 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Humanity has reached the upper limit of silicon computing architecture! AI is expected to consume 50% of global electricity supply by 2030
Humanity has reached the upper limit of silicon computing architecture! AI is expected to consume 50% of global electricity supply by 2030
Humanity has reached the upper limit of silicon computing architecture! AI is expected to consume 50% of global electricity supply by 2030
We have begun to experience the feeling of reaching the upper limit of silicon computing experience. In the next 10 years, there will be a serious computing power gap, and neither existing technology companies nor governments have been able to solve this problem.
Now, we are so accustomed to computing becoming cheaper and cheaper that we never doubt that one day we may not be able to afford it.
Now, Rodolfo Rosini, CEO of a startup, asks a question that shocks us: What if we are reaching the fundamental physical limits of the classical computing model, as if our economy relies on cheap computing? what to do?
The stagnation of large-scale computing
Now, due to a lack of technological innovation, the United States has reached a plateau.
Wright’s Law holds true in many industries—every time the manufacturing process is improved by about 20%, productivity will double.
In the field of technology, it manifests itself as Moore's Law.
In the 1960s, Intel co-founder Gordon Moore noticed that the number of transistors in integrated circuits seemed to have doubled year-on-year and proposed Moore's Law.
Since then, this law has become the basis of the contract between marketing and engineering, leveraging excess computing power and shrinking size to drive the construction of products in the computing stack.
The expectation was that computing power would improve exponentially over time with faster and cheaper processors.
However, the different forces that make up Moore’s Law have changed.
For decades, the driving force behind Moore’s Law was Dennard’s Law of Scaling. Transistor size and power consumption are simultaneously halved, doubling the amount of computation per unit of energy (the latter is also known as Koomey’s LawKoomey’s Law).
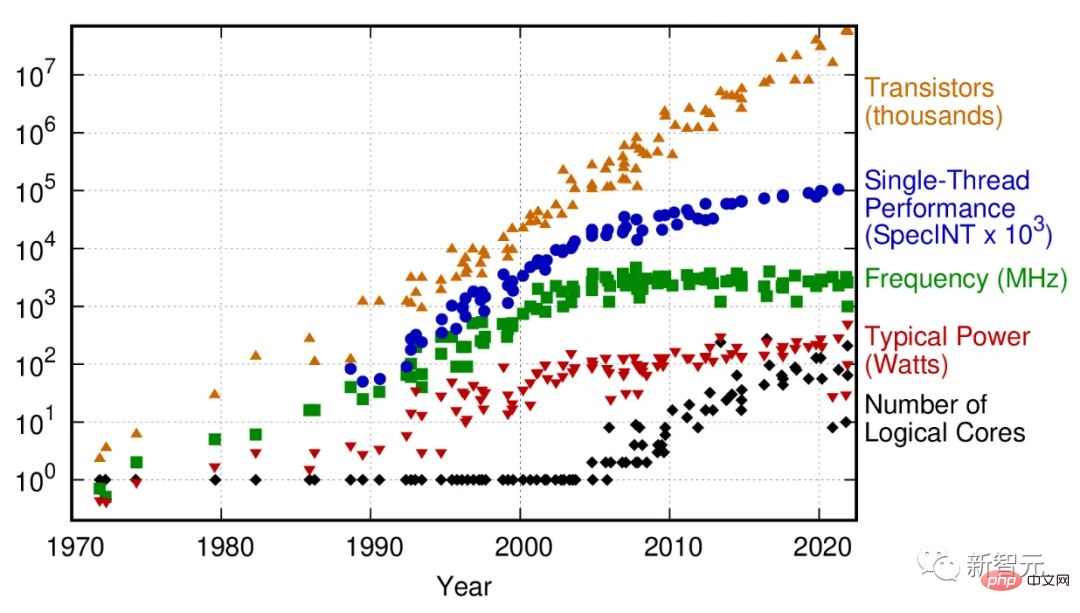
50 Years of Microprocessor Trend Data
In 2005, this scaling began to fail due to current leakage causing the chip to heat up, and the The problem is that the performance of chips with a single processing core has stagnated.
To maintain its computing growth trajectory, the chip industry has turned to multi-core architectures: multiple microprocessors "glued" together. While this may extend Moore's Law in terms of transistor density, it increases the complexity of the entire computing stack.
For certain types of computing tasks, such as machine learning or computer graphics, this brings performance improvements. But for many general-purpose computing tasks that are not well parallelized, multi-core architectures are powerless.
