 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What impact does deleting a partition have on data in Linux?
What impact does deleting a partition have on data in Linux?
What impact does deleting a partition have on data in Linux?
In Linux, deleting a partition will also delete the data in the partition, resulting in data loss. How to delete a partition: 1. Install the GParted tool, select the partition you want to delete in the GParted interface, and select the "Delete" option from the partition menu; 2. Use the fdisk command to delete, with the syntax "sudo fdisk --list partition name".

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
Each partition in the Linux system is a file system and has its own directory hierarchy.
linux What impact does deleting a partition have on data?
Deleting a partition will also delete the data in the partition, resulting in data loss.
So whenever you are working on a partition, be sure to back up your data. A slight typo or slippage can be costly. Don't say we didn't warn you!
Linux disk partition
1. Primary partition, extended partition and logical partition
Linux There are three types of hard disk partitions: primary partition, extended partition and logical partition.
The partitions of the hard disk are mainly divided into two types: primary partition (Primary Partion) and extended partition (Extension Partion). The sum of the number of primary partitions and extended partitions cannot be greater than four.
Primary Partion: It can be used immediately but cannot be partitioned again.
Extension Partion: It must be partitioned before it can be used, which means it must be partitioned twice.
Logical partition ((Logical Partion)): A partition established by an extended partition. There is no limit on the number of logical partitions.
The extended partition is just a "container" for the logical partition. In fact, only the primary partition and the logical partition are used for data storage.
2. The identification of hard disk partition under Linux
The identification of hard disk partition is generally /dev/hd[a-z]X or /dev/sd[a-z]X. Identification, where [a-z] represents the hard disk number, and X represents the partition number in the hard disk.
The block number identification of the entire hard disk partition: under Linux, hda, hdb, sda, sdb, etc. are used to identify different hard disks;
Among them:
IDE interface hard disk: represented as /dev/hda1, /dev/hdb...;
SCSI interface hard disk and SATA interface hard disk are represented as /dev/sda, /dev/ sdb... ... ;
Partitions in the hard disk: If the value of For example, /dev/hda5 must be a logical partition;
For example:
Use hda1, hda2, hda5, and hda6 to identify different partitions. Among them, the letter a represents the first hard disk, b represents the second hard disk, and so on. The number 1 represents the first partition of a hard disk, 2 represents the second partition, and so on. 1 to 4 correspond to the primary partition (Primary Partition) or extended partition (Extension Partition). Starting from 5, they all correspond to the logical partition of the hard disk (Logical Partition). Even if a hard disk has only one primary partition, the logical partitions are numbered starting from 5, so special attention should be paid to this.
How to delete a partition in Linux
1. Use GParted to delete a disk partition (GUI Method)
As a desktop Linux user, you may feel more comfortable, and perhaps more secure, with GUI-based tools. There are several tools that let you manage partitions on Linux. Depending on your distribution, you may have one or more of these tools installed on your system. In this tutorial, I will use GParted. It is a popular open source tool that is very simple and intuitive to use.
The first step is to install GParted if it is not already on your system. You should be able to find it in your distribution's Software Center.

Alternatively, you can install it using your distribution’s package manager. In Debian and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, you can use the apt install command:
sudo apt install gparted
After the installation is complete, let us open GParted. Since you are dealing with disk partitions, you need root access. It will ask for authentication and once it opens, you should see a window similar to this:

In the upper right corner you can select the disk and below select the one you want to delete Partition.
Next, select the “Delete” option from the partition menu:

这个过程是没有完整完成的,直到你重写分区表。这是一项安全措施,它让你在确认之前可以选择审查更改。
要完成它,只需点击位于工具栏中的 “应用所有操作” 按钮,然后在要求确认时点击 “应用”。

