of disk space in the partition for storing file allocation tables, directory tables, etc. for file management based on the file system selected by the user. Users use this partition to manage files.
Methods to Create and Format Partitions
Method 1. Via Command Prompt
First, we will show how Create partitions and format the hard drive in the command prompt. The specific steps are as follows:
Press the "Windows R" key on the keyboard to open the run dialog box and enter "cmd" , and click Click "OK" to open the command prompt window.
Then enter "diskpart" and press Enter to start the DiskPart.exe tool.
Create partitions on the hard disk. Enter the following command lines in sequence, and press Enter after each command is entered.
list disk
select disk n (n is the corresponding disk number)
create partition primary
This command will create a primary partition containing all unallocated space. If you want to create a smaller partition, you can enter "create partition primary size=n" to create a partition of a specific size. You can also replace the primary partition with an extended or logical partition to create an extended or logical partition.
After the hard disk partition is created, we can use the command command to format the hard disk partition. Just execute the following command:
list disk
select disk n (n refers to the disk number)
format fs=fat32 quick
If you want to use other file formats, you can replace FAT32 with NTFS or exFAT. But you need to note that Diskpart cannot format FAT32 partitions exceeding 32GB. Method 2. Through Disk Management
 on the keyboard to open the Run dialog box, enter
on the keyboard to open the Run dialog box, enter and click
"OK"to open Disk Management. Creating a partition in Disk Management also requires an unallocated space, so you can compress a large partition to gain unallocated space. The specific steps are as follows:
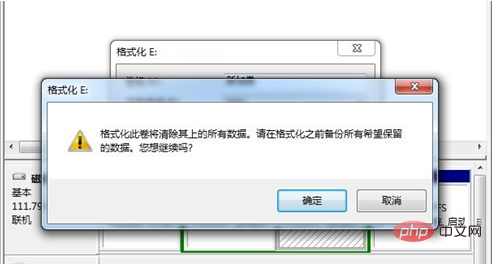
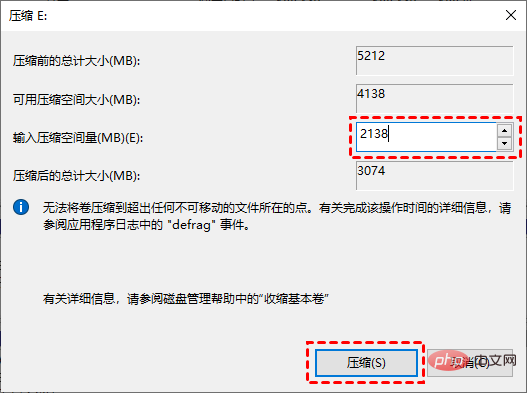
Right-click the partition you want to compress, and then select "Compress Volume".
-
In the pop-up window, enter the amount of space you want to compress and click"Compress"
.

When completed, you will be left with an unallocated space.

- Right-click on the unallocated space, select
"New Simple Volume"
and follow the wizard Create new partition. During this process, you will be asked to format this new partition to a specific file system.
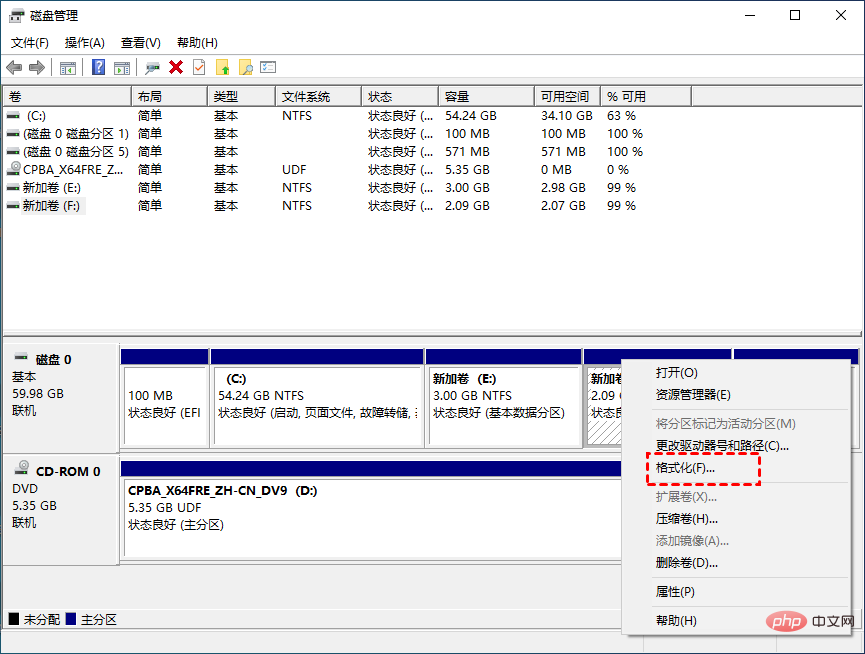
- After the new hard disk partition is created, we can also format the hard disk partition in Disk Management. Just right-click on the target partition, select the
"Format" option, select the correct file system, and click "OK"
. Usually, there are NTFS and FAT32 file systems for you to choose from on the internal hard drive. For external hard drives, exFAT is also available in the file system list.

