 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 ChatGPT and Google Bard: Which one is better and which one is worse? A big review of the differences!
ChatGPT and Google Bard: Which one is better and which one is worse? A big review of the differences!
ChatGPT and Google Bard: Which one is better and which one is worse? A big review of the differences!
The two biggest competitors in the AIGC industry: ChatGPT vs Google Bard! This article introduces the technical differences between these two artificial intelligence engines.
Translator | Cui Hao
Reviewer | Sun Shujuan
Opening
The two biggest competitors in the AIGC industry: ChatGPT vs Google Bard! This article Describe the technical differences between these two artificial intelligence engines.
The biggest difference so far between Google Bard and ChatGPT is: Bard knows about ChatGPT, but ChatGPT is ignorant of Bard. While we can play around with ChatGPT, Bard is still out of reach for most of us.

The battle between ChatGPT and Google Bard begins
ChatGPT and Google Bard are both artificial intelligence chatbots. A simplified version of artificial intelligence is already available on mobile phones. When you type "good", the phone can predict that the next word will be "morning".
ChatGPT was originally developed by OpenAI and then funded by Microsoft for an eye-popping $10 billion (in addition to an earlier $1 billion investment). Google, for its part, was slightly panicked that their search monopoly might be ending, so it launched Bard, but this version still had some flaws. During his first live demonstration, Bard made several factual errors that embarrassed Google.
ChatGPT and Google Bard are more complex than the predictive text functions of smartphones. If you want to understand the differences between these two intelligent robots, you can’t miss the following content.
Here we will describe in depth the technical differences between the two artificial intelligence engines.
ChatGPT and Bard: Hidden secrets?
We can quickly understand the technical differences between them through the following table, through which you can see many details.
#ChatGPT |
Bard |
|
| Model | GPT-3.5 | LaMDA, That is, the language model for dialogue applications |
| Neural network structure | Transformer | Transformer |
Training data |
Network text, mainly The dataset, called "commoncrawl", is due in mid-2021. |
1.56 million words of public dialogue data and network text |
Purpose |
Become a multipurpose text-generating chatbot |
Dedicated to assisting with searches |
Parameters |
##175 billion parameters | 137 billion parameters |
| Creator | OpenAI | Google |
| Advantages | - Open to everyone- More flexible and able to handle open text- Training data is as of 2021 |
-Training data as of now - Specifically trained for conversation, so when you talk to it, it sounds more like a human. |
Disadvantages |
- The dialogue is not that convincing - Not that Careful fine-tuning |
-Not yet -May not be suitable for general text creation |
After understanding the differences between the two through the above table, let’s take a deeper look at other indicators.
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT suddenly appeared on the stage on November 30, 2022. As of December 4, 2022, the service has over one million daily users. In January 2023, this number swelled to more than 100 million users.
The basic reason for its sudden popularity is that it can provide you with reliable answers to many topics in an almost human-sounding way, and it can be used by anyone with an Internet connection. .
ChatGPT was created by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence laboratory located in San Francisco that focuses on creating friendly artificial intelligence solutions. The chatbot is developed based on GPT-3.5, a large language model that can continuously provide responses to the requester when given text.
ChatGPT adds some additional training on this basis-human trainers improve the model through interaction with the model, and give the model the ability to provide high-quality answers through "rewards".
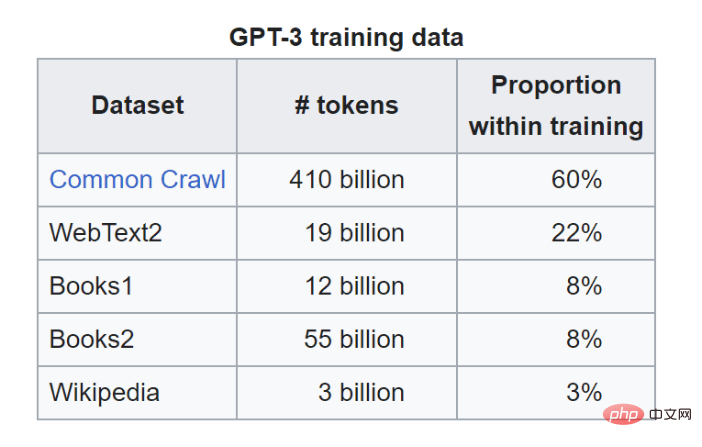
Training Data
GPT-3.5 is trained on a huge web text dataset, including a popular dataset called Common Crawl. Common Crawl contains petabytes of web data, including raw web page data, metadata extraction, and text extraction. For example, it includes a collection of URLs from StrataScratch. Isn’t it crazy to think that ChatGPT uses training data from netizens’ input on ChatGPT?
