What are the characteristics of red hat linux?
Features of red hat linux: 1. Multi-user and multi-task operating system, one computer can be used by multiple users at the same time, and can execute multiple tasks submitted by multiple users at the same time; 2. Good Compatibility; 3. Powerful portability, whether it is a handheld computer, a personal computer, a small computer, a medium-sized computer, or even a large computer can run Linux; 4. High stability, reliability and security; 5 , openness and low cost.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.1 system, Dell G3 computer.
Introduction to red hat linux
What is red hat linux
Red Hat Linux ((RHEL)) is developed by Red An open source Linux distribution compiled by Hat Company. It was active from 1995 to 2004, with several versions of the software released during this period.
Various versions of Red Hat Linux have been released, with the first version released on May 13, 1995. Red Hat Linux was created to be easy to use and install compared to other Linux distributions . It included a graphical installer that was later used by other Linux distributions. Later versions included UTF-8 encoding, making it more suitable for a wider range of languages. However, due to copyright and patent issues, Red Hat Linux lacks many features, such as support for the NTFS file system and MP3, but these features can be installed later.
In 2003, Red Hat Linux merged with the community-based Fedora project, which replaced the original retail and download versions of Red Hat Linux.
Red Hat Linux (RHEL) is a Linux-based operating system designed by Red Hat specifically for enterprises. RHEL can run on a desktop, server, hypervisor, or cloud. Red Hat is one of the most widely used Linux distributions in the world.
RedHat is an operating system based on LINUX core architecture. RedHat Linux is currently the most used Linux operating system in the world. Because it has the best graphical interface, it is very convenient to install, configure and use, and it runs stably, so both novices and experienced players speak highly of it.

Characteristics of red hat linux
1. Multi-user multi-tasking operating system
refers to a A computer can be used by multiple users at the same time and can perform multiple tasks submitted by multiple users at the same time.
-
Multi-user: Linux supports multiple users using the same computer from the same or different terminals at the same time, without the so-called license restrictions of commercial software;
Linux treats different types of users differently, granting them different permissions and storage spaces respectively. Each user has specific permissions to use their own software and hardware resources (such as files and devices), which are independent of each other and do not affect each other. .
Multi-tasking: Within the same time period, Linux can respond to different operation requests from multiple users.
2. Good compatibility
Complies with IEEE's POSIX (Portable Operating System Interface of UNIX, Portable Operating System Interface for UNIX) standard and is compatible with current mainstream UNIX system. Programs that can run in UNIX can almost entirely run in Linux, which makes it possible to transfer application systems from UNIX to Linux.
3. Powerful portability
Whether it is a handheld computer, a personal computer, a small computer, a medium-sized computer, or even a large computer, Linux can be run.
4. High stability, reliability and security
Linux inherits the excellence of UNIX and can run continuously for months or years without restarting.
So far, only a handful of viruses have infected Linux. This strong immunity is attributed to Linux’s robust infrastructure.
Linux's infrastructure consists of multiple layers that have nothing to do with each other. Each layer has specific functions and strict permissions to ensure maximum stable operation.
5. Openness and low fees.
Red Hat Redhat—Linux basic command line usage
bash shell
A command line is a text-based interface that can be used to enter instructions into a computer system; the linux command line is provided by a program , this program is called a shell.
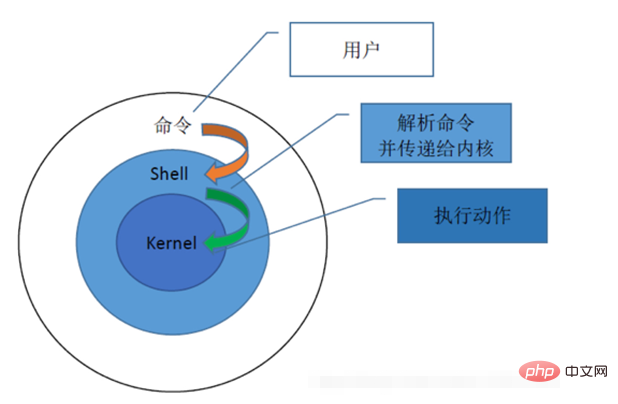
#What is a shell prompt?