点击 “应用” 后,你会看到一个进度条和一个结果消息说所有的操作都成功了。你可以关闭该信息和主窗口,并认为你的分区已从磁盘中完全删除。
现在你已经知道了 GUI 的方法,让我们继续使用命令行。
2、使用 fdisk 命令删除分区(CLI 方法)
几乎每个 Linux 发行版都默认带有 fdisk,我们今天就来使用这个工具。你需要知道的第一件事是,你想删除的分区被分配到哪个设备上了。为此,在终端输入以下内容:
sudo fdisk --list
这将打印出我们系统中所有的驱动器和分区,以及分配的设备。你 需要有 root 权限,以便让它发挥作用。
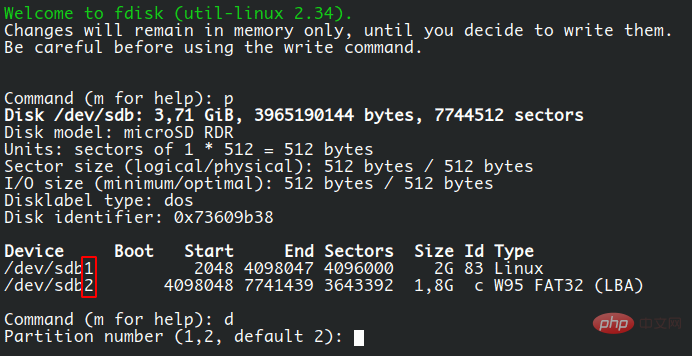
在本例中,我将使用一个包含两个分区的 USB 驱动器,如下图所示:

系统中分配的设备是 /sdb,它有两个分区:sdb1 和 sdb2。现在你已经确定了哪个设备包含这些分区,你可以通过使用 fdisk 和设备的路径开始操作:
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
这将在命令模式下启动 fdisk。你可以随时按 m 来查看选项列表。
接下来,输入 p,然后按回车查看分区信息,并确认你正在使用正确的设备。如果使用了错误的设备,你可以使用 q 命令退出 fdisk 并重新开始。
现在输入 d 来删除一个分区,它将立即询问分区编号,这与 “Device” 列中列出的编号相对应,在这个例子中是 1 和 2(在下面的截图中可以看到),但是可以也会根据当前的分区表而有所不同。

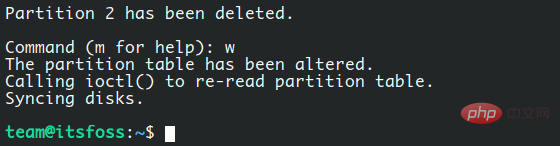
让我们通过输入 2 并按下回车来删除第二个分区。你应该看到一条信息:“Partition 2 has been deleted”,但实际上,它还没有被删除。fdisk 还需要一个步骤来重写分区表并应用这些变化。你看,这就是完全网。
你需要输入 w,然后按回车来使这些改变成为永久性的。没有再要求确认。
在这之后,你应该看到下面这样的反馈:
现在,使用
sudo fdisk --list /dev/sdb
查看该设备的当前分区表,你可以看到第二个分区已经完全消失。你已经完成了使用终端和 fdisk 命令来删除你的分区。成功了!
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What impact does deleting a partition have on data in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1381
1381
 52
52
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS installation steps: Download the ISO image and burn bootable media; boot and select the installation source; select the language and keyboard layout; configure the network; partition the hard disk; set the system clock; create the root user; select the software package; start the installation; restart and boot from the hard disk after the installation is completed.
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 Centos options after stopping maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Centos options after stopping maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
CentOS has been discontinued, alternatives include: 1. Rocky Linux (best compatibility); 2. AlmaLinux (compatible with CentOS); 3. Ubuntu Server (configuration required); 4. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (commercial version, paid license); 5. Oracle Linux (compatible with CentOS and RHEL). When migrating, considerations are: compatibility, availability, support, cost, and community support.
 What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
After CentOS is stopped, users can take the following measures to deal with it: Select a compatible distribution: such as AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and CentOS Stream. Migrate to commercial distributions: such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux. Upgrade to CentOS 9 Stream: Rolling distribution, providing the latest technology. Select other Linux distributions: such as Ubuntu, Debian. Evaluate other options such as containers, virtual machines, or cloud platforms.
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)