In short, the computing power for many tasks is no longer increasing exponentially.
Even in terms of the performance of multi-core supercomputers, judging from the TOP500 (ranking of the world's fastest supercomputers), there was an obvious turning point around 2010.

What are the impacts of this slowdown? The growing role computing plays in different industries shows that the impact is immediate and will only become more important as Moore's Law falters further.
To take two extreme examples: Increased computing power and reduced costs have led to a 49% increase in the productivity of oil exploration in the energy industry, and a 94% increase in protein folding predictions in the biotechnology industry.
This means that the impact of computing speed is not limited to the technology industry. Much of the economic growth of the past 50 years has been a second-order effect driven by Moore's Law. Without it, the world economy may stop growing.
Another prominent reason for the need for more computing power is the rise of artificial intelligence. Today, training a large language model (LLM) can cost millions of dollars and take weeks.
The future promised by machine learning cannot be realized without continued increase in number crunching and data expansion.
As the growing popularity of machine learning models in consumer technology heralds huge and potentially hyperbolic demands for computing in other industries, cheap processing is becoming the cornerstone of productivity.
The death of Moore's Law may bring about a great stagnation in computing. Compared with the multi-modal neural networks that may be required to achieve AGI, today's LLMs are still relatively small and easy to train. Future GPTs and their competitors will require particularly powerful high-performance computers to improve and even optimize.
Perhaps many people will feel doubtful. After all, the end of Moore's Law has been predicted many times. Why should it be now?
Historically, many of these predictions stem from engineering challenges. Human ingenuity has overcome these obstacles time and time again before.
The difference now is that instead of being faced with engineering and intelligence challenges, we are faced with constraints imposed by physics.
MIT Technology Review published an article on February 24 stating that we are not prepared for the end of Moore’s Law
Overheating causes inability to process
Computers work by processing information.
As they process information, some of it is discarded as the microprocessor merges computational branches or overwrites the registry. It's not free.
The laws of thermodynamics, which place strict limits on the efficiency of certain processes, apply to calculations just as they do to steam engines. This cost is called Landauer’s limit.

It is the tiny amount of heat emitted during each computational operation: approximately 10^-21 joules per bit.
Given that this heat is so small, the Landauer limit has long been considered negligible.
However, engineering capabilities have now evolved to the point where this energy scale can be achieved because the real-world limit is estimated to be 10-100 times larger than Landauer's bound due to other overheads such as current leakage. Chips have hundreds of billions of transistors that operate billions of times per second.
Add these numbers together, and perhaps Moore’s Law still has an order of magnitude left to grow before reaching the thermal barrier.
At that point, existing transistor architectures will be unable to further improve energy efficiency, and the heat generated will prevent transistors from being packed more tightly.
If we don’t figure this out, we won’t be able to see clearly how industry values will change.
Microprocessors will be constrained and industry will compete for lower rewards for marginal energy efficiency.
The chip size will expand. Look at Nvidia's 4000-series GPU card: despite using a higher-density process, it's about the size of a small dog and packs a whopping 650W of power.
This prompted NVIDIA CEO Jen-Hsun Huang to declare in late 2022 that "Moore's Law is dead"—a statement that, while mostly true, has been denied by other semiconductor companies.
The IEEE releases a semiconductor roadmap every year. The latest assessment is that 2D shrinkage will be completed in 2028, and 3D shrinkage should be fully launched in 2031.
3D scaling (where chips are stacked on top of each other) is already common, but in computer memory, not in microprocessors.
This is because the heat dissipation of the memory is much lower; however, heat dissipation is complex in 3D architecture, so active memory cooling becomes important.
Memory with 256 layers is on the horizon, and is expected to reach the 1,000-layer mark by 2030.
Back to microprocessors, multi-gate device architectures that are becoming commercial standards (such as FinFETs and Gates-all-round) will continue to follow Moore's Law in the coming years.
However, due to inherent thermal problems, true vertical scaling was impossible after the 1930s.
In fact, current chipsets carefully monitor which parts of the processor are active at any time to avoid overheating even on a single plane.
2030 Crisis?
A century ago, American poet Robert Frost once asked: Will the world end in frost or fire?
If the answer is fire, it almost heralds the end of computing.
Or, just accept the fact that electricity use will increase and scale up microprocessor manufacturing.
For this purpose, humans have consumed a large portion of the earth's energy.
Perhaps another option is to simply accept increased power use and scale up microprocessor manufacturing. We already use a large portion of the Earth's energy supply for this purpose.