Common Crawl is responsible for 60% of the training data, but GPT-3.5 also has other data sources.
What is Google Bard?
Google Bard is an intelligent chat robot launched by Google when ChatGPT became very popular. Unlike ChatGPT, Bard is powered by Google's own model, LaMDA. LaMDA is the abbreviation of Language Model for Conversational Applications. Unlike ChatGPT, it is not that amazing for the simple reason that most people do not have access to it yet. While Google did have an awkward demo of Bard in early February, Bard is currently only available to a select few.
The main advantage of Google Bard is that it is open to the Internet. Ask ChatGPT "Who is the president now?" and it doesn't know. This is because the training data was cut off around mid-2021. Bard, on the other hand, drew on information available on the Internet today. In theory, Bard should be able to pull from data on the Internet today and tell you who is president right now.
It’s easy to see how Bard stands out from ChatGPT in several key aspects.
Training data
First of all, LaMDA is trained on conversations, specifically for conversations, rather than just producing text like the GPT-n model . While ChatGPT is unabashed about its training data, we don’t know much about the data Bard was trained on and can infer by looking at LaMDA’s research paper. Google researchers say that 12.5% of training data comes from Common Crawl, such as the GPT-n model. Another 12.5% comes from Wikipedia. According to the research paper, they used 1.56 trillion words of "public conversation data and network text."
Here is the complete breakdown:
- 12.5% based on C4 data (a derivative of Common Crawl data).
- 12.5% of English Wikipedia
- 12.5% comes from programming Q&A websites, tutorials and other code documents
- 6.25% of English online documents
- 6.25% of non-English online documents
- 50% of dialogue data from public forums
From the above information, we can know the data jointly used by the two. Obviously, there are Wikipedia. The rest of the data was clearly hidden intentionally by Google, presumably to protect Bard (and LaMDA) from being imitated.
LaMDA was formed by fine-tuning the neural language model of Transformer, an open source neural network architecture originally developed by Google. (GPT is also based on Transformer).
There are some barriers to ChatGPT to prevent it from being annoying or talking nonsense, but Google emphasizes how to ensure quality to make Bard a better and more secure chat robot. Bard has been fine-tuned to be "high quality, grounded and safe".
Google has a lot to say about this, and I recommend reading their related blog posts, but if you don’t have much time, it can basically be divided into the following aspects:
- Bard should give a meaningful response - nothing ridiculous, nothing contradictory
- Bard should give a response that is insightful, witty, or unexpected.
- Bard should avoid anything that may cause harm to users - blood, prejudice, hateful stereotypes, etc.
- Bard does not make things up
It is well known that due to a wrong launch, Google has not fully figured out the underlying requirements. But it's worth noting that Google is very clear about its design requirements, while ChatGPT is not as clear - at least for now.
Comparison between ChatGPT and Google Bard: Why are model parameters important?
ChatGPT does have more model parameters than Bard - 175 billion versus 137 billion. You can think of parameters as knobs or levers that the model adjusts to fit the data it is trained on. More parameters usually mean the model has more ability to capture complex relationships in language, but there is also a risk of overfitting. Google Bard may be less flexible than ChatGPT, but it may also be more powerful because of new language use cases.
ChatGPT and Google Bard: What do they have in common?
It is worth emphasizing that the models of Bard and ChatGPT (LaMDA and GPT-3.5 respectively) are based on Transformer-based deep learning neural networks.
For example, Transformer can enable a trained model to read a sentence or paragraph, note the relationship between those words, and then predict what words it thinks will come next—similar to the intelligence mentioned earlier The power of predictive text on mobile phones.
