Does linux come with ssh?
Linux comes with ssh. The Linux system will come with its own ssh software. The default is the OpenSSH related software package, and the ssh service is added to start automatically at boot. You can use the "ssh -V" command to view the installed ssh version information. Execute the "systemctl start sshd" command to start the sshd service. The default port is port 22.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
Does Linux come with ssh?
The server is usually in the computer room. If you have to go to the computer room every time to maintain the server, it will not be comfortable. . So Linux has a function that allows you to send messages remotely using a shell, which is ssh (abbreviation for Secure Shell). That is to say, a service will be started on the server to receive remote access data, and then forward the data to the system kernel to complete these operations, so that R&D colleagues can maintain the server without going to the computer room.
ssh requires the server to open the corresponding network port. The default is port 22, which can also be modified to other ports, such as 9022, etc.
Because the server reserves ports for external use and is for management purposes (you can control the server through the shell), ssh provides various security restrictions. The more common ones are to prohibit root account login and only allow Log in with trusted IP and use certificate method. This can prevent strangers from logging into the server, even if they have obtained relevant accounts and permissions.
External computers use ssh to log in to the server, which requires corresponding client software. If it is Linux or Mac, the system will come with ssh software (although it is in command line mode). The default is OpenSSH. You can use the ssh -V command to view the installed ssh version information:
[root@xiaoluo xiaoluo]# ssh -V OpenSSH_5.3p1, OpenSSL 1.0.0-fips 29 Mar 2010
From the above information, you can As you can see, the SSH protocol installed by default on my CentOS 6.4 installed on the virtual machine is 1.0.
OpenSSH server configuration file
Service name: sshd
Server main program:/usr/sbin/sshd
Server configuration file:/etc/ssh/sshd_config
openSSH is an open source software project that implements the SSH protocol and is suitable for various UNIX and Linux operating systems.
centos 7 system has openssh related software packages installed by default, and the ssh service is added to start automatically at boot.
Execute the "systemctl start sshd" command to start the sshd service. The default port is port 22.
ssh_confiog and sshd_config are both configuration files of the ssh server
The difference between the two is that the former is a configuration file for the client, and the latter is a configuration file for the server.
The ssh server mainly includes two service functions, ssh remote connection and sftp service
Function: The SSHD service uses the SSH protocol to perform remote control or transfer files between computers. Compared with using Telnet to transfer files before, it is much safer because Telnet transfers files in plain text and SSH transfers files encrypted.
ssh remote login method
There are two ways to log in via ssh.
When logging in to the server for the first time, the system does not save the information of the remote host. In order to confirm the identity of the host, the user will be prompted whether to continue the connection. Enter yes and then log in. At this time, the system will write the remote server information to the user's home directory. : $HOME/.ssh/known_hosts file, the next time you log in, because the host information is saved, you will not be prompted again.
1. Method 1
Format: ssh [remote host user name] @ [remote server host name or IP address] -p port
When a Linux host remotely connects to another Linux host, if the currently logged-in user is root, when connecting to another host and also logging in as the root user, you can use ssh directly. IP login. The port is the default. If it is not the default, you need to use -p to specify the port.
Remote login to other hosts
ssh root@192.168.100.10 The first interactive input is yes. The second interactive input is the root password and the login is successful
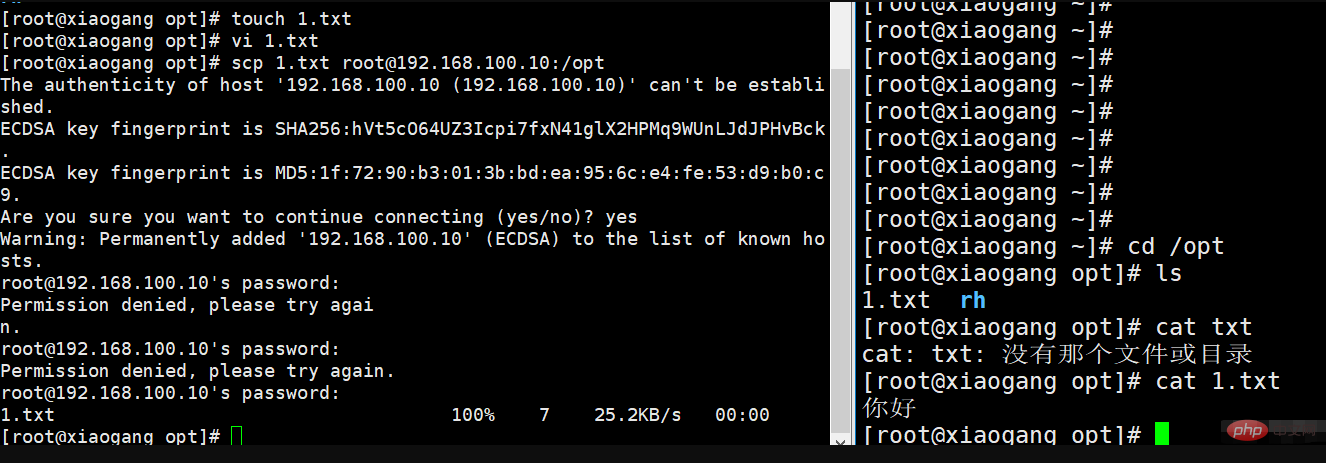
After logging in and then logging out, a .sshd directory will be generated in the local home directory, with files recording login information.