In Ireland, just 70 data centers consume 14% of the country’s energy. By the 2030s, it is expected that 30-50% of globally produced electricity will be used for computing and cooling.
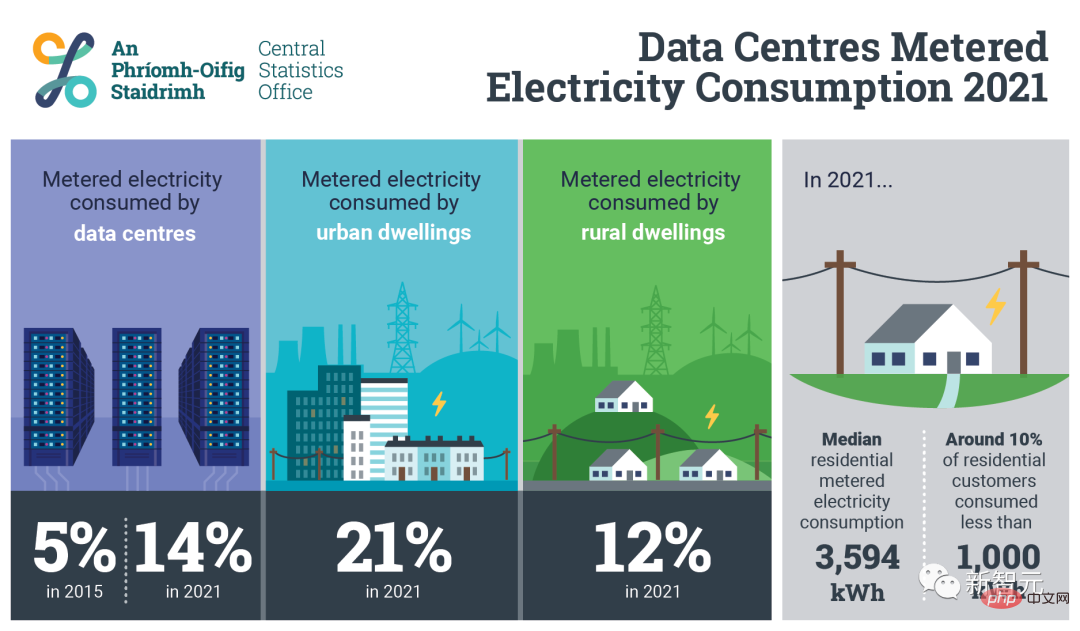
(Interestingly, after the blog post was published on March 19, the author deleted this prediction. His explanation was that this was based on the worst-case scenario in the Nature paper. The extrapolation of the situation, which has now been deleted for the sake of clarity and precision of the argument)
And the current scale of energy production will lead to a slight increase in the cost of Moore's Law scale in the future.
A series of one-time optimization measures at the design (energy efficiency) and implementation levels (replacing old designs still in use with the latest technology) will allow developing economies such as India to catch up with the global overall productive forces.
After the end of Moore's Law, mankind will run out of energy before the manufacturing of microprocessor chips reaches its limit, and the pace of decline in computing costs will stagnate.
Although quantum computing is touted as an effective way to surpass Moore's Law, there are too many unknowns in it. It is still decades away from commercial development, and it will not be useful for at least the next 20 to 30 years. .
Clearly, there will be a serious computing power gap in the next 10 years, and no existing technology companies, investors, or government agencies will be able to solve it.
The collision between Moore's Law and Landauer's limit has been going on for decades, and it can be said to be one of the most significant and critical events in the 2030s.
But now, it seems that not many people know about this matter.
The above is the detailed content of Humanity has reached the upper limit of silicon computing architecture! AI is expected to consume 50% of global electricity supply by 2030. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
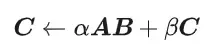 CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) is a vital part of many applications and algorithms, and is also one of the important indicators for evaluating computer hardware performance. In-depth research and optimization of the implementation of GEMM can help us better understand high-performance computing and the relationship between software and hardware systems. In computer science, effective optimization of GEMM can increase computing speed and save resources, which is crucial to improving the overall performance of a computer system. An in-depth understanding of the working principle and optimization method of GEMM will help us better utilize the potential of modern computing hardware and provide more efficient solutions for various complex computing tasks. By optimizing the performance of GEMM
 How to calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in word document
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
How to calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in word document
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
WORD is a powerful word processor. We can use word to edit various texts. In Excel tables, we have mastered the calculation methods of addition, subtraction and multipliers. So if we need to calculate the addition of numerical values in Word tables, How to subtract the multiplier? Can I only use a calculator to calculate it? The answer is of course no, WORD can also do it. Today I will teach you how to use formulas to calculate basic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in tables in Word documents. Let's learn together. So, today let me demonstrate in detail how to calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in a WORD document? Step 1: Open a WORD, click [Table] under [Insert] on the toolbar, and insert a table in the drop-down menu.