I won’t get into the discussion here, but what you need to know is that this means that at their core, Bard and ChatGPT are not very different from each other.
ChatGPT vs. Google Bard: Ownership
While ownership isn’t exactly a technical difference, it’s worth remembering.
Google Bard is made and fully owned by Google, on top of LaMDA, which was also created by Google.
ChatGPT was developed by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research laboratory based in San Francisco. OpenAI was originally a non-profit, but it created a for-profit subsidiary in 2019. OpenAI is also behind Dall-E, the artificial intelligence text-to-image generation you may have played with.
Although Microsoft has invested heavily in OpenAI, for now, it is an independent research organization.
Which one is better, ChatGPT or Google Bard?
It is difficult to give a fair answer to this question because there are many similarities between the two, but there are also differences. First, almost no one has access to Google Bard right now. In addition, ChatGPT’s training data was cut off almost two years ago.
Both are text generators - you provide a prompt and both Google Bard and ChatGPT can answer it. Both have billions of parameters to fine-tune the model. Both have overlapping training data sources and are built on Transformer, the same neural network model.
They are also designed for different purposes, Bard will help you browse Google searches, and it is designed to be conversational. ChatGPT can generate entire blog posts. It is designed to output meaningful text.
Even if we talk about the differences between ChatGPT and Google Bard, it only proves how far artificial intelligence-driven text generation technology has come. While they both have a way to go, and both face copyright and ethical controversies, both generators are strong testaments to the development of modern AI models.
Translator Introduction
Cui Hao, 51CTO community editor and senior architect, has 18 years of software development and architecture experience and 10 years of distributed architecture experience.
Original title: ChatGPT vs Google Bard: A Comparison of the Technical Differences, author: Nate Rosidi
The above is the detailed content of ChatGPT and Google Bard: Which one is better and which one is worse? A big review of the differences!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1414
1414
 52
52
 1307
1307
 25
25
 1253
1253
 29
29
 1228
1228
 24
24
 ChatGPT now allows free users to generate images by using DALL-E 3 with a daily limit
Aug 09, 2024 pm 09:37 PM
ChatGPT now allows free users to generate images by using DALL-E 3 with a daily limit
Aug 09, 2024 pm 09:37 PM
DALL-E 3 was officially introduced in September of 2023 as a vastly improved model than its predecessor. It is considered one of the best AI image generators to date, capable of creating images with intricate detail. However, at launch, it was exclus
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year
 A new era of VSCode front-end development: 12 highly recommended AI code assistants
Jun 11, 2024 pm 07:47 PM
A new era of VSCode front-end development: 12 highly recommended AI code assistants
Jun 11, 2024 pm 07:47 PM
In the world of front-end development, VSCode has become the tool of choice for countless developers with its powerful functions and rich plug-in ecosystem. In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, AI code assistants on VSCode have sprung up, greatly improving developers' coding efficiency. AI code assistants on VSCode have sprung up like mushrooms after a rain, greatly improving developers' coding efficiency. It uses artificial intelligence technology to intelligently analyze code and provide precise code completion, automatic error correction, grammar checking and other functions, which greatly reduces developers' errors and tedious manual work during the coding process. Today, I will recommend 12 VSCode front-end development AI code assistants to help you in your programming journey.
 Laying out markets such as AI, GlobalFoundries acquires Tagore Technology's gallium nitride technology and related teams
Jul 15, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
Laying out markets such as AI, GlobalFoundries acquires Tagore Technology's gallium nitride technology and related teams
Jul 15, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
According to news from this website on July 5, GlobalFoundries issued a press release on July 1 this year, announcing the acquisition of Tagore Technology’s power gallium nitride (GaN) technology and intellectual property portfolio, hoping to expand its market share in automobiles and the Internet of Things. and artificial intelligence data center application areas to explore higher efficiency and better performance. As technologies such as generative AI continue to develop in the digital world, gallium nitride (GaN) has become a key solution for sustainable and efficient power management, especially in data centers. This website quoted the official announcement that during this acquisition, Tagore Technology’s engineering team will join GLOBALFOUNDRIES to further develop gallium nitride technology. G