2. Use the domain name process to log in
①Modify the local mapping relationship

②Log in

3. Troubleshooting
At work, sometimes you need to SSH to log in to other computers Linux host, but sometimes SSH login is prohibited, and a prompt similar to the following pops up:
warning: Permanently added '192.168.100.10'(ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Authentication failed.
这时直接删除家目录下面的 .ssh 目录下面的文件,即可解决。
4、sshd服务支持的两种登录验证方式
1)密码验证
对服务器中本地系统用户的登录名称、密码进行验证。这种方式使用最为简便,但从客户端角度来看,正在连接的服务器有可能被假冒;从服务器角度来看,当遭遇密码穷举(暴力破解)攻击时,防护能力比较弱。
18位密码复杂性(大写、小写、字符、数字),修改端口为高位端口,可以提高安全性。
2)秘钥对验证
要求提供相匹配的秘钥信息才能通过验证。通常先在客户端中创建一对秘钥文件(公钥、私钥),然后将公钥文件放到服务器中指定位置,远程登录时,系统将使用公钥、私钥进行加密/解密关联验证,
大大增强了远侧还能够管理的安全性。该方式不易被假冒,且可以免交互登录,在shell中被广泛使用
当密码验证、秘钥验证都启用时,服务器将优先使用秘钥对验证。 对于安全性要求高的服务器,建立将密码验证方式禁用,只允许启用秘钥对验证方式。
配置文件中修改启用密码验证还是秘钥验证
配置文件:/etc/ssh/sshd_config
PasswordAuthentication yes #启用密码验证 PubkeyAuthentication yes #启用密钥对验证 AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #指定公钥库文件(ls -a可查看)
配置文件中其它的设置
LoginGraceTime 2m #登录验证时间为2分钟(默认2分钟) PermitRootLogin no #禁止root用户登录 MaxAuthTries 6 #最大重试次数为6次 PermitEmptyPasswords no #禁止空密码登录 PrintLastLog yes #显示上次登入的信息!默认为 yes AllowUsers #只允许或禁止某些用户登录
配置文件修改完之后,需要重启配置sshd服务
systemctl restart sshd #重启sshd服务
构建秘钥对验证的SSH
公钥和私钥的关系
在对称加密技术中,有两种秘钥,分为私钥和公钥,私钥是秘钥的创建人拥有,不可公布,公钥是创建者公布给他人的。
公钥用来给数据加密,用公钥加密的数据只能使用私钥解。
构建秘钥对验证SSH的原理
首先ssh通过加密算法在客户端产生秘钥对(公钥和私钥),公钥发送给服务端,自己保留私钥。
如果要想连接带有公钥的SSH服务器,客户端SSH软件就会向SSH服务器发出请求,请求联机的用户密钥进行安全验证。
SSH服务器收到请求之后,便在被连接的用户的家目录下寻找事先放上去的对应用户的公用秘钥
然后把它和连接的SSH客户端发送过来的公用秘钥进行比较,如果两个秘钥一致,SSH服务器就用公钥加密“质询”并把它发送给SSH客户端。
简单理解
生成密钥可以在客户端和服务端两边生成,但是我们需要将使用客户端登录到服务端,那么,客户端就一直需要的是私钥,服务端要存在公钥,所以不关密钥对在客户端还是服务端生成,客户端拿到的都会是私钥,服务端拿到的都是公钥。
通俗理解
公钥(public key)相当于一扇门,私钥(pribate key)相当于是开门的钥匙,当一台机器A需要登录到机器B的时候,就得拿着钥匙去开门,但是前提的是机器B必须要有门,所以需要给机器B装上门,那就是把机器A的公钥给到机器B。然后机器A使用私钥就可以打开机器B的公钥门。
1、scp远程复制
scp复制 :是secure copy (安全复制)的简写,用在Linux下进行远程拷贝的命令,而且scp传输时加密的。
应用场景
在系统误删环境配置文件且没有备份的时候,可以远程从其它主机上拷贝过来。
本地文件复制到服务器 scp 1.txt root@192.168.100.10:/opt 复制服务器的目录到本地 scp root@192.168.100.10:/home/sky/ ./ 本地目录复制到服务器 scp -r / root@192.168.100.10:/home

2、sftp 安全性传输
sftp 是secure file transfer protocol(安全文件传送协议) 的缩写,可以为传输文件提供一种安全的网络加密方法。
sftp与ftp有着几乎一样的语法和功能,sftp 为ssh的其中一部分,sftp本身没有单独的守护进程,它必须使用sshd守护进程(端口号默认是22)来完成相应的连接和答复操作。所以使用sftp是非常安全的,但是,由于这种传输方式使用了加密/解密技术,所以传输效率比普通的FTP要低的多。对网络安全要求更高时,可以使用SFTP代替FTP。
从服务端下载文件到本地主机
从本地主机上传文件到服务端
3、配置密钥对实验
通过ssh-keygen工具为当前用户创建密钥对文件,可用的加密算法有“RAS”、“ECDSA”、“DSA”,通过-t 选项调用相应的算法。
3.1 在服务端创建密钥对
查看密钥对的位置
3.2、修改密钥对的配置文件
修改ssd_config配置文件没关闭,关闭密码验证,开启密钥验证
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
加载服务
3.3、发送私钥到客户端
3.4用xshell登录
3.5、客户端创建秘钥
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 修改公钥位置文件
重启服务
总结
-
ssh为远程登录服务器的服务
优点是使用该登录,传输数据会先 压缩再加密 ,保证安全性
登录方式有两种,配置各种参数进行登录,最为长常用的是 ssh ip地址或主机名 scp可以跨主机传输文件。
sftp也可以远程登录,传输具有安全性,功能与ftp类似,但是没有独立的守护进程,它依赖于sshd服务,22端口,只有启用sshd服务才能使用sftp服务。
-
ssh生成密钥对
可在客户端和服务端两边生成,
但是最终 客户端 拿的必须是 私钥 , 服务端 拿的是 公钥 ,
且在服务器中需要修改配置文件: /etc/ssh/sshd_config 内容,比如:开启密钥对验证,关闭密码验证,设置公钥路径。