Use the shell interactively and display a string while waiting for the user to enter a command. This interface is called a prompt.
When ordinary users start the shell, the interface ends with a dollar and a $ character.
When the root user starts the shell, the interface ends with the # character.
[root@localhost ~]#
When ordinary users start the shell, the interface ends with the $ character.
[user@localhost ~]$
对Linux系统的管理方式可以通过物理控制台和虚拟控制台管理物理控制台就是使用键盘鼠标和显示器对Linux系统进行管理,或者通过串行端口管理。
虚拟控制台是通过网络或者其它虚拟控制方式管理Linux系统。
RHEL8.0的版本同时提供6个控制台管理,第一个控制台为图形化管理也叫GUI管理,另外二至六控制台为命令行管理方式;可以通过按住Ctrl+Alt并按住功能键(F2~F6)切换。
标准Linux命令行语法格式:command + -option + argument。
command (命令字):运行程序的名字,永远写在开头。
option (选项):由一个或两个“-”引导,改变命令的行为。
argument(参数):通常是命令要操作的目标,注意先后顺序,大多数命令可以使用--help 显示用法信息。
大多数参数一般可以与选项颠倒使用,不需要刻意规定(不是所有)。
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /etc/passwd -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2658 12月 9 14:56 /etc/passwd
#命令(ls)、 选项(l)、参数(/etc/passwd)
命令、选项、参数 之间都必须要使用空格隔开。
选项: 用于修饰或者调整命令,不同选项会使命令有不同的作用。
短选项:-
长选项:--
可以同时跟多个选项,比如 -l -h = -lh
注:
ls -a ls--all
一个“-”后面跟简写 。 两个“--”后面跟全称
[root@localhost ~]# usermod -L rhel
#命令(usermod) 选项(L) 和参数(rhel)
该命令的意思是锁定用户user帐户的密码。
exit或ctrl + d退出当前shell
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname server [root@localhost ~]# bash [root@server ~]#
exit退出再次登录shell或者bash
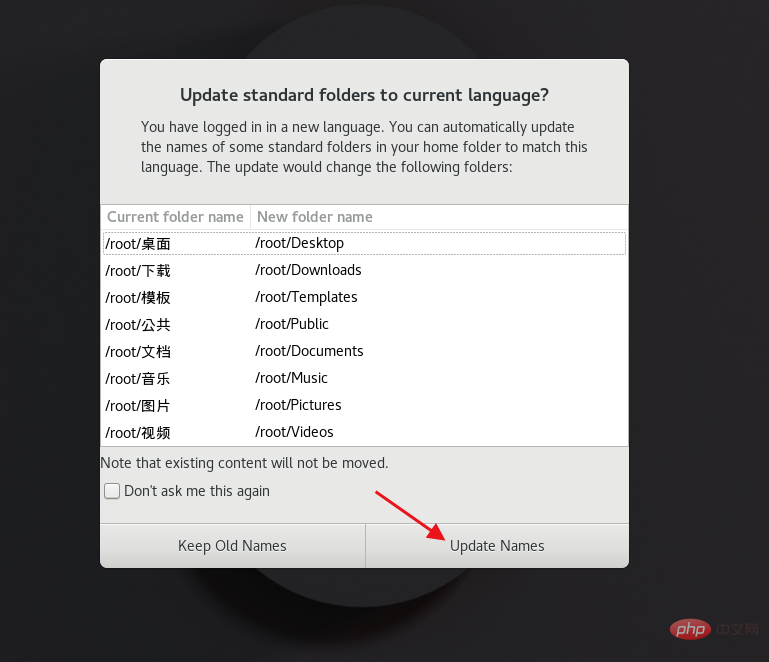
[root@server ~]# locale //查看系统语言包 LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8 LC_CTYPE="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_NUMERIC="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_TIME="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_COLLATE="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_MONETARY="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_MESSAGES="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_PAPER="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_NAME="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_ADDRESS="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_TELEPHONE="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_MEASUREMENT="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_IDENTIFICATION="zh_CN.UTF-8" LC_ALL= [root@server ~]# localectl set-locale.UTF-8 //英语 [root@server ~]# reboot //重启系统
更改语言后要重启系统才能生效,GUI登陆时会有更改家目录文件夹名字的弹窗点击Update Names。

[root@server ~]# localectl set-locale LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8 简体中文
在Linux系统中,命令是严格区分大小写的(谨记)。
系统语言问题:
[root@server ~]# echo $LANG //显示目前所支持的语言 en_US.UTF-8
zh_CN.UTF8 简体中文
en_US.UTF8 英文
[root@server ~]# useradd rhel1 //创建rhel1用户 [root@server ~]# passwd rhel1 //后面跟的是用户名 Changing password for user rhel1. New password: //此处为输入的密码,不显示位数 BAD PASSWORD: The password is shorter than 8 characters Retype new password: //此处为输入的密码,不显示位数 passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
创建一个用户名为rhel1 密码为redhat
或者:
[root@server ~]# echo "redhat" | passwd --stdin rhel1 //可以看见密码
对在线处理用户的锁定及管理操作