 The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
StableDiffusion3’s paper is finally here! This model was released two weeks ago and uses the same DiT (DiffusionTransformer) architecture as Sora. It caused quite a stir once it was released. Compared with the previous version, the quality of the images generated by StableDiffusion3 has been significantly improved. It now supports multi-theme prompts, and the text writing effect has also been improved, and garbled characters no longer appear. StabilityAI pointed out that StableDiffusion3 is a series of models with parameter sizes ranging from 800M to 8B. This parameter range means that the model can be run directly on many portable devices, significantly reducing the use of AI
 How to count the number of elements in a list using Python's count() function
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:53 PM
How to count the number of elements in a list using Python's count() function
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:53 PM
How to use Python's count() function to calculate the number of an element in a list requires specific code examples. As a powerful and easy-to-learn programming language, Python provides many built-in functions to handle different data structures. One of them is the count() function, which can be used to count the number of elements in a list. In this article, we will explain how to use the count() function in detail and provide specific code examples. The count() function is a built-in function of Python, used to calculate a certain
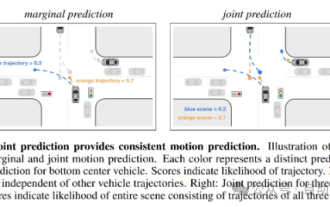 This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
Trajectory prediction plays an important role in autonomous driving. Autonomous driving trajectory prediction refers to predicting the future driving trajectory of the vehicle by analyzing various data during the vehicle's driving process. As the core module of autonomous driving, the quality of trajectory prediction is crucial to downstream planning control. The trajectory prediction task has a rich technology stack and requires familiarity with autonomous driving dynamic/static perception, high-precision maps, lane lines, neural network architecture (CNN&GNN&Transformer) skills, etc. It is very difficult to get started! Many fans hope to get started with trajectory prediction as soon as possible and avoid pitfalls. Today I will take stock of some common problems and introductory learning methods for trajectory prediction! Introductory related knowledge 1. Are the preview papers in order? A: Look at the survey first, p
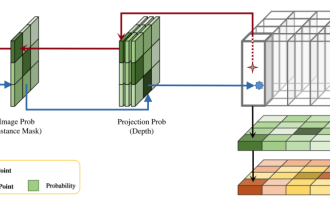 DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
This paper explores the problem of accurately detecting objects from different viewing angles (such as perspective and bird's-eye view) in autonomous driving, especially how to effectively transform features from perspective (PV) to bird's-eye view (BEV) space. Transformation is implemented via the Visual Transformation (VT) module. Existing methods are broadly divided into two strategies: 2D to 3D and 3D to 2D conversion. 2D-to-3D methods improve dense 2D features by predicting depth probabilities, but the inherent uncertainty of depth predictions, especially in distant regions, may introduce inaccuracies. While 3D to 2D methods usually use 3D queries to sample 2D features and learn the attention weights of the correspondence between 3D and 2D features through a Transformer, which increases the computational and deployment time.
 How to use the Math.Pow function in C# to calculate the power of a specified number
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:32 AM
How to use the Math.Pow function in C# to calculate the power of a specified number
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:32 AM
In C#, there is a Math class library, which contains many mathematical functions. These include the function Math.Pow, which calculates powers, which can help us calculate the power of a specified number. The usage of the Math.Pow function is very simple, you only need to specify the base and exponent. The syntax is as follows: Math.Pow(base,exponent); where base represents the base and exponent represents the exponent. This function returns a double type result, that is, the power calculation result. Let's
 'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
Please note that this square man is frowning, thinking about the identities of the "uninvited guests" in front of him. It turned out that she was in a dangerous situation, and once she realized this, she quickly began a mental search to find a strategy to solve the problem. Ultimately, she decided to flee the scene and then seek help as quickly as possible and take immediate action. At the same time, the person on the opposite side was thinking the same thing as her... There was such a scene in "Minecraft" where all the characters were controlled by artificial intelligence. Each of them has a unique identity setting. For example, the girl mentioned before is a 17-year-old but smart and brave courier. They have the ability to remember and think, and live like humans in this small town set in Minecraft. What drives them is a brand new,



