
The ranges are: 1. The class A address range is "10.0.0.0~10.255.255.255", that is, "10.0.0.0/8"; 2. The class B address range is "172.16.0.0~172.31. 255.555", that is, "172.16.0.0/12"; 3. The class C address range is "192.168.0.0~192.168.255". Private IP addresses are IP addresses reserved among the three types of IP addresses A, B, and C that are used when allocating addresses to the enterprise's internal network.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
Internet Protocol Address (English: Internet Protocol Address, also translated as Internet Protocol Address), abbreviated as IP Address. The IP address is a unified address format provided by the IP protocol. It assigns a logical address to each network and each host on the Internet to shield the differences in physical addresses.
Every host (Host) on the Internet has a unique IP address. The IP protocol uses this address to transfer information between hosts, which is the basis for the Internet to run. The length of the IP address is 32 bits (a total of 2^32 IP addresses), divided into 4 segments, each segment is 8 bits, expressed in decimal numbers, each segment ranges from 0 to 255, and segments are separated by periods. .
What is a private IP address
IP address types are divided into public addresses and private addresses. Public addresses are allocated to the public network and can be directly accessed. Internet address. Private addresses are non-registered addresses that can be used internally by each organization. We often use private addresses for company network networking, network cameras, switch router configurations, such as: 192.168.1.1; 10.0.0.1, etc. Private address.
To put it simply, the so-called private address is the IP address reserved among the three types of IP addresses A, B, and C that is used when allocating addresses to the enterprise's internal network.
Private addresses are mainly used for allocation in LAN and are invalid on the Internet. This provides a good isolation between the LAN and the Internet. Private addresses cannot be identified on the public network. The internal IP address must be converted into an IP address available on the public network through NAT, so that the internal IP address can communicate with the external public network. Public addresses are addresses used within WANs, but they can also be used in LANs. All addresses except private addresses are public addresses.
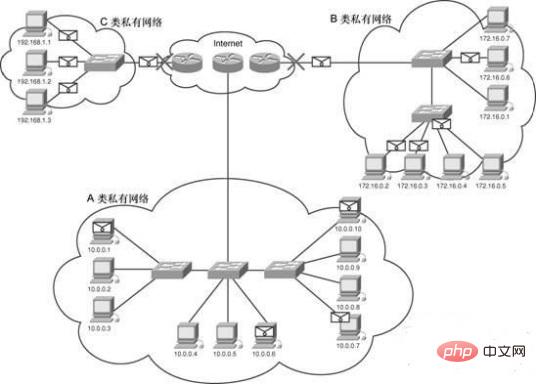
Private IP address range
Private IP is a non-registered address and is exclusively for internal use of the organization . RFC1918 defines the private IP address range:
Class A address range: 10.0.0.0—10.255.255.255, that is, 10.0.0.0/8
Class B address range: 172.16.0.0---172.31.255.555, that is, 172.16.0.0/12
Class C address range: 192.168.0.0---192.168.255.255, that is 192.168.0.0/16
These addresses will not be assigned by the Internet, nor will they be routed on the Internet. Although they cannot be directly connected to the Internet, they can be connected through technical means. It is still possible to communicate with the Internet (NAT technology). We can choose the appropriate address class according to our needs and use these addresses like public IP addresses in the internal LAN. On the Internet, some devices that do not need to communicate with the Internet, such as printers, manageable hubs, etc., can also use these addresses to save IP address resources.
Extended Knowledge:
Due to the scarcity of IPv4 addresses (i.e. approximately 4 billion IP addresses), IANA reserves private IP address blocks, So that any organization can use them without registering with IANA. Private IP address blocks can be used by homes, small businesses, and even medium to large enterprises to create their own networks. Computing devices with private IP addresses cannot be accessed directly from the Internet unless NAT (Network Address Translation) is used.
Advanced network planning technology also enables network planners to use the same private IP address in different private networks, allowing them to save valuable IP address space. A private address may also be called a local IP address. It can also hide a user's identity on the Internet.
The range of private IP addresses belongs to different IP Classes. It helps determine the total number of possible IP addresses that can be allocated from the reserved address space. It also allows plans to reuse these IP addresses in different private networks without routing these IPs over the Internet.
Private IP Address Space hides your entire private network behind a router and saves public IP address space. NAT, or Network Address Translation technology, enables devices that reside within a private network to provide services to the Internet. It is implemented by routers that allow messages to be exchanged between private and public (Internet) networks.
Because IPv4 is limited to 32 bits, we have a very limited pool of public or Internet IP addresses within the IPv4 address space. We can't assign a new public IP address to every device in the world because there are more than 232 or approximately 4 billion addresses. If a private network is connected to the Internet through a router, devices at the private address can still access the Internet.
Assign a public IP address to the router. All computers in the private network will share the router's public IP address when accessing the Internet. As more and more devices connect to the Internet, private IP address blocks allow enterprises to create private networks without consuming globally unique public IP addresses.
The router implements the NAT (Network Address Translation) function to complete the communication process between two devices from two different private networks, which may have the same or different private IP addresses.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What is the private IP address range?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!