[root@server ~]# who //查看当前在线用户 root pts/0 2020-12-14 18:18 (192.168.2.108) root tty2 2020-12-14 18:34 (tty2) rhel tty3 2020-12-14 18:35 (tty3) [root@server ~]# pkill -19 -t tty3 //锁定tty3用户 [root@server ~]# pkill -18 -t tty3 //释放tty3用户
cat [选项] [文件]或绝对路径
cat主要有三大功能:
1)一次显示整个文件:cat /etc/passwd
[root@server ~]# cat /etc/passwd //显示整个passwd文件 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin …… rhel:x:1000:1000:rhel:/home/rhel:/bin/bash rhel1:x:1001:1001::/home/rhel1:/bin/bash
2)从键盘创建一个文件:cat > filename 只能创建新文件,不能编辑已有文件。
[root@server ~]# cat > filename
3)将几个文件合并为一个文件:cat file1 file2 > file3
[root@server ~]# touch file1 file2 file3 //创建file1 file2 file3 [root@server ~]# vim file1 //i编辑hello1 按esc :wq保存退出 [root@server ~]# vim file2 //i编辑hello1 按esc :wq保存退出 [root@server ~]# cat file1 file2 > file3 //把file1 file2文件的内容输入到file3 [root@server ~]# cat file3 //查看file3文件 hello1 hello2
rm -f 文件名 [将会强行删除文件,且无提示]
rm -rf 目录名字 [删除文件夹以及文件夹中的所有文件命令]
其中:
-r:向下递归删除-f:直接强行删除,且没有任何提示
注意:
使用rm -rf要格外注意,linux中没有回收站,慎重操作。
[root@server ~]# date //查看当前用户的年月日星期时间 Mon Dec 14 19:24:30 CST 2020 [root@server ~]# date +%R //查看当前用户时间 19:24 [root@server ~]# date +%x //查看当前用户年月日 12/14/2020 [root@server ~]# date -s 20201215 //修改时间为2020年12月15日 Tue Dec 15 00:00:00 CST 2020 [root@server ~]# date -s 20:20:20 //修改时间为20点20分20秒 Tue Dec 15 20:20:20 CST 20
-s 修改时间
date +%Y.%m.%d (Y大写,m、d小写)
date +%H:%M:%S (大写)
[root@server ~]# cal //直接执行,显示系统当月的日历
December 2020
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
20 21 22 23 24 25 26
27 28 29 30 31[root@server ~]# cal 2020 //显示2020年整个年度的日历
2020
January February March
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
26 27 28 29 30 31 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 29 30 31
April May June
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
26 27 28 29 30 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 28 29 30
31
July August September
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 4 5
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
26 27 28 29 30 31 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 27 28 29 30
30 31
October November December
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 29 30 27 28 29 30 31[root@server ~]# cal 12 2020 //显示2020年12月份的日历
December 2020
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
20 21 22 23 24 25 26
27 28 29 30 31bc [回车]scale=3 显示小数点后面三位quit 退出
cd 退回到当前用户家目录cd a/b/c 相对路径:以当前目录作为起点,切换目录 *cd /root/a/b/c 绝对路径:以根目录作为起点,切换目录cd .. 返回上一级目录cd ~ 退回当前用户的家目录
[root@server ~]# reboot //重启主机
其它一些关机命令:halt、poweroff
shutdown的一些参数使用:
shutdown [-t seconds] [-arkhncfF] Time [warning message]
-t sec: Add the number of seconds after -t, which is how many seconds have passed The meaning of shutting down after seconds
Parameters:
-k: Don’t actually shut down, just send a warning message-r: Restart the system after stopping the service-h: Stop the system service Shut down after shutdown-n: Shut down directly using the shutdown function without going through the init program-f: After shutdown, force the disk check of fsck to be skipped-F: After restart, force the disk check of fsck to be performed-c: Cancel the content of the shutdown command that is already in progress.