密钥对验证使用的是非对称密钥,优点是:可以免密登录,提高安全性。
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Does linux come with ssh?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Linux is suitable for servers, development environments, and embedded systems. 1. As a server operating system, Linux is stable and efficient, and is often used to deploy high-concurrency applications. 2. As a development environment, Linux provides efficient command line tools and package management systems to improve development efficiency. 3. In embedded systems, Linux is lightweight and customizable, suitable for environments with limited resources.
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
This article describes how to effectively monitor the SSL performance of Nginx servers on Debian systems. We will use NginxExporter to export Nginx status data to Prometheus and then visually display it through Grafana. Step 1: Configuring Nginx First, we need to enable the stub_status module in the Nginx configuration file to obtain the status information of Nginx. Add the following snippet in your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or its include file): location/nginx_status{stub_status
 How to start monitoring of oracle
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:00 AM
How to start monitoring of oracle
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:00 AM
The steps to start an Oracle listener are as follows: Check the listener status (using the lsnrctl status command) For Windows, start the "TNS Listener" service in Oracle Services Manager For Linux and Unix, use the lsnrctl start command to start the listener run the lsnrctl status command to verify that the listener is started
 How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to set up a recycling bin in Debian system
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
This article introduces two methods of configuring a recycling bin in a Debian system: a graphical interface and a command line. Method 1: Use the Nautilus graphical interface to open the file manager: Find and start the Nautilus file manager (usually called "File") in the desktop or application menu. Find the Recycle Bin: Look for the Recycle Bin folder in the left navigation bar. If it is not found, try clicking "Other Location" or "Computer" to search. Configure Recycle Bin properties: Right-click "Recycle Bin" and select "Properties". In the Properties window, you can adjust the following settings: Maximum Size: Limit the disk space available in the Recycle Bin. Retention time: Set the preservation before the file is automatically deleted in the recycling bin
 How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
To restart the Apache server, follow these steps: Linux/macOS: Run sudo systemctl restart apache2. Windows: Run net stop Apache2.4 and then net start Apache2.4. Run netstat -a | findstr 80 to check the server status.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information





