Due to the FAT32 partition size limit, Disk Management does not allow you to create a 32GB FAT32 partition or format a 32GB partition into the FAT32 file system. Disk Management cannot format the internal hard drive to the exFAT file system, which is only optimized for flash drives such as USB flash drives and SD cards.
For more related knowledge, please visit theFAQ column!
column!
The above is the detailed content of What does it mean to format a data partition?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1375
1375
 52
52
 How to format c drive with dos command
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:23 PM
How to format c drive with dos command
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:23 PM
DOS command is a command line tool used in Windows operating system, which can be used to perform various system management tasks and operations. One of the common tasks is to format the hard drive, including the C drive. Formatting the C drive is a relatively dangerous operation because it will erase all data on the C drive and reinitialize the file system. Before performing this operation, make sure you have backed up important files and have a clear understanding of the impact that formatting will have on your computer. The following is formatted in the DOS command line
 Why can't the D drive be formatted?
Aug 30, 2023 pm 02:39 PM
Why can't the D drive be formatted?
Aug 30, 2023 pm 02:39 PM
The reasons why the D drive cannot be formatted include that the drive is being used by other programs or processes, there is a damaged file system on the drive, hard disk failure and permission issues. Detailed introduction: 1. The reason why the D drive cannot be formatted may be because the drive is being used by other programs or processes. In the Windows operating system, if a program is accessing the files or folders on the D drive, the system will not be able to perform the format operation. ;2. The reason why the D drive cannot be formatted may be because there is a damaged file system on the drive. The file system is used by the operating system to organize and manage files and folders on the storage device, etc.
 What is disc formatting
Aug 17, 2023 pm 04:02 PM
What is disc formatting
Aug 17, 2023 pm 04:02 PM
Disc formatting refers to the process of rebuilding and clearing the disc's file system. During the disc formatting process, all data will be completely deleted, and the file system will be re-established to re-store data on the disc. Disc formatting can be used to protect data security, repair disc failures, and remove viruses. When formatting a disc, you need to back up important data, select an appropriate file system, and wait patiently for the formatting to complete.
 Methods to improve Java time and date formatting parsing performance
Jul 01, 2023 am 08:07 AM
Methods to improve Java time and date formatting parsing performance
Jul 01, 2023 am 08:07 AM
How to optimize the performance of time and date formatting and parsing in Java development Summary: In Java development, time and date formatting and parsing are common operations. However, due to the complexity and variety of time and date formats and the huge amount of data processed, it often becomes a performance bottleneck. This article will introduce several methods to optimize the performance of time and date formatting parsing in Java development, including using cache, reducing object creation, selecting appropriate APIs, etc. 1. Introduction Time and date formatting and parsing are very common in Java development. However, in practical applications, since
 Computer formatting tutorial
Jan 08, 2024 am 08:21 AM
Computer formatting tutorial
Jan 08, 2024 am 08:21 AM
Many times when using a computer, you will encounter too much garbage, but many users still don’t know how to format the computer. It doesn’t matter. Here is a tutorial on computer formatting for you to take a look at. How to format a computer: 1. Right-click "This PC" on the desktop and click "Manage". 2. Click "Storage" in "Computer Management" to open "Disk Management". 3. Select the hard drive you want to clean, right-click and select "Format". 4. Check "Perform Quick Format" and click "OK" to start formatting.
 Revealed secrets of cell phone format recovery methods (mobile phone malfunction? Don't worry)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Revealed secrets of cell phone format recovery methods (mobile phone malfunction? Don't worry)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Nowadays, we will inevitably encounter some problems such as being unable to turn on the phone or lagging, such as system crash, but during use, mobile phones have become an indispensable part of our lives. We are often at a loss, and sometimes, there are no solutions to these problems. To help you solve cell phone problems, this article will introduce you to some methods of cell phone format recovery and restore your phone to normal operation. Back up data - protect important information, such as photos and contacts, from being lost during the formatting process. Before formatting your phone, the first thing to consider is to back up important data and files on your phone. To ensure data security, or choose to transfer files to a cloud storage service, you can back it up by connecting to a computer. Use the system's built-in recovery function - simple
 Will formatting a laptop make it faster?
Feb 12, 2024 pm 11:54 PM
Will formatting a laptop make it faster?
Feb 12, 2024 pm 11:54 PM
Will formatting a laptop make it faster? If you want to format your Windows laptop but want to know if it will make it faster, this article will help you know the right answer to this question. Will formatting a laptop make it faster? There are many reasons why users format their Windows laptops. But the most common reason is slow performance or speed of your laptop. Formatting a laptop will completely delete all data stored on the C drive or the hard drive partition where Windows operating system is installed. Therefore, every user will think twice before taking this step, especially when it comes to the performance of the laptop. This article will help you understand whether formatting your laptop will speed it up. Formatting your laptop helps
 Use the fmt.Sprint function to format multiple values into strings and return them, including type information
Jul 25, 2023 am 09:01 AM
Use the fmt.Sprint function to format multiple values into strings and return them, including type information
Jul 25, 2023 am 09:01 AM
Use the fmt.Sprint function to format multiple values into strings and return them, including type information. In the Go language, the fmt package provides many functions for formatting data into strings. Among them, the fmt.Sprint function can format multiple values into strings and return them. Unlike the fmt.Sprintf function, the fmt.Sprint function returns a string instead of a formatted string. Here is a simple example code using the fmt.Sprint function: pa