Time: This refers to the time when the system is shut down.
Example:
/sbin/shutdown -h 10 "I will shutdown after 10 mins"
Let me tell you that this machine will shut down after 10 minutes. And send this warning message to everyone's screen
init: service level, there are 7 levels in Linux, now let's learn about the 4 commonly used levels
init 0 Shutdown
init 3 Pure command line mode
init 5 Mode with graphical interface
init 6 Restart
What is the difference between shutdown and halt?
shutdown is to gradually shut down the services that have been started before performing a hardware shutdown. Halt does not consider what service is currently started and directly shuts down the hardware.
12. Commonly used shortcut keys under Linux
tab: Complete command or path
ctrl c: Terminate the currently executed Task
ctrl l: Clear the screen
ctrl d: exit
ctrl u: Delete the content with the cursor to the beginning of the line
ctrl e: Move the cursor to the end of the line
ctrl a: Move the cursor to the beginning of the line
ctrl plus sign/minus sign: adjust the shell window font size
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What are the characteristics of red hat linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Linux is suitable for servers, development environments, and embedded systems. 1. As a server operating system, Linux is stable and efficient, and is often used to deploy high-concurrency applications. 2. As a development environment, Linux provides efficient command line tools and package management systems to improve development efficiency. 3. In embedded systems, Linux is lightweight and customizable, suitable for environments with limited resources.
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
This article describes how to effectively monitor the SSL performance of Nginx servers on Debian systems. We will use NginxExporter to export Nginx status data to Prometheus and then visually display it through Grafana. Step 1: Configuring Nginx First, we need to enable the stub_status module in the Nginx configuration file to obtain the status information of Nginx. Add the following snippet in your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or its include file): location/nginx_status{stub_status
 How to start monitoring of oracle
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:00 AM
How to start monitoring of oracle
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:00 AM
The steps to start an Oracle listener are as follows: Check the listener status (using the lsnrctl status command) For Windows, start the "TNS Listener" service in Oracle Services Manager For Linux and Unix, use the lsnrctl start command to start the listener run the lsnrctl status command to verify that the listener is started
 How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
This article introduces two methods of configuring a recycling bin in a Debian system: a graphical interface and a command line. Method 1: Use the Nautilus graphical interface to open the file manager: Find and start the Nautilus file manager (usually called "File") in the desktop or application menu. Find the Recycle Bin: Look for the Recycle Bin folder in the left navigation bar. If it is not found, try clicking "Other Location" or "Computer" to search. Configure Recycle Bin properties: Right-click "Recycle Bin" and select "Properties". In the Properties window, you can adjust the following settings: Maximum Size: Limit the disk space available in the Recycle Bin. Retention time: Set the preservation before the file is automatically deleted in the recycling bin
 How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
To restart the Apache server, follow these steps: Linux/macOS: Run sudo systemctl restart apache2. Windows: Run net stop Apache2.4 and then net start Apache2.4. Run netstat -a | findstr 80 to check the server status.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information



